 |
Blender Materials: A Glass Object |
|
Introduction
Like its name implies, an object is said to be glass-based if it is crystal-based so that it can be seen through. Such an object is said to be transparent. Blender provides the ability to create an object that is transparent.
 Practical Learning: Starting the Project
Practical Learning: Starting the Project
- Start Blender
- In the Properties window, click the Object button

- Position the mouse on the default cube and press X
- On the menu that comes up, click Delete
 Practical Learning:
Creating a Classic Cup
Practical Learning:
Creating a Classic Cup
- On the Tools window, click Create
- Click Cylinder
- On the menu bar of the 3D-View, click Object Mode and click Edit Mode
- On the menu bar of the 3D-View, click the Face Select button

- Right-click the top face of the cylinder to select it
- Press S to resize
- Type 1.25 and press Enter
- Press G to move the face
- Press Z to move the face vertically
- Type 1.5 and press Enter:

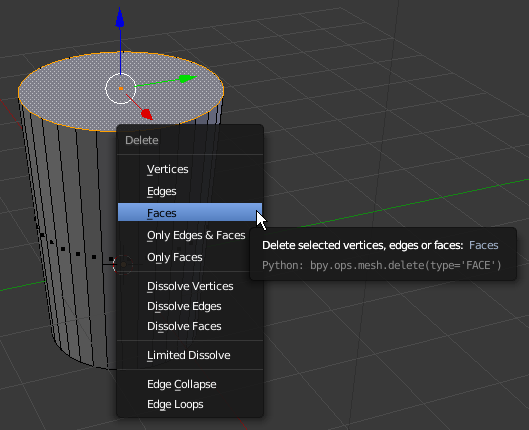
- Position the mouse on the cylinder and press X to delete
- In the menu that appears, click Faces:
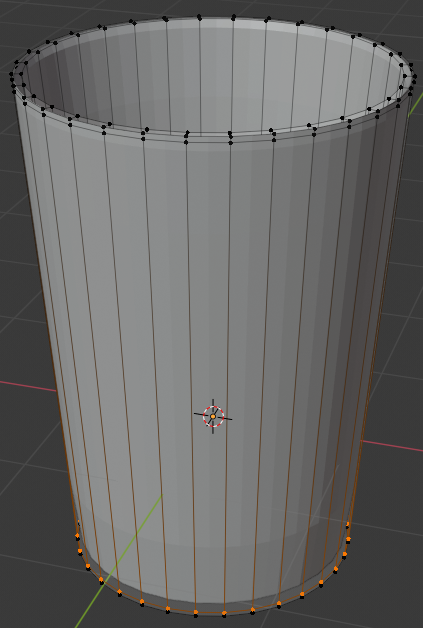
- On the menu bar of the 3D-View, click the Vertex Select button

- Press and hold Alt
- Right-click one of the top vertices to select all of them
- Release Alt:
- Press E as if you want to extrude and press Enter
- Press S as if you want to resize
- Type .95 and press Enter:
- Press Z to display in wireframe
- In the Numeric Pad, press 1 and press 5 to display the orthogonal front view
- Press E and press Enter
- Press G
- Press Z
- Type -3.25 and press Enter:

- Press S
- Type .75 and press Enter:
- Press Z to display in Solid view
- Press Tab to display in Solid Mode
- Move the view to display the cup in perspective:
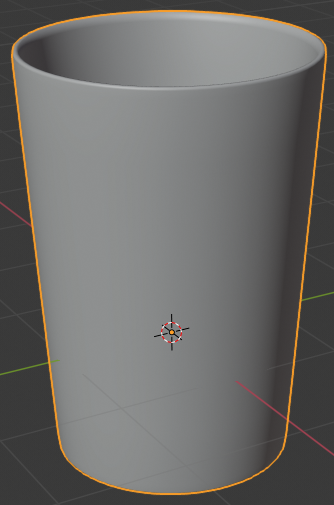
- In the Properties window, click the Object button

- Click Cylinder to select it
- Type Classic Cup and press Enter
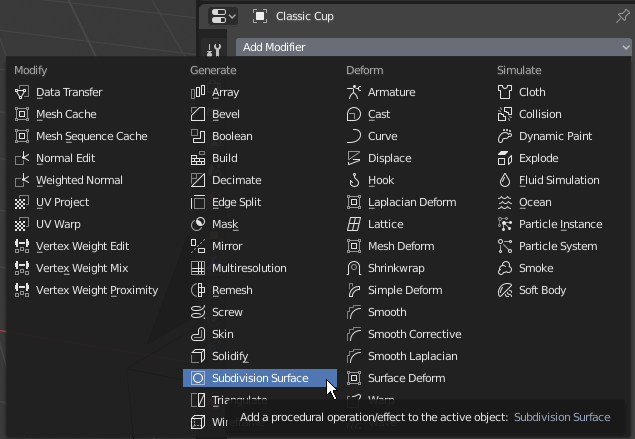
- In the Properties window, click the Modifiers button

- Click Add Modifier and click Subdivision Surface:
:
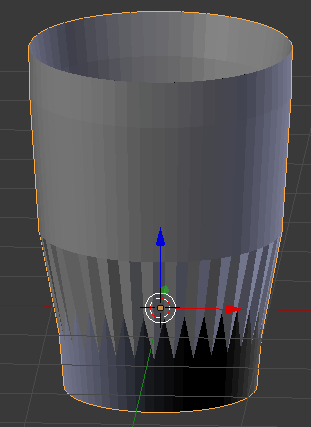
- Set the View value to 2
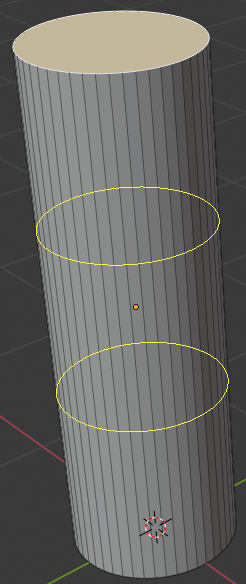
- Position the mouse on the cylnder and press Tab to display in Edit Mode
- Press Ctrl + R and get a horizontal ellipse on the cylinder
- Click to create a cut
- Move the cut as close as possible to the top border:

- Press Ctrl + R and get a horizontal ellipse on the cylinder
- Click to create a cut
- Move the cut as close as possible to the top border:

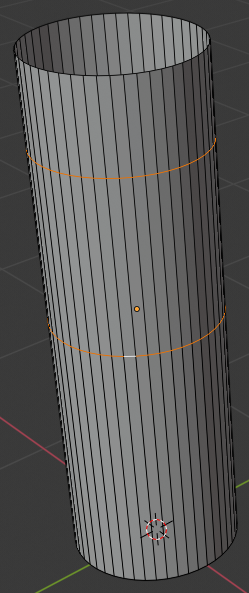
- Position the mouse inside the top border. Press Ctrl + R to get a horizontal inside cut
- Click to create a cut
- Move the inside cut as close as possible to the top border:
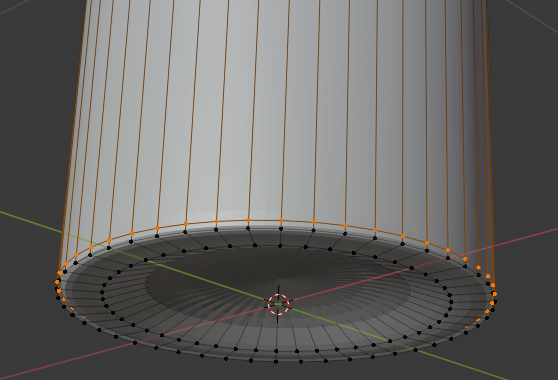
- Press Z to display in wireframe
- Psition the mouse inside the top border. Press Ctrl + R to get a horizontal inside cut
- Click once to create the cut
- Move the inside cut as close as possible to the inside bottom border:
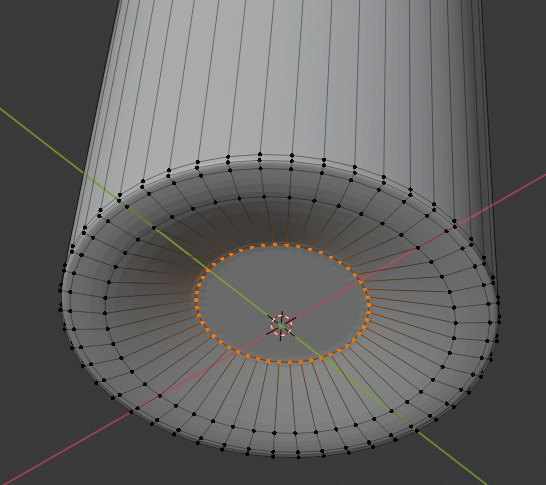
- Press Z to exit the wireframe
- Move the view so you can see the bottm side of the cylinder
- Press and hold Alt
- Right-click one of hte bottom vertices to select them
- Release Alt:
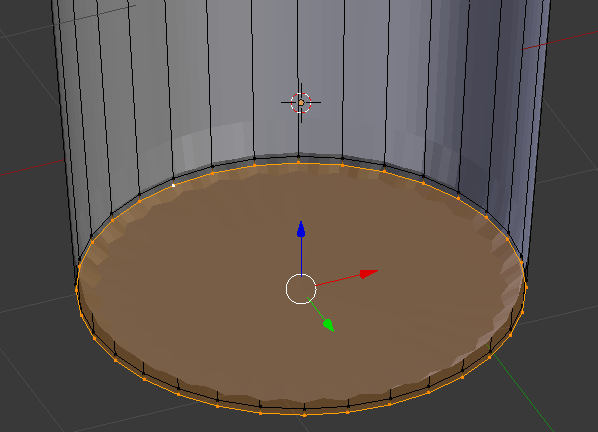
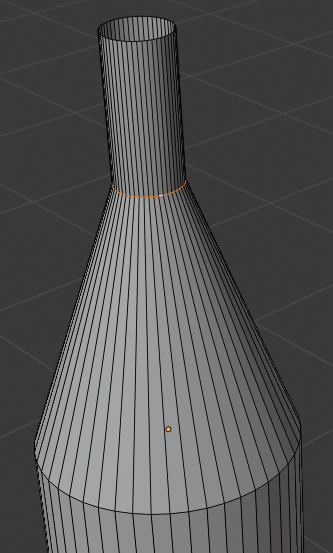
- Press E and press Enter
- Press S
- Type .95 and press Enter:
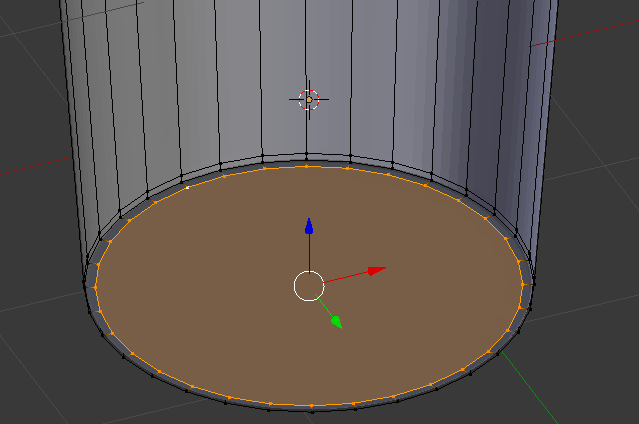
- Press Tab to display in Object Mode
- In the Properties window, click Apply
- In the Tools window and in the Tools tab, click Smooth:

- In the Outliner, click the Restricted Viewport Visibility button (the eye) on the right side of Classic Cup
 Practical Learning: Creating a Bottle of Red Wine
Practical Learning: Creating a Bottle of Red Wine
- In the Tools window, click Create
- Click Cylinder
- In the Add Cylinder section below the Tools window, change the following values:
Vertices: 48
Radius: .4
Depth: 2.5
Location - Z: 1.25
- To prepare to edit the cylinder, on the menu bar of the 3D View, click Object Mode and click Edit Mode
- Move the view and zoom in so you can see the top side of the cylinder
- On the menu bar of the 3D-View, click the Face Select button

- On the cylinder, right-click the top face of the cylinder:
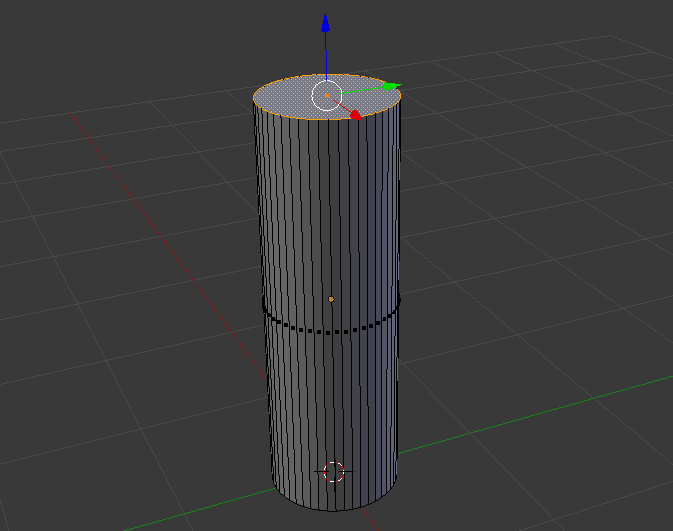
- Press X to delete
- On the menu that appears, click Faces
- Position the mouse on the cylinder, press Ctrl + R and make sure you see a horizontal ellipse or line
- Click twice to confirm the cut
- Press G and press Z to move vertically
- Type .75 and press Enter:
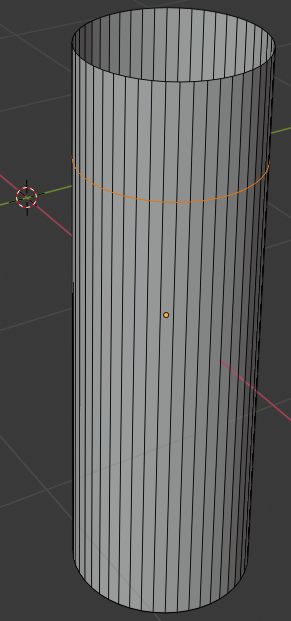
- Position the mouse above the bottom border of the cylinder, press Ctrl + R and make sure you see a horizontal ellipse or line
- Click twice to confirm the cut:
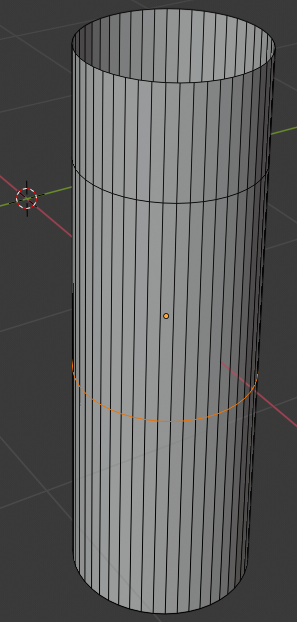
- Press G and press Z to move vertically
- Type .5 and press Enter:
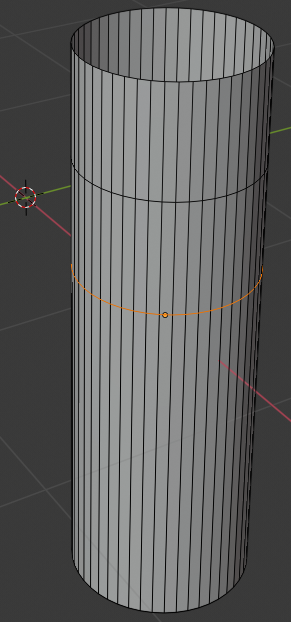
- On the menu bar of the 3D-View, click the Vertex Select button

