
Introduction to Records
 |
Introduction to Records |
Data Entry Fundamentals
|
Introduction |
|
After creating a table, you (actually the user) can start(s) populating it with information. Data entry consists of entering values into the database. To do this, you can use a table or some of the other objects we will study. Data is entered in a table by typing it into cells. Some fields can be configured to accept some types of data and reject others. Some other fields would allow anything. This depends on how the database fields were setup. |
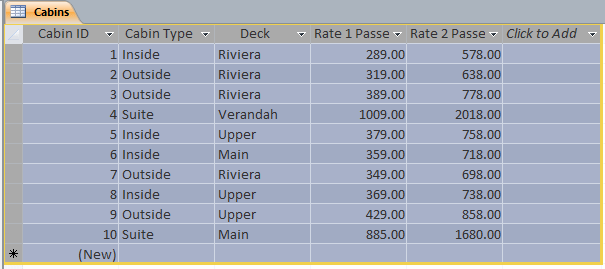
A table's cell holds one particular unit of data. All cells on the same (vertical) column belong to the same category of information. As reviewed in the previous lesson, a horizontal range of cells is called a record; and all cells on this range belong to the same record:

|
Data Entry on a Table |
To perform data entry on a table, you can click a cell under a column header and type a value. Although a table appears with many rows of cells, when a table is empty with no record, only the cells just under the column header are accessible. Those cells appear with a type of blue color. If you click one of those cells, its background becomes white and its borders are orange, indicating that it is ready:

Another way to indicate an empty record, the field of the most left column is marked with (New) and its row of records uses the same light-blue color. After typing a value in a cell, you can press Enter or Tab to move the caret to the next cell. In many circumstances you will also be able to move to the next cell by pressing the right arrow key. Sometimes you can move to the next record even if the current record is not completed. In this case, you could press the down arrow key.
When a record has been completed, the background color of its cells changes. The next record under it has the first cell marked as (New) and its empty cells are in blue. The other cells remain white:

The white cells cannot receive data: if you click them (with the left mouse button), nothing happens. You can only right-click them to get a context-sensitive menu.
There are three kinds of fields or cells the user will face: a field in which the user can type data, a field that displays a list as a combo box the user has to select from, and a field that does not receive input from the user. If you as the user have to select from a list, click the field that holds the list and select from the combo box. There are two kinds of combo boxes, those that accept new entries from the user and those that allow only a selection from a preset list. The classic field allows the user to just type the appropriate data in a field.
After setting the data in a particular field, you can click another cell and type the desired data. The easiest way is to press the right arrow key to move to the next field or the left arrow to move to the previous field; pressing Enter would work as well. After typing data, if you press Enter at the end of a record, the caret would move to the beginning of the next record. At anytime, you can press the up arrow key to move to the same category field of the previous record. If you press the down arrow key, the same category of the next record would receive focus.
![]() Practical
Learning: Performing Data Entry on a Table
Practical
Learning: Performing Data Entry on a Table
| Category | Make | Model | Date Acquired | Purchase Price |
| Printer | HP | LaserJet 4200dtn | 10/08/2010 | 1950.95 |
| Desktop Computer | IBM | NetVista M42 | 10/08/2010 | 1035.00 |
| Laptop | Gateway | 200XL | 12/05/2010 | 2095.95 |
| Printer | Xerox | Phaser 8200 | 10/22/2010 | 1250.55 |
| Digital Camera | Olympus | C-50 | 11/06/2010 | 450.75 |
| Desktop Computer | IBM | ThinkCentre S50 | 10/08/2010 | 1055.55 |
Record Management in Datasheet View
|
Record Selection |
Record maintenance consists of copying, pasting, or deleting records, etc. Some of the operations you will perform on one or more records on a table require that the record(s) be selected first:

To select all records of a table:
![]() Practical
Learning: Selecting Records
Practical
Learning: Selecting Records




|
Record Deletion |
If a record is not needed anymore or has become irrelevant in a table, you can delete it. To do this:

In both cases, a message box would come up to warn you. If you find out you were making a mistake, you can click No. If you still want to delete the record, click Yes.
You can use this same approach to delete more than one record.
![]() Practical
Learning: Deleting Records
Practical
Learning: Deleting Records




|
Copying/Pasting Records |
If you have a list of records from one table and you want to use those records in another table, you can copy the records from one table and paste them in another table. You have various options.
You can copy the values of a column from one table and paste the values in another column. Both columns should be of the same type. That is, you should not attempt to paste the names of people in a column of a Boolean type (a Yes/No column that display check boxes). You can also copy and paste many columns. When selecting the columns, they should be selected in a range. After selecting and copying, you can paste the values in a range of columns of another table. The columns from the originating table and the range of columns from the target table must be of the same type. That is, the first column in each range must be of the same type; the second column of both ranges must be of the same type, and so on.
You can also copy a whole record or a range of columns. First select the range of records. Then, either right-click the selection and click Copy, or press Ctrl + C. You can then paste the records in another table.
If you display a table in Datasheet View, to copy a record, you can right-click the box on the left side of the most left field of the column and click Paste:

To apply the copied record to a new one, right-click the left box of the first empty record and click Paste.
Before copying a record in a form, the form should have the Record Selectors property set to Yes. To copy a record, you can right-click the record selector and click Copy:

After copying the record, you can get to the first empty record, right-click its record selector and click Paste.
After pasting a record, you can make the necessary changes. You must also manually take care of ensuring the uniqueness of values in the appropriate fields. For example, if a column is meant to hold unique values such as employee numbers or Social Security numbers, after pasting the record, to finalize it, you must make sure you change the value in the new record. Otherwise, before moving on, you would receive an error.
![]() Practical
Learning: Copying and Pasting Data Into a Table
Practical
Learning: Copying and Pasting Data Into a Table
 |
 |




|
Introduction |
You will usually not provide tables to the users for data entry. Instead, you will use objects called forms. A form appears in a view friendlier than that of a table. Here is an example of a form presented to a user:

For you as the database developer, a form only serves as a relay between the source of data, which can be a table, and the user who looks at it. Of course, in order to have a form in your application, you must first create it.
When it comes to data of a database, there are two broad types of form: data-unrelated and data-related.
|
Unrelated Forms |
Although most of the forms you will use in a database are meant to display data from a table, you can create an independent form whose functionality and behavior do not depend on the data from a database. Such a form can be used to display other types of information to the user. The form can be referred to as unrelated.
To create a blank form, on the Ribbon, click Create and, in the forms section, click Blank Form. You would be presented with an empty rectangular object.
The other category of form involves those used to display data to the user. Such forms are primarily made for data entry. Before creating such a form, you must decide where data would come from. The source object can be a table or other means we will study in future lessons. If the data of a form will be based on a table, you can specify it, before or while creating the form.
To easily create a form that would display data, in the Navigation Pane, select the table. In the Ribbon, click Create. In the Forms section, click Form.
![]() Practical
Learning: Creating a Form Automatically
Practical
Learning: Creating a Form Automatically
|
The Name of a Form |
Like a table, you can create a temporary form to test something and get rid of the form after use (you do this by not saving the form). As done for a table, if you intend to preserve a form, you must save it. To save a form:
If the form was not saved previously, you would be prompted to give it a name. Like every object of a database, a form must have a name. Microsoft Access is very flexible when it comes to names of objects. For example, a form can be named D#%bb or 5&#GM* or anything like that. As you can imagine, such names are not realistic. For this reason, you should give easily recognizable names to your form so you would be able to predict what the form is used for. If a form is based on a table, it may be a good idea to give the same name as the table. If a form is independent, that is, if it doesn't display data from a table, you can give it a name that reflects its role in the database.
![]() Practical
Learning: Naming a Form
Practical
Learning: Naming a Form
|
The From Wizard |
For a typical database, a form is used to view, enter, manipulate, and search data. Because users spend a great deal of their time looking at forms, you should create and make them as attractive and friendly as possible. Form design can take a long time in database development but Microsoft Access provides quick means to get around. The Form Wizard provides an easy and fast means of creating a form.
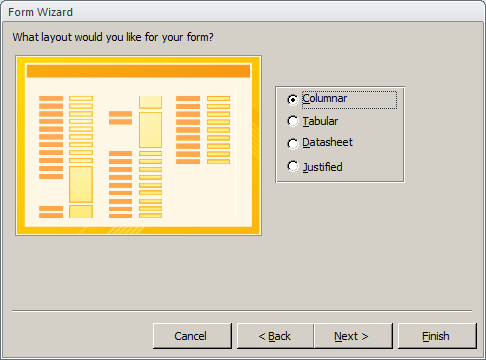
To launch the Form Wizard, on the Ribbon, click Create. In the Forms section, click Form Wizard. This would start the wizard. The first page of the Form Wizard allows you to choose the originating table that will supply the necessary fields in the form. Once you have selected the object, its corresponding fields display in the Available Fields list box, you can select all fields or decide which ones you want to include in the form. The 2nd page of the wizard allows you to select the desired layout of the form. The 3rd page of the Form Wizard allows you to name the form.
![]() Practical
Learning: Using the Form Wizard
Practical
Learning: Using the Form Wizard