- Press and hold Alt
- Right-click one of the vertices on the top side of the cylinder to select all top vertices of the bottle
- Release Alt:
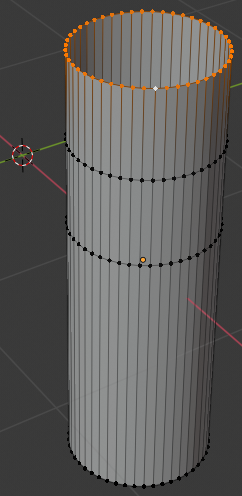
- Press S to resize
- Type .25 and press Enter
- Press and hold Alt
- Right-click the second line from the top of the cylinder to select the horizoontal cut
- Release Alt:
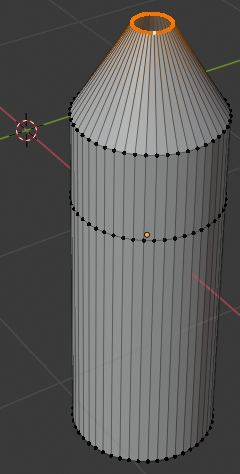
- Press S to resize
- Type .25 and press Enter:
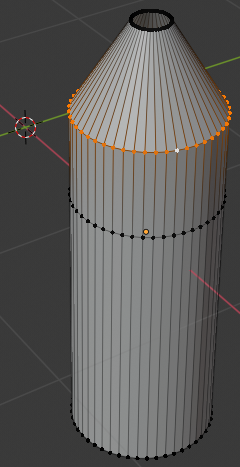
- The second and third horizontal lines are the neck of the bottle.
Position the mouse on the neck of the bottle, press Ctrl + R and make sure you see a horizontal ellipse or line
- Click twice to confirm the cut:
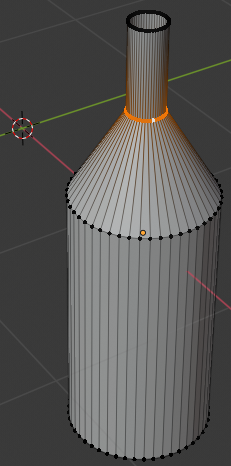
- Press S to resize
- Type 1.35 and press Enter:
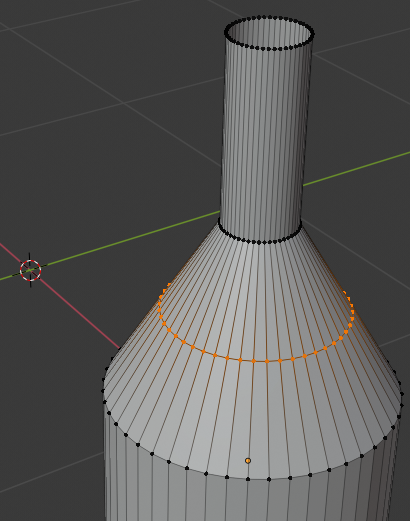
- Position the mouse between the third line from the top of the bottle and the fourth line, press Ctrl + R and make sure you see a horizontal ellipse or line
- Click twice to confirm the cut
- Press S to resize
- Type 1.05 and press Enter:
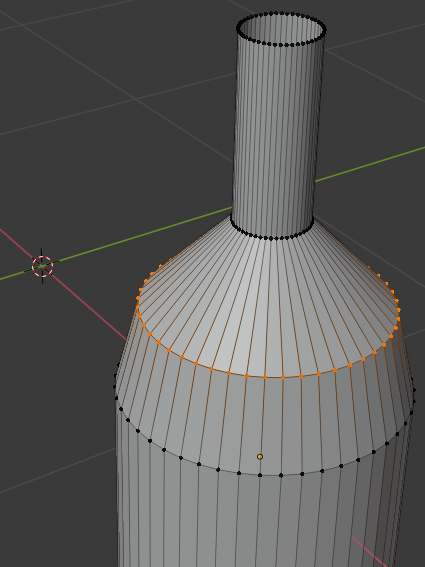
- Position the mouse between the second line from the top of the bottle and the third line, press Ctrl + R and make sure you see a horizontal ellipse or line
- Click twice to confirm the cut
- Press S to resize
- Type .85 and press Enter:
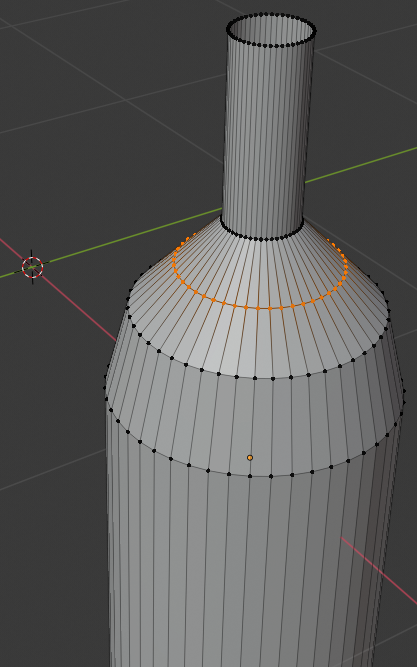
- Position the mouse between the second line from the top of the bottle and the third line, press Ctrl + R and make sure you see a horizontal ellipse or line
- Click twice to confirm the cut
- Press S to resize
- Type 1.05 and press Enter:
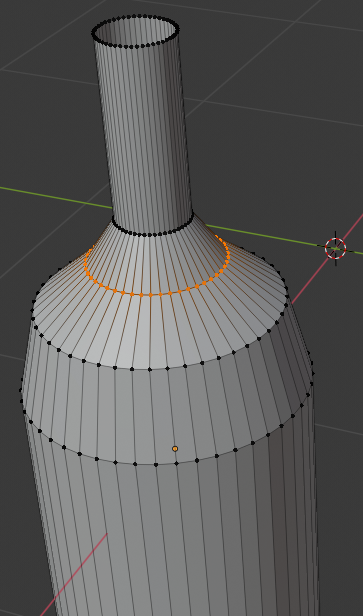
- Position the mouse between the third line from top and the fourth line from top, press Ctrl + R and make sure you see a horizontal ellipse or line
- Click twice to confirm the cut
- Press S
- Type .92 and press Enter:
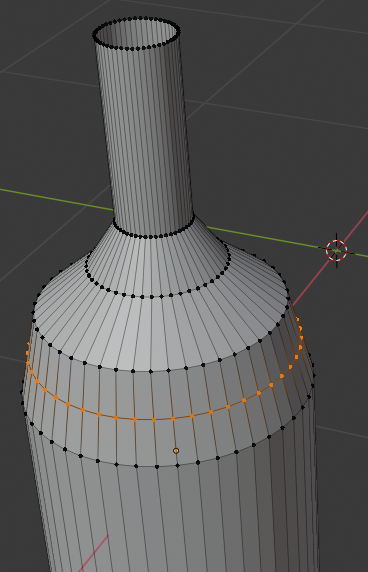
- Move the view so you can see the bottom side of the cylinder
- On the menu bar of the 3D-View, click the Vertex Select button

- Press and hold Alt
- Right-click one of the vertices on the bottom side of the cylinder to select all bottom vertices of the bottle
- Release Alt:
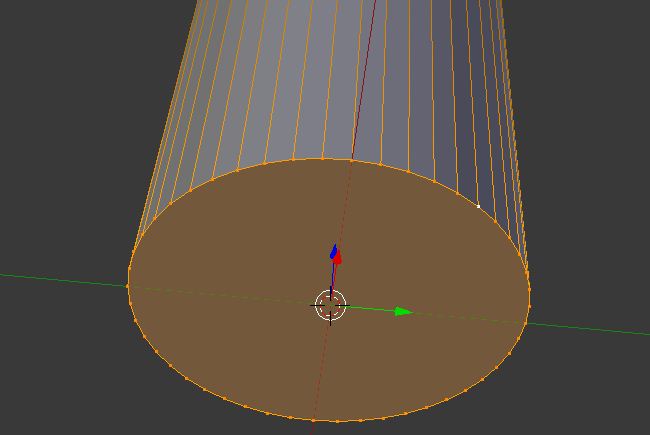
- Press E as if you want to extrude
- Press S to move the vertices
- Type .85 and press Enter:
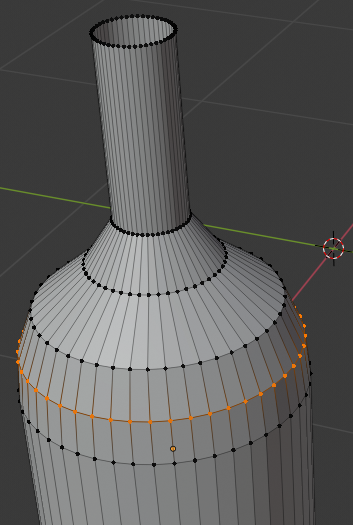
- Press E
- Press S
- Type 0 and press Enter:
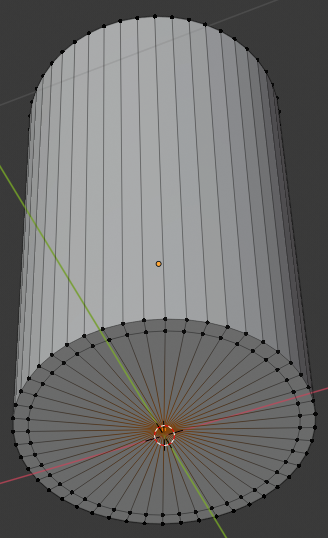
- In the Numeric Pad, press 1 to get the front view
- Press Z to display the object as a wireframe
- Press G to prepare to move the vertex
- Press Z to move vertically
- Type .25 and press Enter:

- Press Z to exit from wireframe
- Press Tab to display in Object Mode
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + D and press Enter
- In the Properties window, click the Object button
- Click Cylinder.001 to select it
- Type Red Wine and press Enter
- In the Outliner, click the Restricted Viewport Visibility button on the right side of Red Wine to hide it
- In the work area, right-click the bottle to select it
- In the Object tab of the Properties window, click Cylinder to select it
- Type Bottle of Red Wine and press Enter
- In the Properties window, click the Modifiers button
- Click Add Modifier and click Solidify:
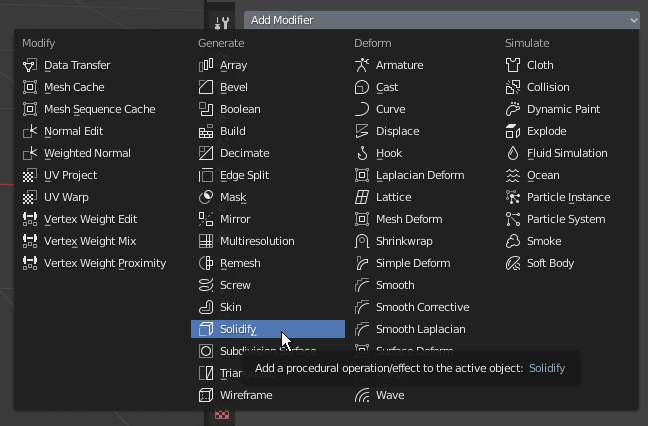
- Click the Thickness value, type.02 and press Enter
- Click Apply
- Click Add Modifier and click Subdivision Surface
- Set the View value to 2
- Position the mouse on the bottle and press Tab to display in Edit Mode
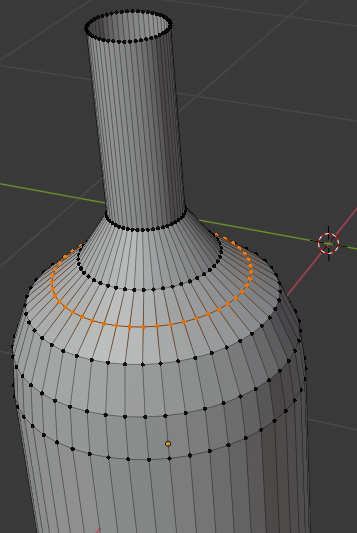
- Position the mouse in the upper section of the bottle, press Ctrl + R to get a horizontal line
- Click once to accept the line
- Move the line up as close as possible to the top border:
- Position the mouse inside the top opening of the bottle, press Ctrl + R to get a horizontal line
- Click once to confirm
- Move the cut up as close as possible to the top border:

- Move the shape so you can see the lower part of the bottle
- Press Ctrl + R to get a horizontal cut and click once to cut
- Move the line down close to the bottom border:

- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click Edit Mode and click Object Mode
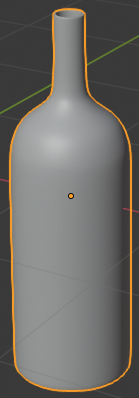
- In the Properties window, click Apply
- In the Tools window, click the Tools tab and click Smooth:
 Practical Learning: Creating an Empty Bottle
Practical Learning: Creating an Empty Bottle
- If necessary, right-click the bottle to select it
Press Shift + D to make a copy of the bottle and press Enter
- In the Properties window, click the Object button

- Click Bottle of Red Window.001 to select it
- Type Chantilly and press Enter
- In the Outliner, click the Restricted Viewport Visibility button on the right side of Chantilly
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click Add -> Mesh -> Cylinder
- In the Add Cylinder section below the Tools window, change the following values:
Vertices: 32
Radius: .105
Depth: .25
Location - Z: 2.4
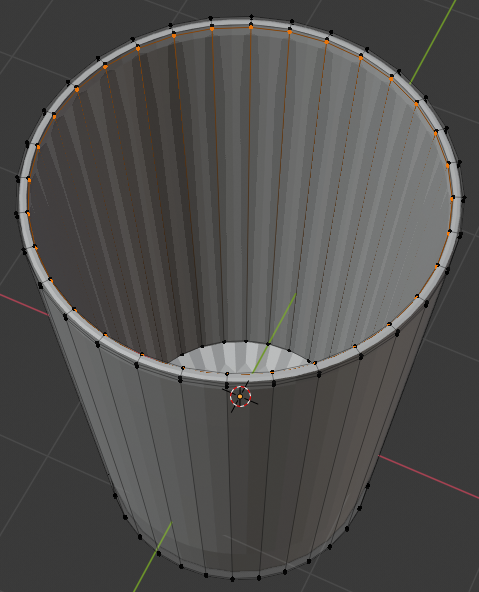
- Position the mouse in the work area and press Tab to display the cap (or cork) in Edit Mode
- Press Ctrl + R and create a horizontal cut on the shape, then move it up as follows:
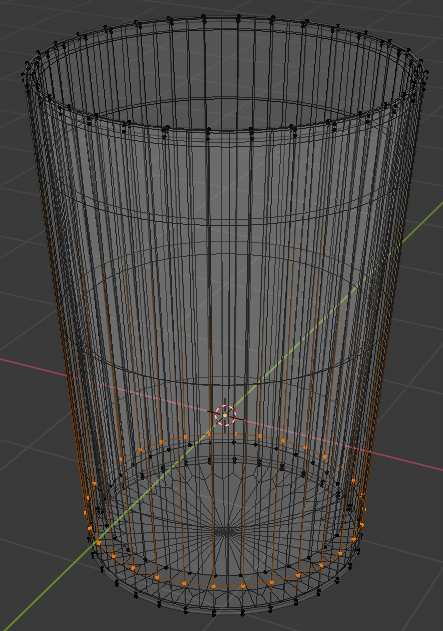
- Create another horizontal cut and position it as follows:
- On the menu bar of the 3D-View, click the Face Select button

- Press and hold Alt
- Right-click one of the middle faces
- Release Shift:
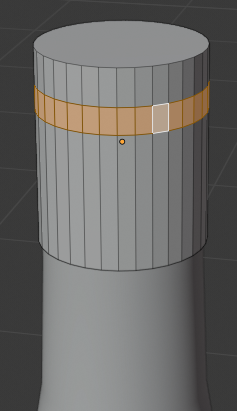
- Press E to extrude
- Press S to move the faces
- Type 1.1 and press Enter:
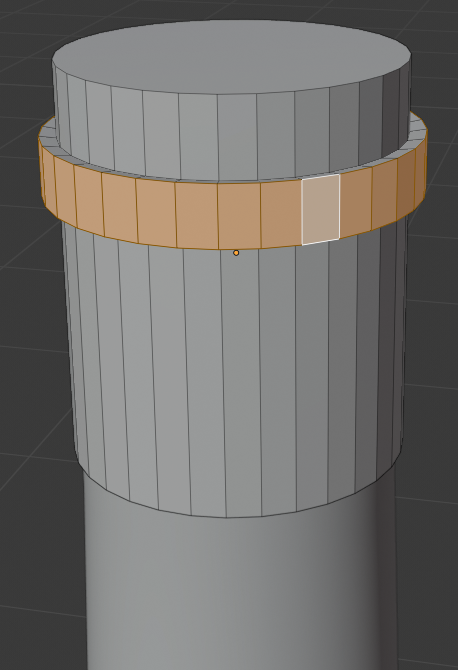
- Press Tab to display the cap (or cork) in Object Mode
- In the Properties window, click the Modifiers button
- Click Add Modifier and click Subdivision Surface

- Set the View value to 2
- Position the mouse on the bottle and press Tab to display in Edit Mode
- By pressing Ctrl + R to get a horizontal cut, movig that cut, and clicking to accept, polish the cap
- Press Tab to display the cap in Object Mode:

- In the Tools section of the Tools window, click the Smooth button
- In the Modifiers section of the Properties window, click Apply
- In the Properties window, click the Object button

- While the cap is still selected, in the Object section of the Properties window, click Cylinder to select it
- Type Bottle Cap and press Enter
- Position the mouse in the work area, make sure the bottle cap is selected.
Press and hold Shift
- Right-click the bottle to select it
- Release Shift:
- Press Ctrl + P
- In the menu that appears, click Object
- In the Outliner, click the + button of Bottle of Red Wine to expand it
- Still in the Outliner, click the Restricted Viewport Visibility button (the eye) on the right side of Bottle Cap
- In the Outliner, click the Restricted Viewport Visibility button (the eye) on the right side of Bottle of Red Wine
 Practical Learning: Creating Red Wine
Practical Learning: Creating Red Wine
- In the Outliner, click the Restricted Viewport Visibility button on the right side of Red Wine to display it
- In the work area, right-click the cylinder to select it
- Press Tab to display the object in Edit Mode
- Press Ctrl + R and get a cut in the upper portion of the object
- Click once to create the cut
- Move the line slightly down and click. Here is an example:
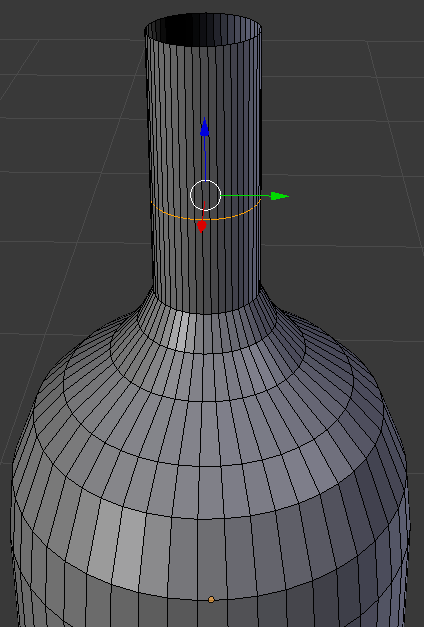
- Press Ctrl + Tab
- In the menu that appears, click Face
- Press and hold Alt
- Right-click a face or edge in the top part
- Release Alt:
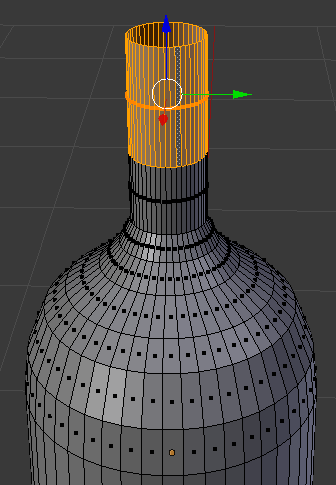
- Press X to delete
- In the menu that appears, click Faces:
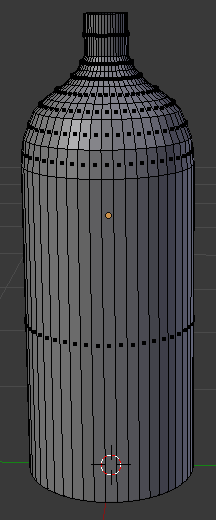
- Press Ctrl + Tab
- In the menu that appears, click Vertex
- Press and hold Alt
- Right-click a vertex in the top border
- Release Alt:
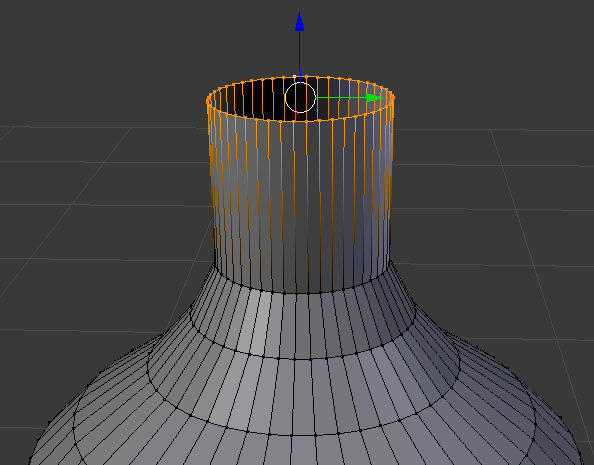
- Press E to extrude
- Press S to resize
- Type 0 to close and press Enter:
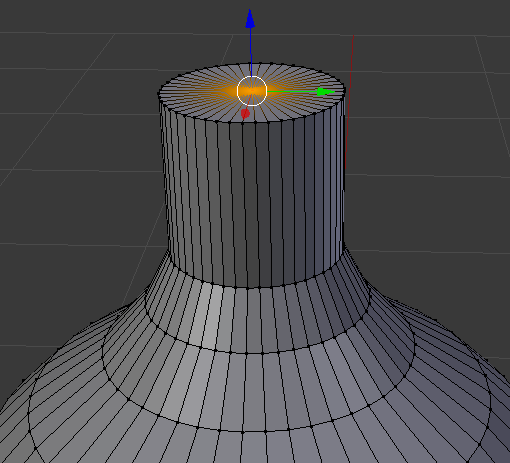
- Press Tab to display the shape in Object Mode
- In the Tools window, click the Tools tab and click the Smooth button
- In the Outliner, click the Restricted Viewport Visibility button (the eye) on the right side of Red Wine
 Practical Learning: Creating a Bottle of White Wine
Practical Learning: Creating a Bottle of White Wine
- In the Tools window, click Create
- Click Cylinder
- In the Add Cylinder section below the Tools window, change the following values:
Vertices: 48
Radius: .4
Depth: 2.5
Location - Z: 1.25
- In the Object section of the Properties window, click Cylinder to select it
- Type White Wine Bottle and press Enter
- Position the mouse in the work area and press Tab to display in Edit Mode
- Move the view so you can see the top side of the cylinder
- Press Ctrl + Tab and, on the menu that appears, click Face
- On the cylinder, right-click the top face of the cylinder, press X, and click Faces
- Press Ctrl + R and make sure you get a horizontal cut on the object
- Roll the middle mouse button slightly up to get 2 cuts:

- Then click once to accept the cuts
- Move the mouse a little bit up. Here is an example:
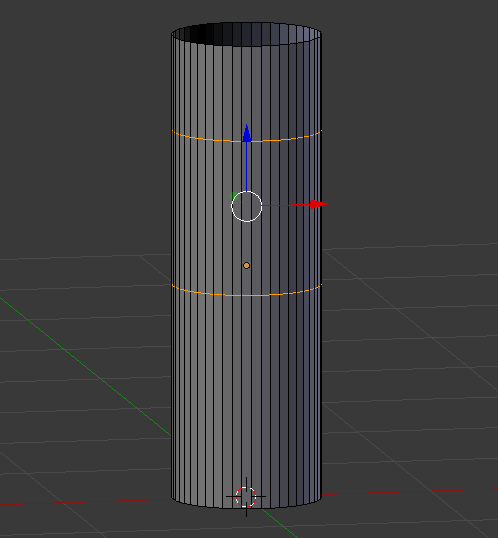
- Press Alt and right-click a vertex in the top border to select all of them
- Release Alt
- Press S
- Type.25 and press Enter
- Press Alt and right-click a vertex in the second cut to select those vertices
- Release Alt
- Press S
- Type .25 and press Enter:
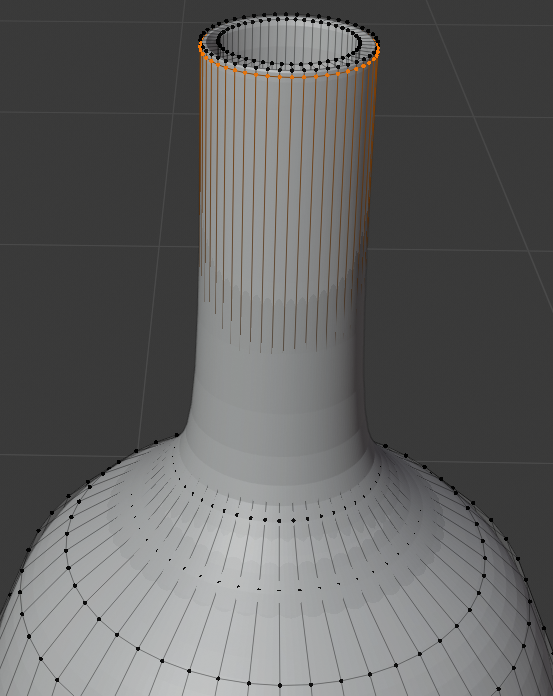