|
Data Entry on a Form |
Data entry of a database is mainly performed on forms as they provide a friendlier display of information than tables. Data entry on a form is performed using various types of Windows controls. On text boxes, the user enters data by typing it. On a combo box, depending on how the object was configured by the database developer, the user may have to only select an item from the list. In some other cases, the user may be allowed to enter new data.
After entering or changing data on a control, to move from one field to the next, the surest way is to press Tab. On most occasions, the user can also press Enter. The Enter key may not move the focus from a text box that allows multiple lines of text. If the user is simply reviewing data without performing data entry, the keyboard's arrow keys can also be used to move among fields.
![]() Practical
Learning: Form Data Entry
Practical
Learning: Form Data Entry
| Full Name | Driver's License # | Address | City | State | ZIP Code |
| Ernestine Aarons | A-682-638-146 | 6044 Lolita Drive | Silver Spring | MD | 20904 |
| Raymond Simms | 629-49-2746 | 815 Arundela Rd NE | Washington | DC | 20008 |
| Johnny Edmondson | 837-62-5860 | 10696 Great Alberta Crt | Alexandria | VA | 21233 |
| Albert Faughty | F-374-590-749-205 | 702 Mechanics Drv | College Park | MD | 20707 |
|
Editing Data |
Editing a value consists of changing it. This can be done on the table or the form (or on a query as we will learn). To do this, first locate the value in the field. If you are working on a table, you can click the value and use the keys (left, right, Home, End, Backspace, or the Space Bar) to edit the value. If you are working on a form, you can click the label next to a field. This would completely select the corresponding value in the control. You can then press F2 to position the caret in the control and edit its value. Alternatively, you can click the control's field and edit the value.
![]() Practical
Learning: Editing Data
Practical
Learning: Editing Data
|
Finding Data |
Sometimes there will be some regular problems in your database. For example during data entry, some information could be missing, mistyped, or entered in the wrong field. These problems would be easy to locate on a small table or form. If the database grows, values could become difficult to locate. Fortunately, Microsoft Access provides many tools you can use to find values and take actions.
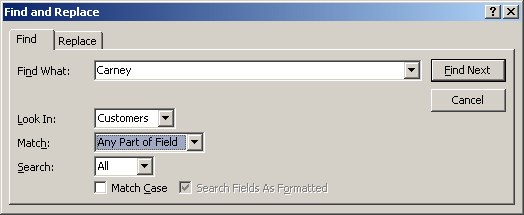
To assist you with finding a value in a table or a form, the Home tab of the Ribbon is equipped with a section named Find:
To start looking for a value, you can click the Find
button
![]() or you can press Ctrl + F. This would open the Find and Replace dialog box
with the Find tab selected:
or you can press Ctrl + F. This would open the Find and Replace dialog box
with the Find tab selected:
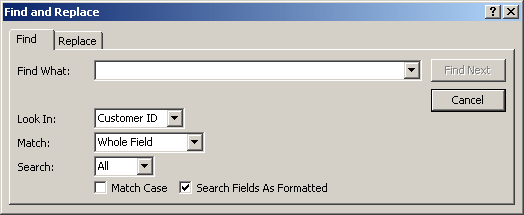
The Find and Replace dialog box is modeless, meaning you can access the table or form in the background while the dialog box is present.