- Position the mouse in the middle part of the bottle and press Ctrl + R to get a horizontal cut
- Roll the middle mouse button to get 3 cut, then click twice to confirm. Here is an example:
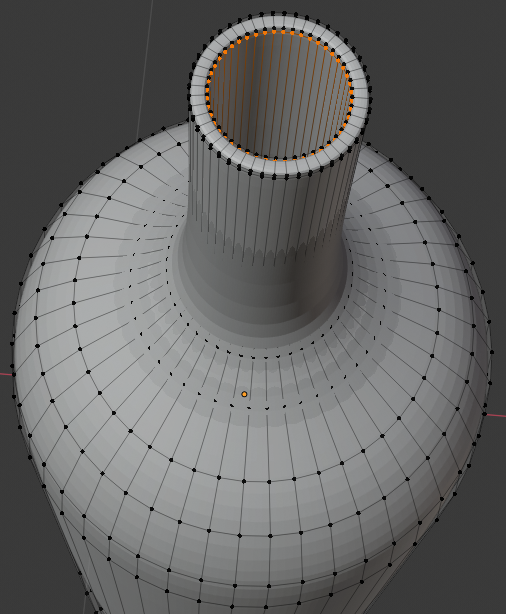
- Press and hold Alt, then right-click a cut to select its vertices, then release Alt, then press S and move the mouse to resize the cut. Model the bottle as follows:
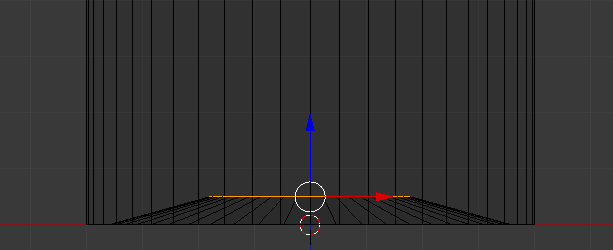
- Move the view so you can see the bottom side of the bottle
- Press Alt, right-click a bottom vertext to select the whole border, then release Alt:
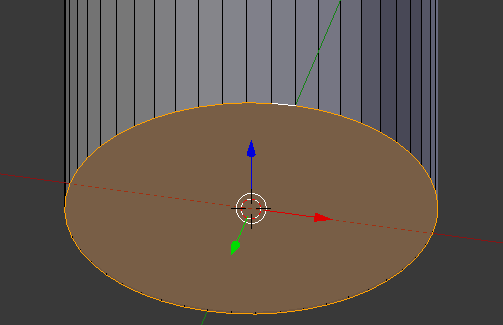
- Press E and press Enter
- Press S
- Type .9 and press Enter:
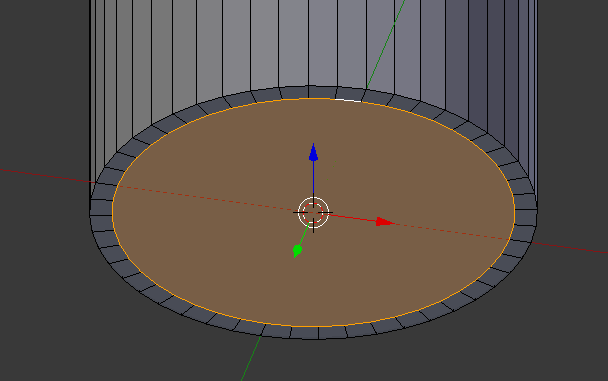
- Press E and press Enter
- Press S
- Type .5 and press Enter:
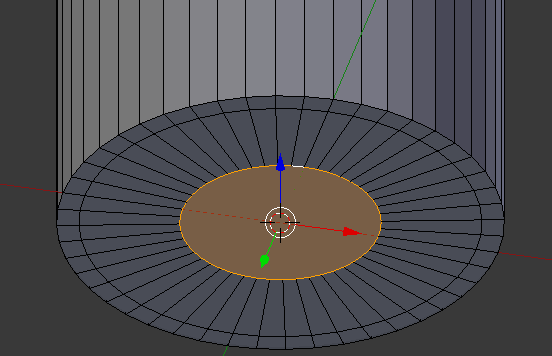
- Press G to prepare to move the vertex
- Press Z to move vertically
- Type .05 and press Enter:
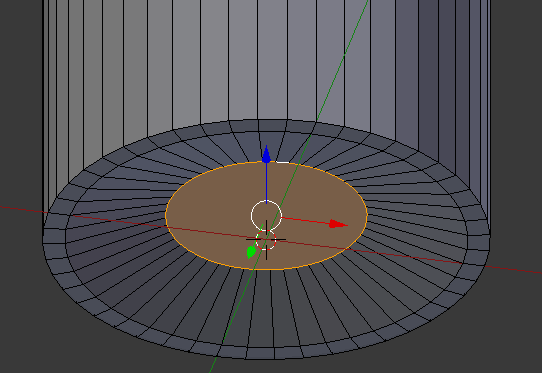
- Press Tab to display the Object Mode
- In the Properties window, click the Modifiers button
- Click Add Modifier and click Solidify:

- Click the Thickness value, type.02 and press Enter
- Click Apply
- Click Add Modifier and click Subdivision Surface
- Set the View value to 2
- Position the mouse on the bottle and press Tab to display in Edit Mode
- Position the mouse in the upper section of the bottle, press Ctrl + R to get a horizontal line
- Click twice to confirm
- Move the blue line (Z axis) up as close as possible to the top border:

- Move the view so you can see the bottom part of the bottle
- Press Ctrl + R to get a horizontal cut and press twice to confirm
- Move the line down close to the bottom border:
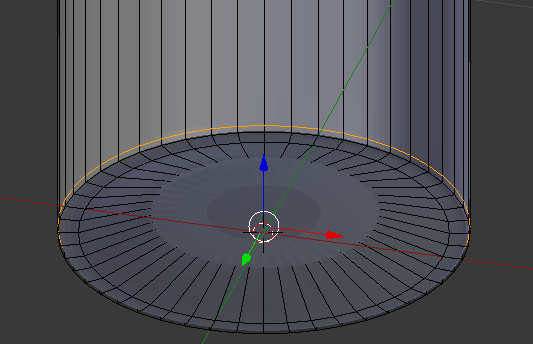
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click Edit Mode and click Object Mode
- In the Properties window, click Apply
- In the Tools window, click the Tools tab and click Smooth:

- In the Outliner, click the Restricted Viewport Visibility button (the eye) on the right side of White Wine Bottle
 Practical Learning: Creating an Empty Wine Glass
Practical Learning: Creating an Empty Wine Glass
- In the Tools window, click Create and click Plane
- In the Object section of the Properties window, click Plane to select it
- Type Empty Glass and press Enter
- In the Transform section, change the following values:
Location - X: 1
Y: 1
Z: 0
- Move the view and zoom in so you can see the top side of the plane
- Position the mouse on the cube and press Tab to switch to Edit Mode
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click the Pivot Point button and click Active Element
- The Vertex Select option should be On (if you have doubt, on the menu bar of the 3D-View, click the Vertex Select button
 )
)
On the plane, right-click the vertex in the top-left side
- Press and hold Shift
- Right-click the vertex in the top-right side and the vertex in the bottom-right side
- Release Shift:
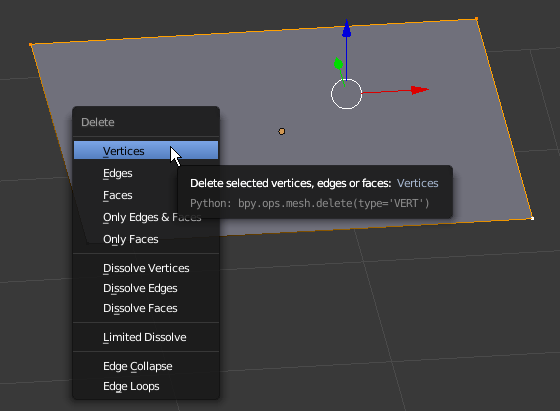
- Press X to delete
- In the menu that appears, click Vertices:
- In the Numeric Pad, press 1 (you should be in the orthogonal view; if you are not, press 5).
Also zoom in to get a bigger view
- Right-click the vertex that was left (if you don't see it, simply press A to select everything)
- Press and hold Ctrl
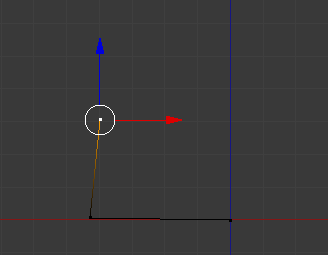
- Position the mouse on the left side by approximately 4 units and click (don't try to be precise; you will make the changes later):
- Still holding down Ctrl, position the mouse anywhere above the new vertex and click (again, don't try to be precise):
- Continue using the Ctrl key and clicking to create a shape that looks approximately as follows. Don't follow exactly the following illustration. You will make any changes later:
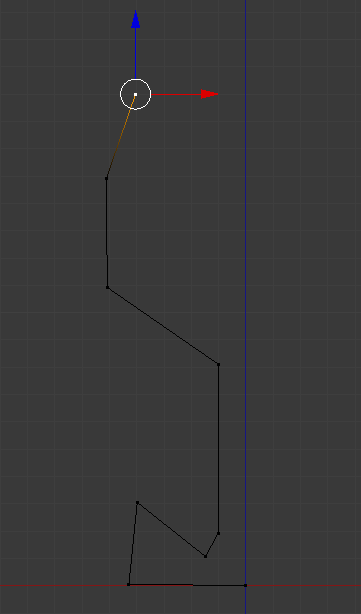
- To select a vertex, you can right-click it. Here is an example:
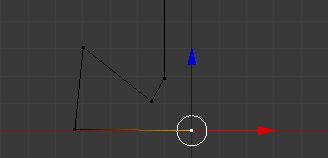
- To select many vertices, first select one of them, press and hold Shift, then right-click the other desired vertices, and release Shift
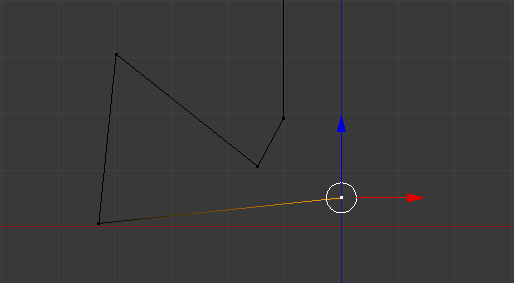
- To move a vertex, first select it. Then, either use the axes arrows and move them, or press G, move the mouse to the desired area, and click. Here is an example:
- To move many vertices, first select them, then either use the G key or the arrows to move them
- To create a new vertex, first select one on one end. Then, either hold down the Ctrl key and click in the desired area, or press E, move the mouse to the desired area, and click. Here is an example:
- To segment a line with one cut (or to create a cut), press Ctrl + R, position the mouse on the edge to be segmented until you see a dertex on it. Here is an example:
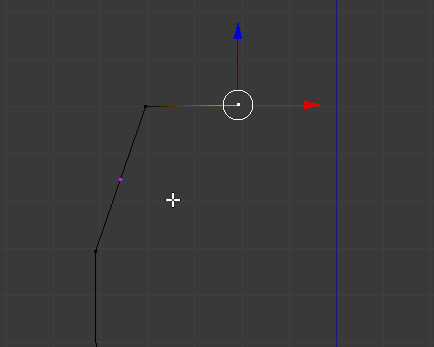
- Then click. Here is an example:
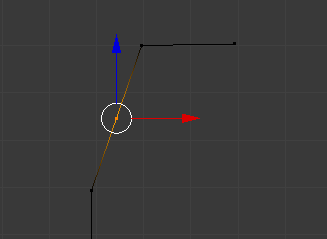
- To create many cuts, press Ctrl + R until you see an orange dot on the line, then roll the middle mouse button to specify the number of cuts, then click
- Based on these techniques, create a shape approximately as follows (yours doesn't have to be exactly like the following shape; we are trying to model a glass, so use your own imagination/inspiration and taste):
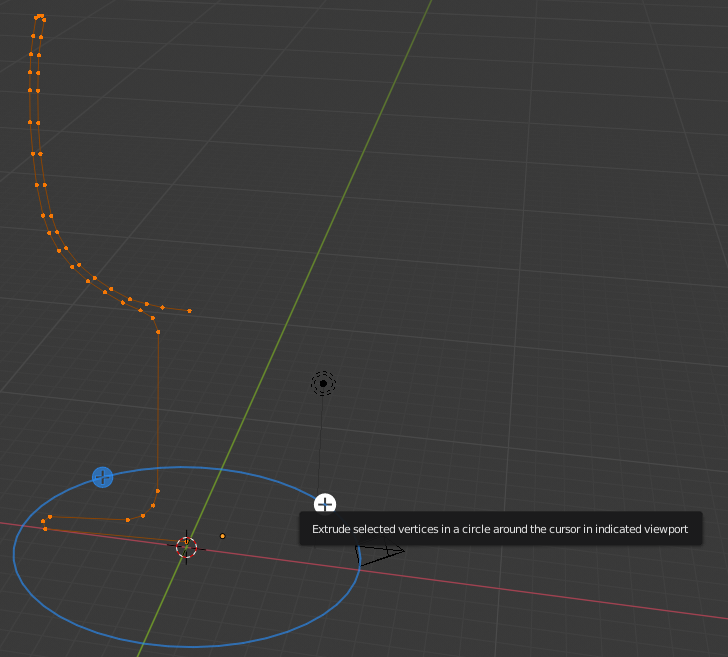
- Press Shift + S
- In the menu that appears, click Cursor to Center
- Press A to select all vertices:
- In the Numeric Pad, press 7 to display the top view
- In the Tools menu, click the Tools tab and, in the Add section, click Spin
- In the Spin section below the Tools window, change the collowing values:
Steps: 72
Angle: 360
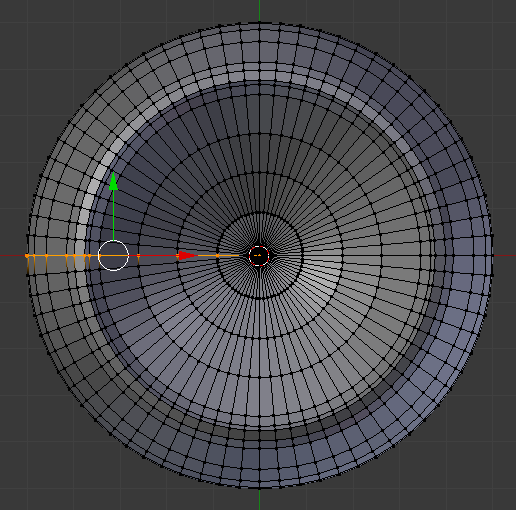
- Move the view to see the glass in perspective:
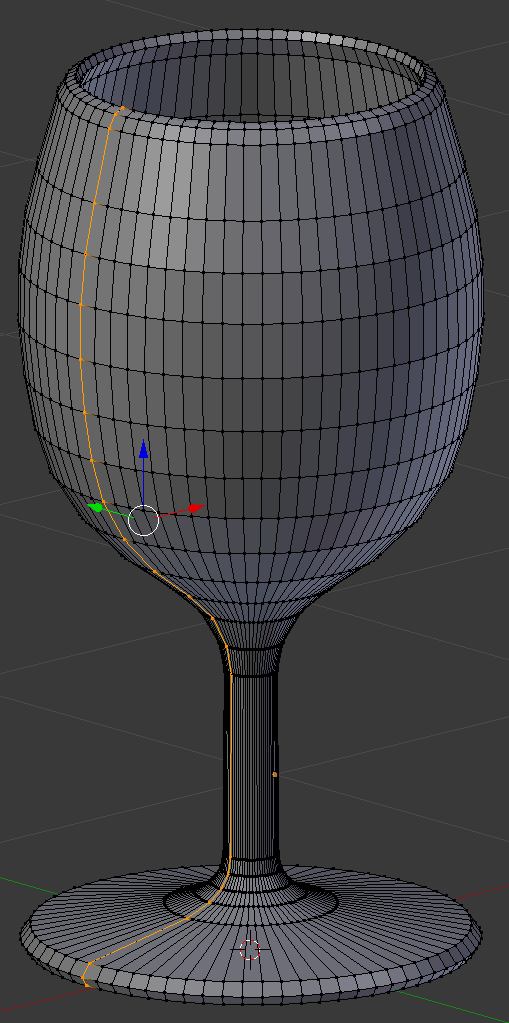
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click Edit Mode and click Object Mode:

- In the Properties window, click the Modifiers button
- Click Add Modifier and click Subdivision Surface
- Set the View value to 2
- In the Tools window, click the Tools tab and click Smooth
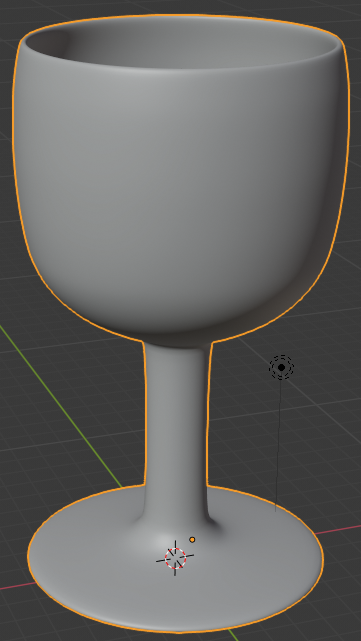
- In the Outliner, click the Restricted Viewport Visibility button (the eye) on the right side of Empty Glass to hide it
 Practical Learning: Creating an Ice Bucket
Practical Learning: Creating an Ice Bucket
- Press Shift + S
- In the menu that appears, click Cursor to Center
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click Add -> Mesh -> UV Sphere
- In the Numeric Pad, press 1 (the sphere should be in orthographic view; if that's not the case, press 5)
- Zoom in to see a larger view of the sphere
- Press Tab to display the sphere in Edit Mode
- Press A to deselect everything
- Press Z to display the sphere in wireframe
- Press B to prepare to box-select
- Draw a rectangle that selects the top portion of the sphere, including the middle line:
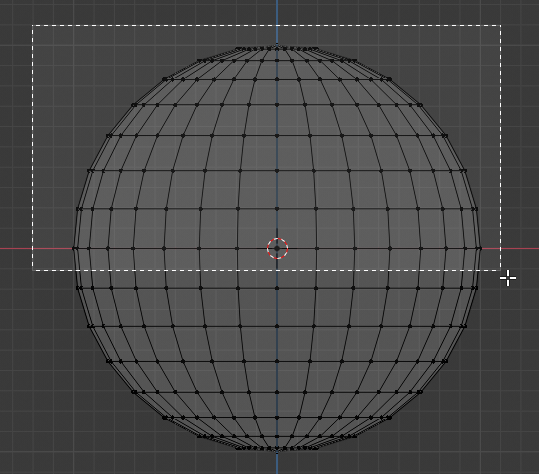
- Release the mouse:
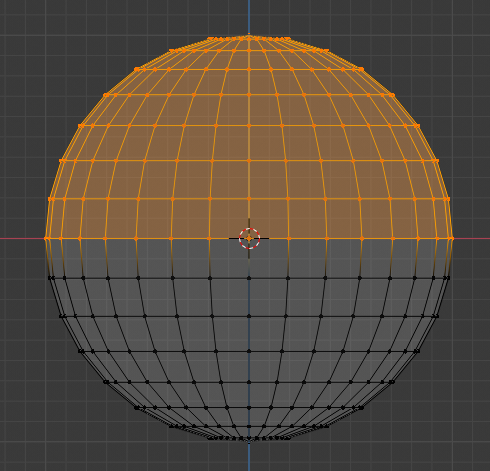
- Press X to delete
- In the menu that appears, click Faces:
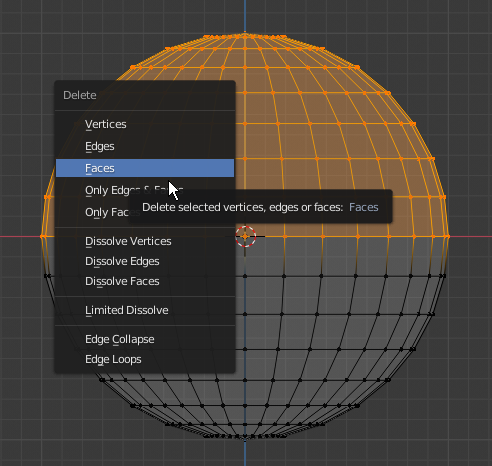
- Move the view so you can see the bottom side of the object
- The Vertex Select should be On (if you have doubt, on the menu bar of the 3D-View, click the Vertex Select button
 )
)
Right-click the central-bottom vertex of the shape:
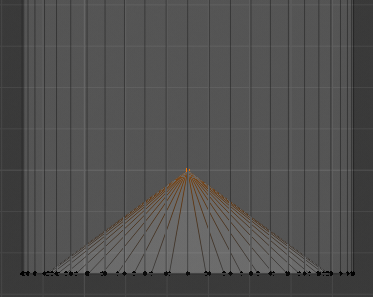
- Press G to move the vertex
- Press Z to move vertically
- Type .02 and press Enter
- In the Numeric Pad, press 1
- Press B to box-select
- Draw a rectangle that selects the group of bottom vertices:
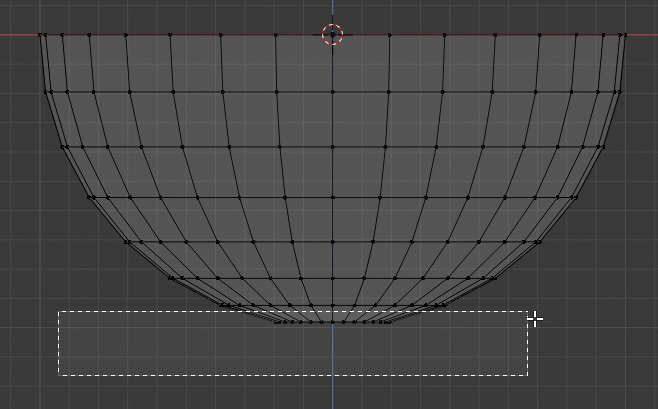
- Press G
- Press Z
- Type .06 and press Enter
- Press B to box-seect
- Draw a rectangle that selects the group of bottom vertices:
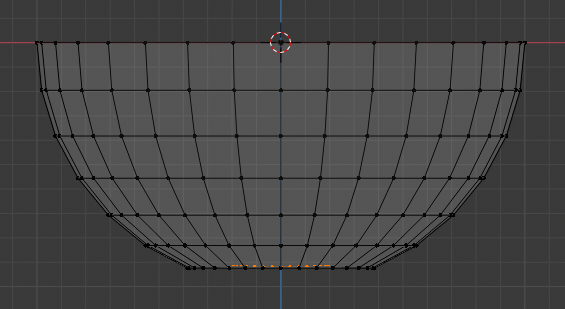
- Press G
- Press Z
- Type .1 and press Enter:
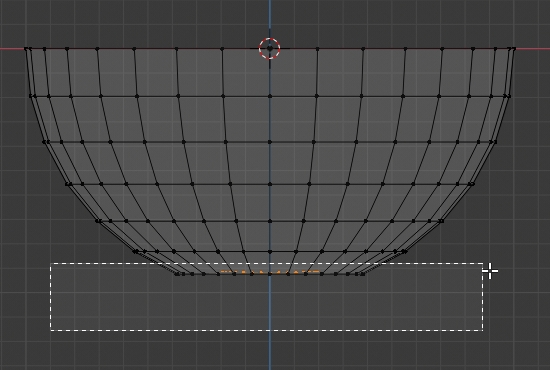
- Press Z to exit the wireframe
- Press Tab to display the shape in Object Mode:
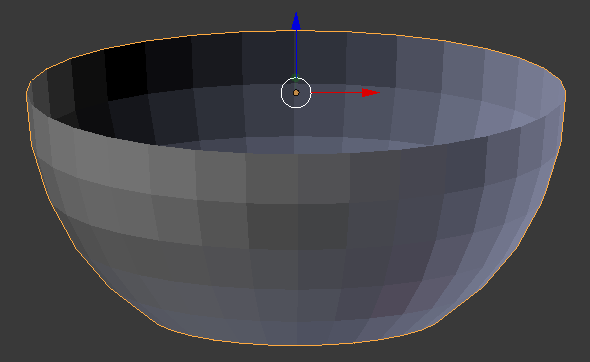
- In the Properties window, click the Object button

- Click Sphere to select it
- Type Ice Bucket and press Enter
- In the Properties window, click the Modifiers button

- Click Add Modifier and click Solidify:

- Click the Thickness value, type .05 and press Enter
- Click Add Modifier and click Subdivision Surface
- Set the View to 2
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click Edit Mode and click Object Mode
- In the Properties window, under Subsurf, click Apply
- Under Solidify, click Apply
- In the Tools tab of the Tools window, in the Shading section, click Smooth:
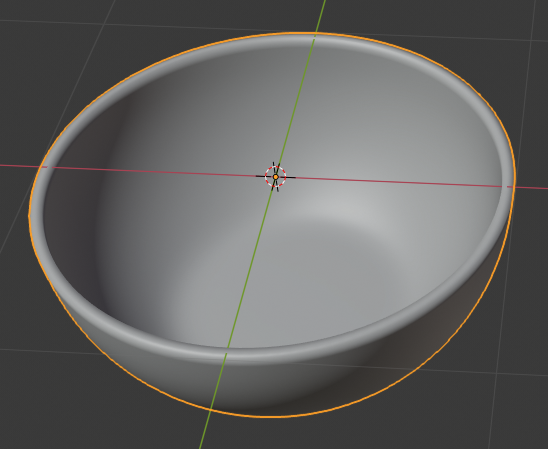
- In the Outliner, click the Restricted Viewport Visibility button (the eye) on the right side of Ice Bucket to hide it
 Practical Learning: Creating a Shelf for Bottles
Practical Learning: Creating a Shelf for Bottles
- In the Tools window, click Create and click Cylinder
- In the Add Cylinder section below the Tools window, change the value of Vertices to 6
- In the Object section of the Properties window, change the collofing values:
Location - X: -2
Y: 6.85
Z: 2.7
Scale - X: .125
Y: .125
Z: 2.15
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + D and press Enter
- In the Properties window, in the Location section, change the X value to -1
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + D and press Enter
- In the Properties window, in the Location section, change the X value to 0
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + D and press Enter
- In the Properties window, in the Location section, change the X value to 1
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + D and press Enter
- In the Properties window, in the Location section, change the X value to 2
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + A -> Mesh, and click Cube
- In the Object tab of the Properties window, change the following values:
Location - X: 0
Y: 6.25
Z: 1
Scale - X: 2.35
Y: .625
Z: .025
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + A -> Mesh, and click Cube
- In the Object tab of the Properties window, change the following values:
Location - X: -1.1
Y: 6.25
Z: 2
Scale - X: 1.25
Y: .625
Z: .025
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + A -> Mesh, and click Cube
- In the Object tab of the Properties window, change the following values:
Location - X: 1.35
Y: 6.25
Z: 3
Scale - X: 1
Y: .625
Z: .025
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + A -> Mesh, and click Cube
- In the Object tab of the Properties window, change the following values:
Location - X: -1.55
Y: 6.25
Z: 4
Scale - X: .85
Y: .625
Y: .025
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + A -> Mesh, and click Cube
- In the Object tab of the Properties window, change the following values:
Location - X: 0
Y: 6.25
Z: 5
Scale - X: 2.35
Y: .625
Z: .025
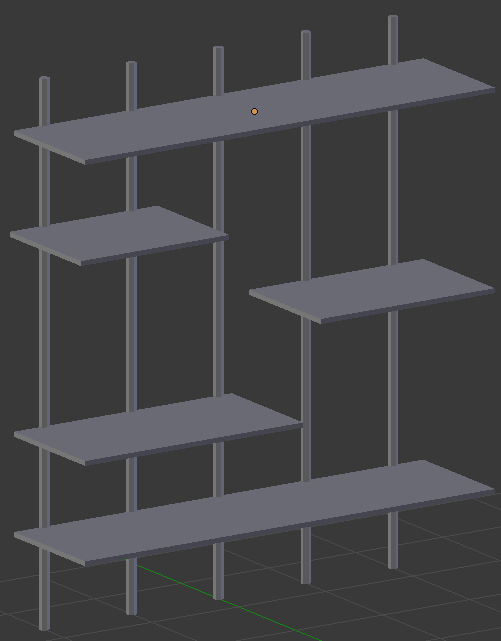
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click Add -> Mesh -> Cube
- In the Transform section of the Properties window, change the following values:
Name: Left Wall Shoe Molding
Location - X: -5.95
Y: 6.15
Z: .2
Scale - X: .05
Y: 1
Z: .2
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click Add -> Mesh -> Plane
- In the Object section of the Properties window, change the following values:
Name: Left Wall
Location - X: -6
Y: 6.15
Z: 4
Rotation - Y: 90
Scale - X: 4
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click Add -> Mesh -> Cube
- In the Transform section of the Properties window, change the following values:
Name: Back Wall Shoe Molding
Location - X: 0
Y: 7
Z: .2
Scale - X: 6.25
Y: .05
Z: .2
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click Add -> Mesh -> Plane
- In the Object section of the Properties window, change the following values:
Name: Back Wall
Location - X: 0
Y: 7.045
Z: 3.5
Rotation - X: 90
Scale - X: 6.15
Y: 3.5
- Position the mouse in the work area, press Shift + A -> Mesh, and click Plane
- In the Object tab of the Properties window, change the following values:
Location - X: 0
Y: 5.5
Z: .01
Scale - X: 6
Y: 2
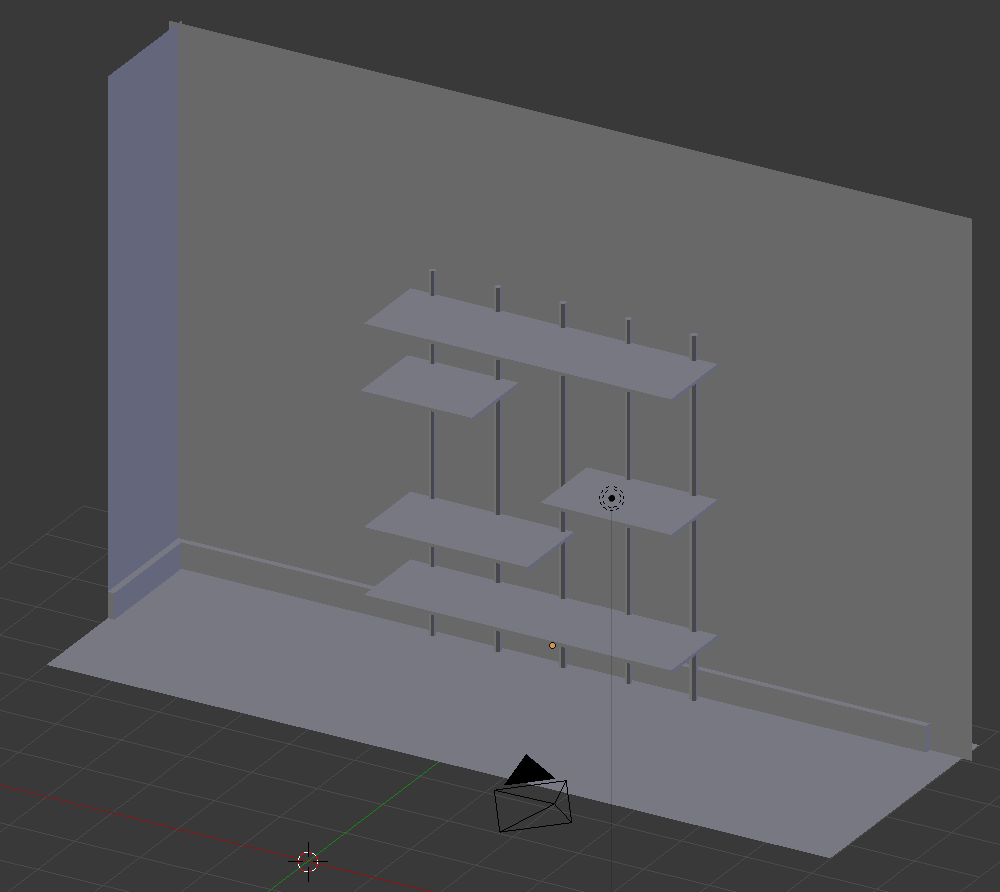
- In the Create tab of the Tools window, click Plane
- In the Object tab of the Properties window, change the following values:
Name: Front Light
Location - X: .25
Y: -4
Z: 5.25
Rotation - X: 45
Scale - X: 3
- In the Create tab of the Tools window, click Plane
- In the Object tab of the Properties window, change the following values:
Name: Left Light
Location - X: -4
Y: 2
Z: 2
Rotation - X: 90
Z: -30
Scale - X: 2
Y: 1.5
- In the Create tab of the Tools window, click Plane
- In the Object tab of the Properties window, change the following values:
Name: Right Light
Location - X: 6
Y: 4
Z: 3
Rotation - X: 30
Y: 105
- In the Outliner, click the Restrict Viewport Visibility of Front Light to hide it
- In the Outliner, click the Restrict Viewport Visibility of Left Light to hide it
- In the Outliner, click the Restrict Viewport Visibility of Right Light to hide it
 Practical Learning: Putting the Objects Together
Practical Learning: Putting the Objects Together
- In the Numeric Pad, press 1 to display the front view (make sure you are in orthogonal view)
- In the Outliner, below the Bottle of Red Wine node, click the Restrict Viewport Visibility button (the eye) on the right side of Bottle Cap to display it
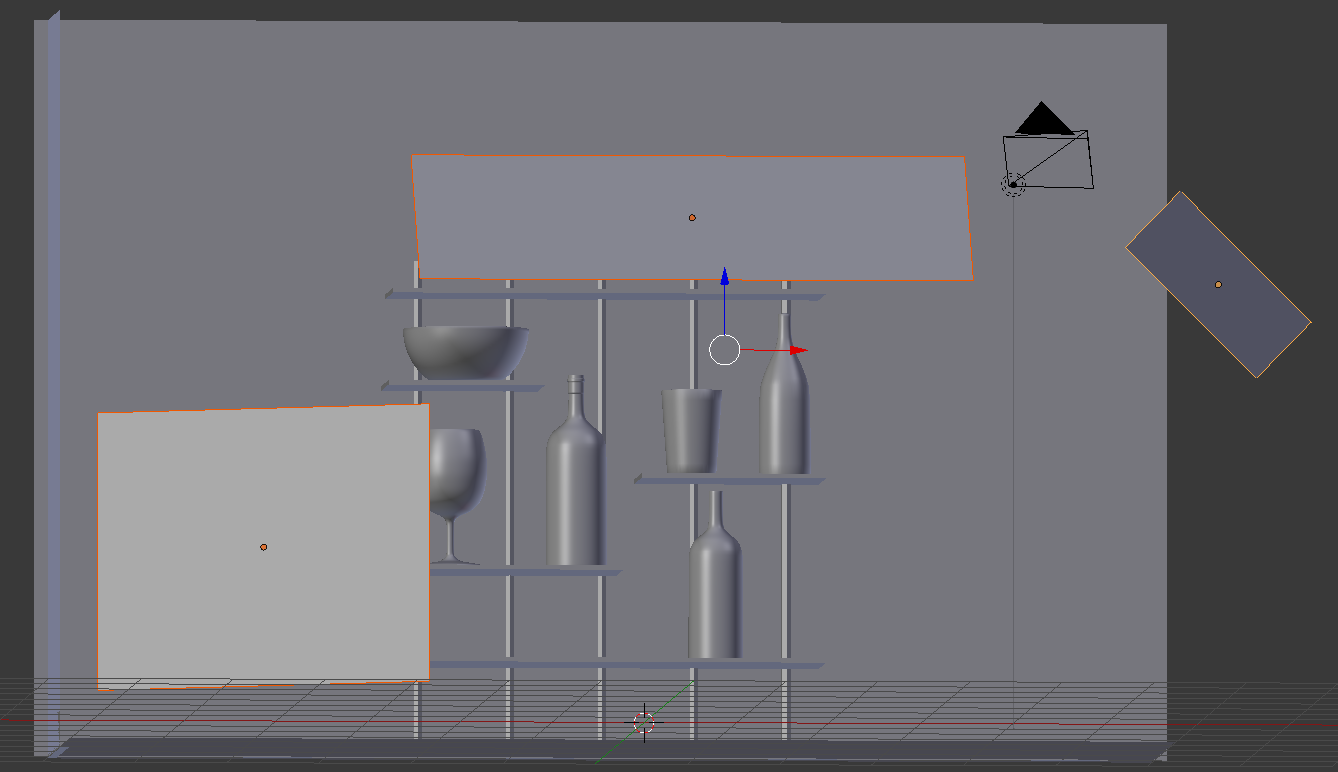
- In the Outliner, you will click the Restrict Viewport Visibility button (the eye) on the right side of Ice Bucket, Classic Cup, Empty Glass, Bottle of Red Wine, White Wine Bottle, and Chantilly to display them.
To work on an object, in the work area, you will right-click the object to select it
- Position the mouse in the work area.
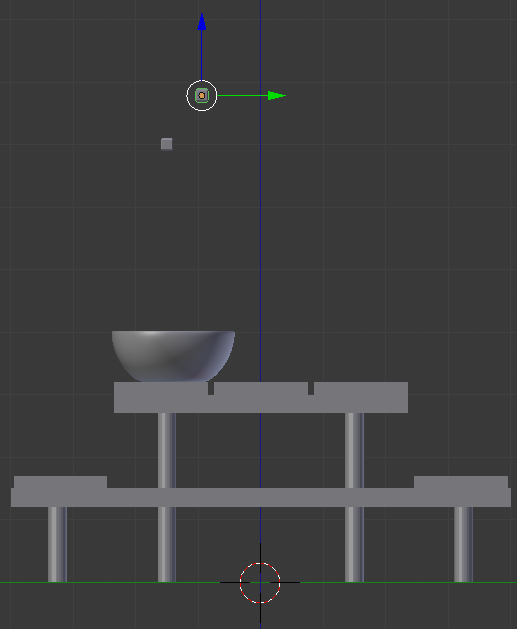
Press S and use the mouse to resize the ice bucket.
Either press G or use the blue and red arrows on the screen to position the ice bucket somewhere on the top-left of the table:
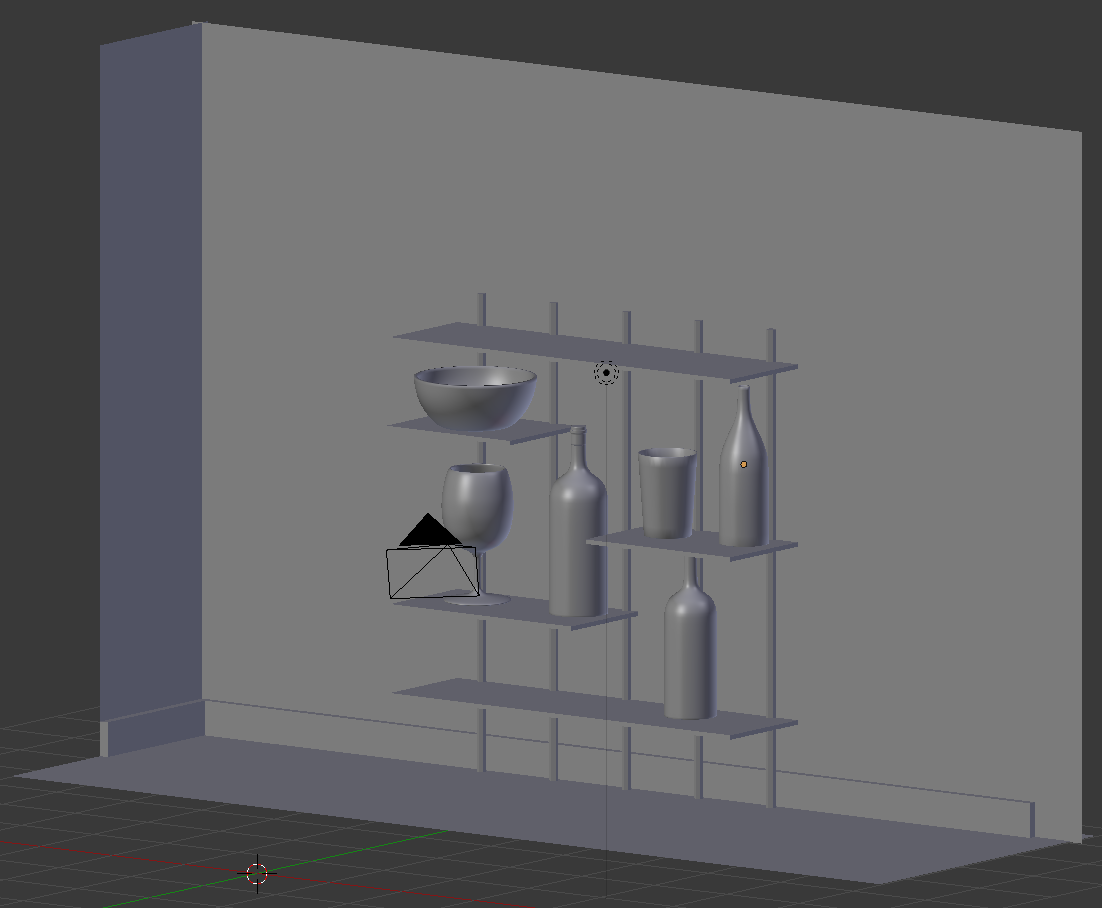
- In the Numeric Pad, press 1
- In the Outliner, click the Restrict Viewport Visibility button on the right side of Red Wine to display it
- Press Z to switch to wireframe
- In the work area, right-click the wine to select it
- Using either the G key or the blue and red arrows on the screen, position the wine within the Bottle of Red Wine:
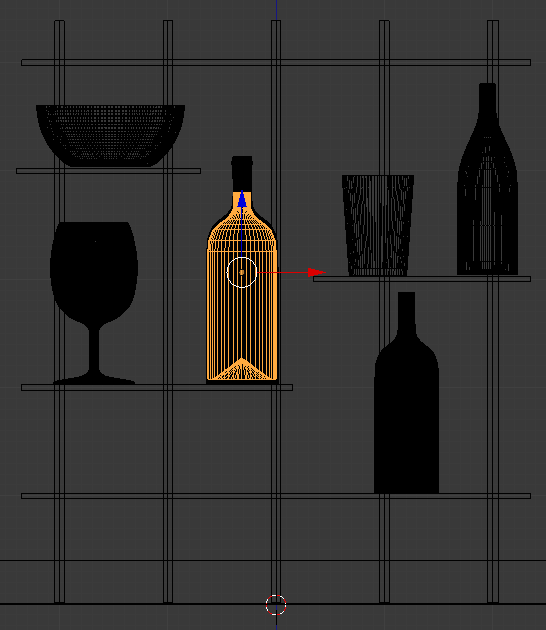

- Press Z to switch to Solid view
 Practical Learning: Applying Introductor Materials
Practical Learning: Applying Introductor Materials
- In the top menu bar, click Blender Render and select Cycles Render
- In the Properties window, in the Resolution section, click 50%, type 100 and press Enter
- Still in the Properties window, click Sampling to expand it
- In the Sampling section, click the Render value, type 500 and press Enter
- On the menu bar of the 3D View, click the Viewport Shading button and select Material:
- In the Properties window, click the Material button

- In the Outliner, click Floor to select it
- In the Materials section of the Properties window, click the New button
- Click the white Color button and click RGB:
- Se the folow values as follows:
R: .105
G: .05
B: .015
- In the Outliner, click Left Wall to select it
- In the Material section of the Properties window, click the New buttton
- Click Material.002 to select the name
- Type Cream and press Enter
- Click the white color button
- Set the color value as follows:
R: .915
G: .85
B: .615
- In the Outliner, click Back Wall to select it
- In the Material section of the Properties window, click the button on the left side of New and click Cream
- Right-click one of the cylinders behind the shelves to select it:

- Right-click one of the column behind the shelves to select it:

- In the Materials section of the Properties window, click New
- Click Material.002 to select it
- Type Gray and press Enter
- Click the Color button
- Click inside the vertical bar on the right side of the color wheel and select a light-gray color (such as R = G = B = .4)
- Right-click another column behind the shelves
- In the Material section of the Properties window, click the button on the left side of New and select Gray
- Apply the Gray material to the other columns behind the shelves
- Right-click one of the shelves to select it
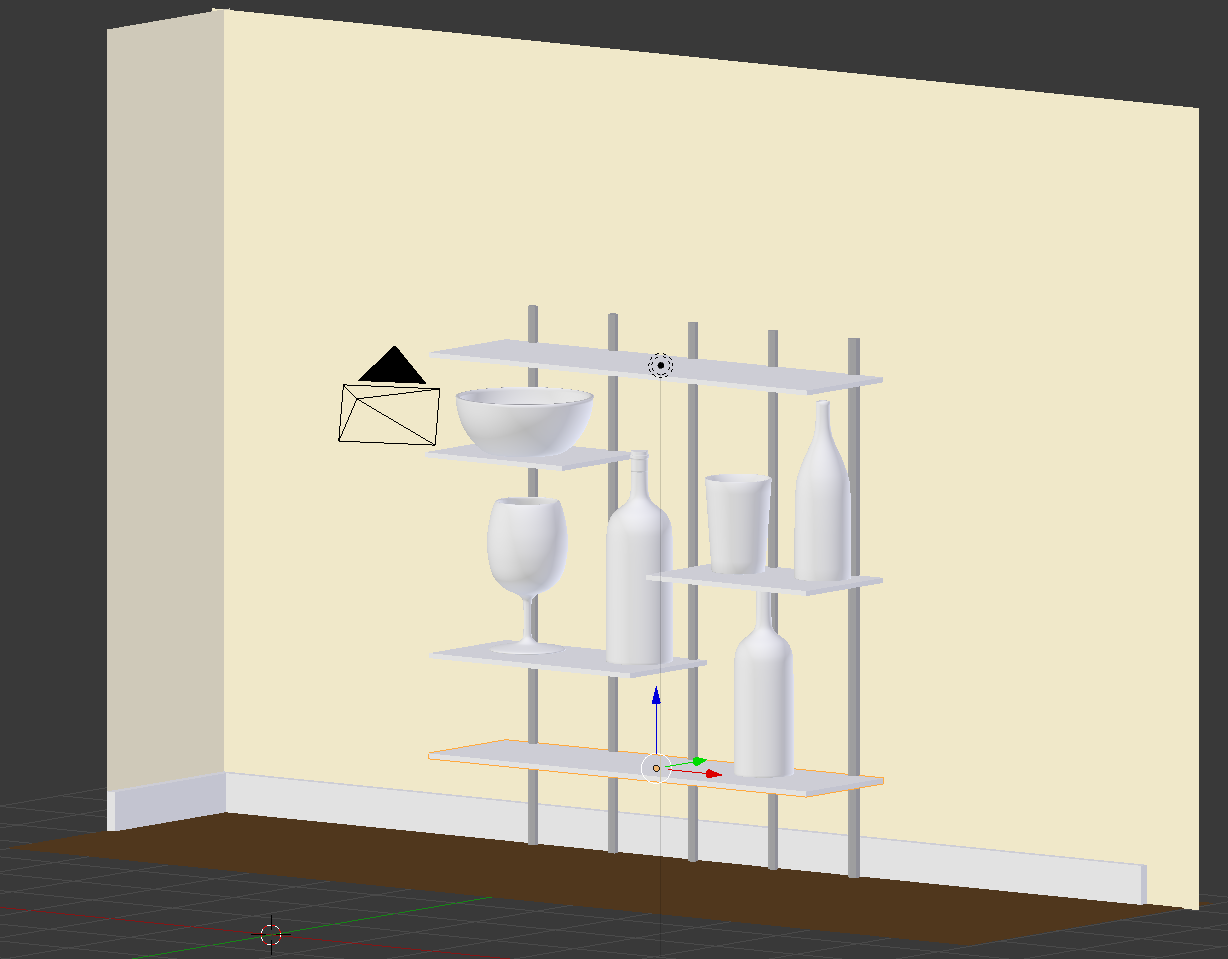
- In the Material section of the Properties window, click the New button
- Click Material.002 to select the name
- Type Woody and press Enter
- Click the Color button and click Hex
- Set the Hex value as BC6B02 and press Enter
- Right-click each of the other shelves. In the Material section of the Propertoies button, click the button on the left side of New and select Woody
- In the Outliner, below Bottle of Red Wine, click Bottle Cap to select it
- In the Properties window, click the New button
- Click the Color button and click Hex
- Set the Hex value to 64110D and press Enter
- In the Outliner, click the Restrict Viewport Visibility of Front Light to display it
- In the Outliner, click the Restrict Viewport Visibility of Left Light to display it
- In the Outliner, click the Restrict Viewport Visibility of Right Light to display it
- In the Outliner, click Front Light to select it
- In the Properties window, click the New button
- Click Diffuse BSDF and, in the menu that appears, click Emission
- Click the Color button
- Scroll completely up in the vertical bar (R = G = B = 1)
- Set the Strength value to 15
- In the Outliner, click Left Light to select it
- In the Properties window, click the New button
- Click Diffuse BSDF and, in the menu that appears, click Emission
- Scroll completely up in the vertical bar (R = G = B = 1)
- Set the Strength value to 10
- In the Outliner, click Right Light to select it
- In the Properties window, click the New button
- Click Diffuse BSDF and, in the menu that appears, click Emission
- Set the Strength value to 5
- Position the mouse on the work area and, in the Numeric Pad, press 0 to display the camera view
- Press N to display the Properties Region
- In the Properties Region, click Lock Camera to View to put a check box on it
- Use the mouse and keyboard to display the view any way you want. Here is an example::
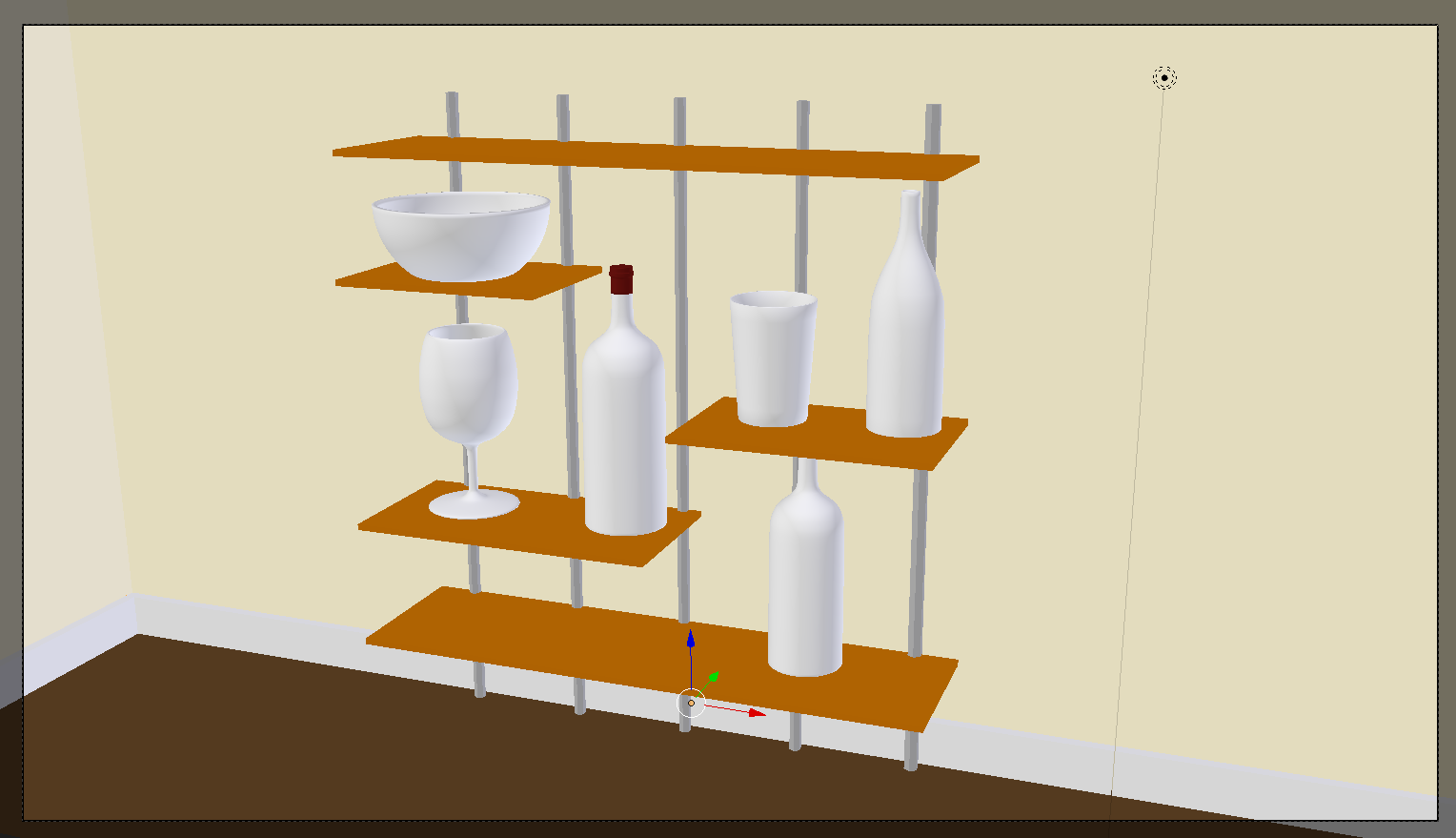
- In the Properties Region, click Lock Camera to View to remove the check mark
- Press N to close the Properties Region
A Glass Material
To support the ability to create glass-based objects, Blender provides a material named Glass BSDF. Like the Diffuse material, the Glass BSDF material is equipped with the color characteristic that can be used to give a colored appearance to an object.
 Practical Learning: Applying a Glass Material
Practical Learning: Applying a Glass Material
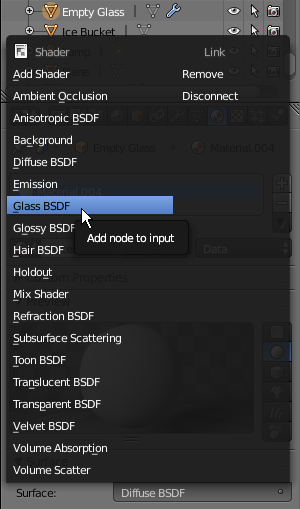
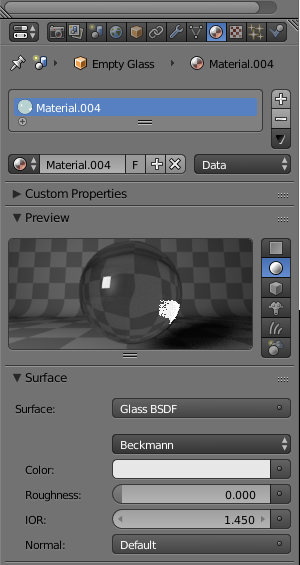
- In the Outliner, click Empty Glass to select it
- In the Material section of the Properties window, click the New button
- Click the Preview button to expand it
- Click Diffuse BSDF
- In the menu that appears, click Glass BSDF:
- On the top menu of Blender, click Render -> Render Image. Here is an example:
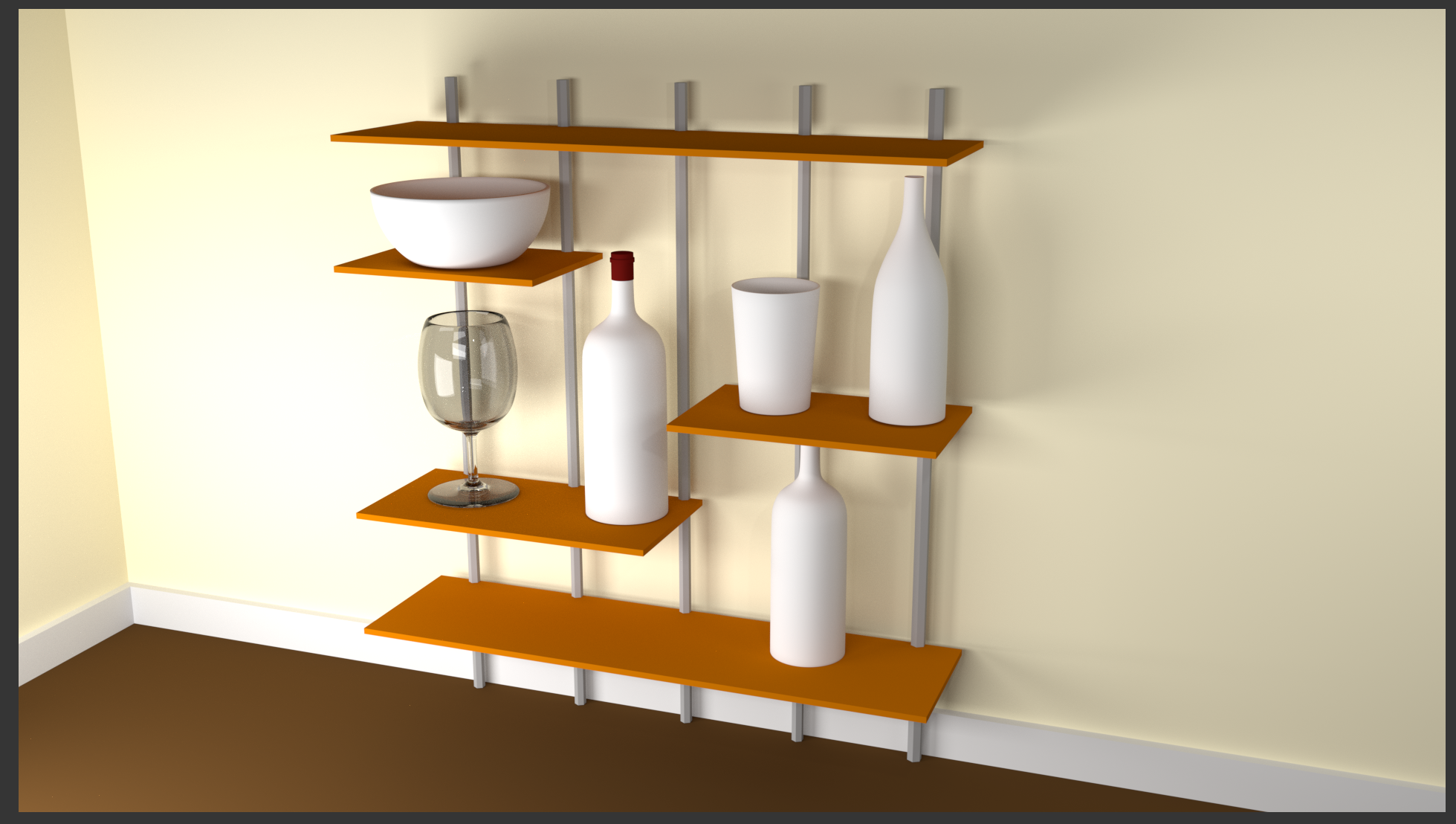

- After viewing the results, press Esc
- Right-click the left border of the Properties window and click Split Area:
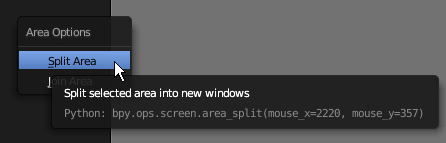
- Position the mouse somewhere between the top border and the center of the work area
- Click to confirm. If necessary, resize the windows
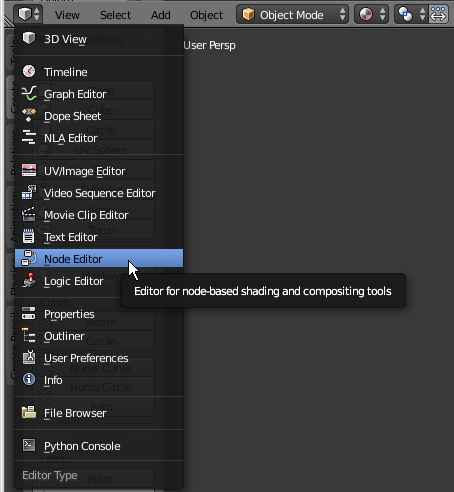
- In the bottom-left side of the new window, click the 3D Viewport button and select Node Editor
- In the Outliner, click White Wine Bottle to select it
- In the Node Editor, click the New Button
- Zoom in the Node Editor to see the material window as much as possible
- In the Material section of the Properties window, click Diffuse BSDF and select Glass BSDF
- In the Node Editor, click the Color button
- Set the RGB value as follows:
R: 1
G: .95
B: .465
- In the Outliner, click Bottle of Red Wine to select it
- On the Node Editor menu bar, click the New button
- In the Node Editor, click somewhere in the Diffuse window to select it
- Press Delete to remove it
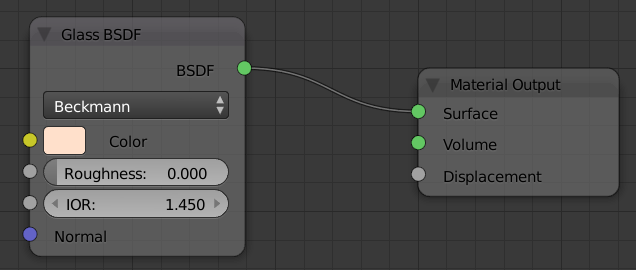
- On the menu bar of the Node Editor, click Add -> Shader -> Glass BSDF
- Position the mouse on the left of the Material Output window and click
- Click the Color button and click RGB
- Se the color value as follows:
R: 1
G: .885
B: .805
- Drag the green button from Glass BSDF to the Surface button:
- In the Properties window, click the Render button

- In the Render section, click the Render button. Here is an example:
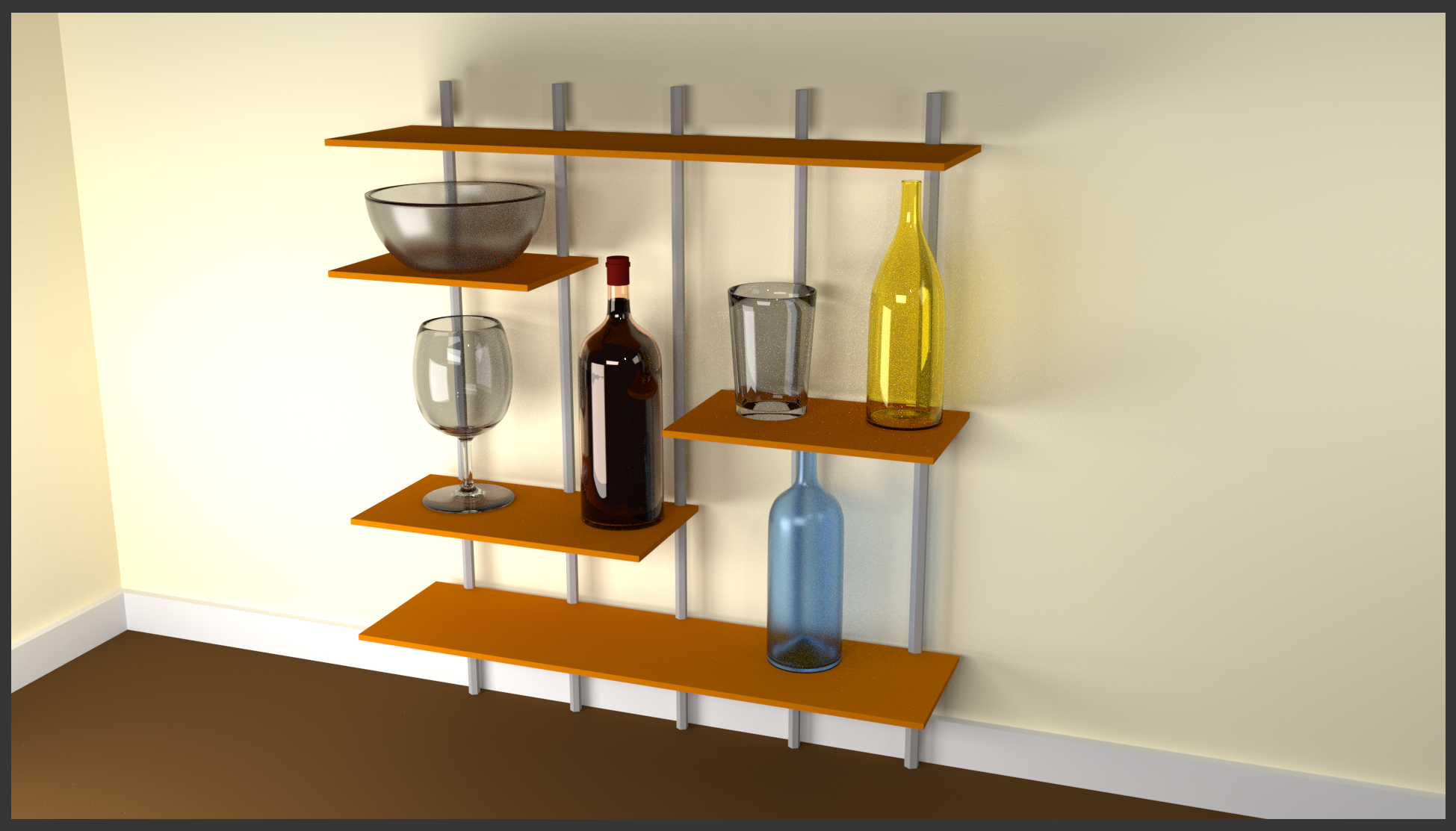

The Roughness of a Glass
Like the Diffuse material, the Glass BSDF has a characteristic named Roughness. The Roughness of a glass is a decimal value between 0.0 and 1.00. When the value is set to 0 (or 0.00), the object is perfectly transparent. In this case, depending on the type of object, you may be able to see what is on the other side of the object. If/When the roughness is set to 1 (or 1.00), the transparency level of the object is semi-completely blurred.An object is referred to as glossy if it shines. To support this, Blender provides a material named Glossy BSDF.
 Practical Learning: Applying Roughness to a Glass
Practical Learning: Applying Roughness to a Glass
- In the Outliner, click Ice Bucket to select it
- In the Material section of the Properties window, click New
- In the Material section of the Properties window, click Diffuse BSDF and click Glass BSDF
- In the Node Editor, Click the Roughness value
- Type .05 and press Enter
- In the Outliner, click Chantilly to select it
- On the menu bar of the Node Editor, click the New button
- In the Material section of the Properties window, click Diffuse BSDF and click Glass BSDF
- In the Node Editor, click Color and set the RGB value as follows:
R: .75
G: .875
B: 1
- Set the Roughness to .075
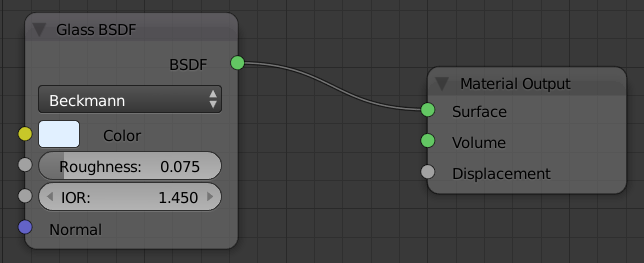
- In the Outliner, click Classic Cub to select it
- In the Node Editor, click the New button
- In the Properties window, click Diffuse BSDF and click Glass BSDF
- Click the Roughness value, type .002 and press Enter
- In the Outliner, click Red Wine to select it
- On the menu bar of the Node Editor, click the New button
- In the Node Editor, right-click anywhere in the Diffuse widow to select it and press X
- Position the mouse in the Node Editor, press Shift + A -> Shader -> Glass BSDF
- Position the mouse on the left side of Material Output and click
- Drag the green button from BSDF to Surface
- Click the Color button and click Hex
- Click the Hex value, type 500508 and press Enter
- Click the Roughness value, type .85 and press Enter
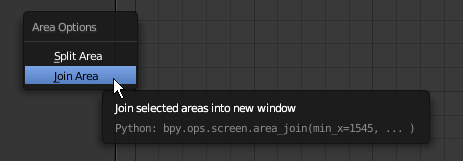
- Right-click the line between the 3D Viewport and the Node Editor
- In the menu that appears, click Join Area:
- Position the mouse in the Node Editor and click
- Press F12 to render:
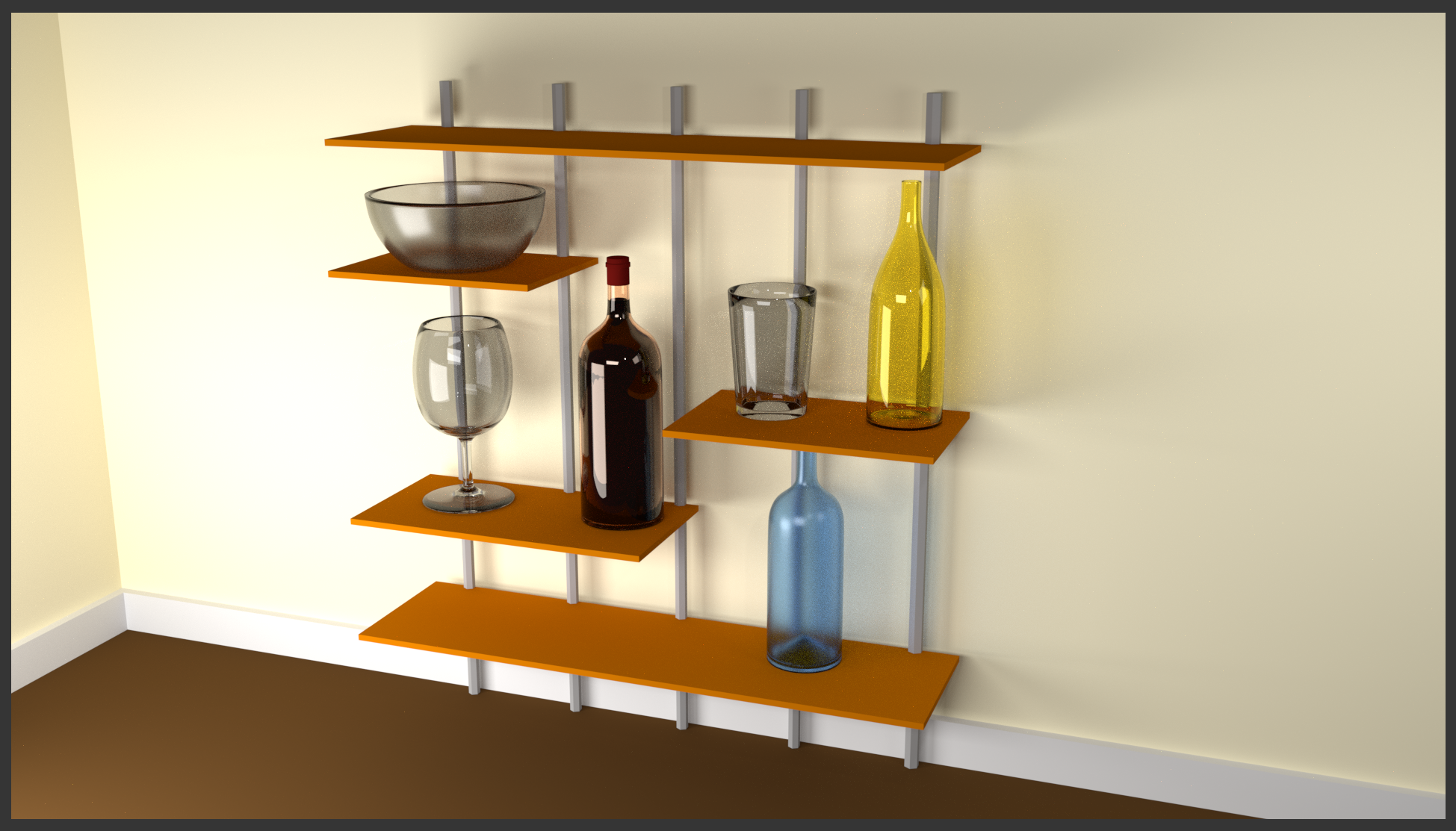

- After viewing the result, press Esc


![]() Practical Learning: Starting the Project
Practical Learning: Starting the Project![]() Practical Learning:
Creating a Classic Cup
Practical Learning:
Creating a Classic Cup















![]() Practical Learning: Creating a Bottle of Red Wine
Practical Learning: Creating a Bottle of Red Wine





















![]() Practical Learning: Creating an Empty Bottle
Practical Learning: Creating an Empty Bottle












![]() Practical Learning: Creating Red Wine
Practical Learning: Creating Red Wine




![]() Practical Learning: Creating a Bottle of White Wine
Practical Learning: Creating a Bottle of White Wine












![]() Practical Learning: Creating an Empty Wine Glass
Practical Learning: Creating an Empty Wine Glass









![]() Practical Learning: Creating an Ice Bucket
Practical Learning: Creating an Ice Bucket









![]() Practical Learning: Creating a Shelf for Bottles
Practical Learning: Creating a Shelf for Bottles
![]() Practical Learning: Putting the Objects Together
Practical Learning: Putting the Objects Together
![]() Practical Learning: Applying Introductor Materials
Practical Learning: Applying Introductor Materials
![]() Practical Learning: Applying a Glass Material
Practical Learning: Applying a Glass Material




![]() Practical Learning: Applying Roughness to a Glass
Practical Learning: Applying Roughness to a Glass