To specify the value to look for, type it in the Find What combo box. If you had previously used the dialog box, the Find What combo box keeps track of the previous searches and stores them in the control. This would allow you to perform a search on a value previously used.
The Look In combo box allows you to select the column where the value should be located. By default, when the Find and Replace dialog box displays, it selects the column or field that had focus and puts its name in the Look In combo box. You can look into that column but, if you want to search the whole table, select its name in the Look In combo box.
The Match combo box allows you to specify how close the match should be. The options are Any Part of Field, Whole Field (the default), and Start of Field.
The Search combo box allows you to specify the direction to follow. The options are Up, Down, and All (the default).
After specifying the options, you can click Find Next. After using the Find and Replace dialog box, to dismiss it, you can click Cancel or press Esc.
![]() Practical
Learning: Editing Data
Practical
Learning: Editing Data
|
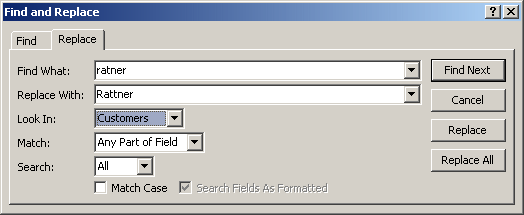
Replacing Data |
We have seen that you can use the Find and Replace
dialog box to simply locate a value. Instead of just finding it, you may
want to replace the found value with an alternate. To assist you with this,
you can use the Replace section of the dialog box. To get it, in the Find
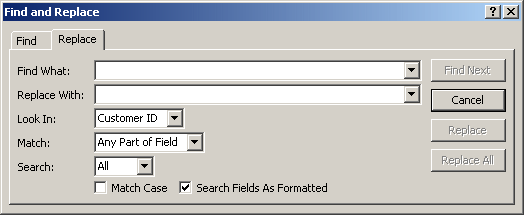
section of the Ribbon, you can click the Replace button
![]() or you can press Ctrl + H. This would open the Find and Replace dialog box
with the Replace tab selected:
or you can press Ctrl + H. This would open the Find and Replace dialog box
with the Replace tab selected:
You can also open the Find and Replace dialog box as we did for finding, then click the Replace tab.
The Replace section of the dialog box provides the same options at the Find counterpart with the addition of the Replace With combo box, the Replace and the Replace All buttons. After specifying what to look for in the Find What combo box, the Replace With combo box allows you to specify the value to replace the Find What with.
![]() Practical
Learning: Editing Data
Practical
Learning: Editing Data
Introduction to Record Printing
|
Table Printing |
The primary function of the table is to provide a means of storing and arranging information of a database. Nevertheless, you can print data of a table, especially if for example you are in a hurry and do not have access to another object. You can print data on a table whether the table is opened or not.
To print a closed table, locate it in the Navigation Pane and click it to select it, then click File, position the mouse on Print and select one of the three options. In the same way, if the table is opened in Datasheet View, click its tab to give it focus, then click File -> Print and select to print or to preview.
The Print menu of the Office Button presents three options:

![]() Practical
Learning: Printing Tables
Practical
Learning: Printing Tables
|
Form Printing |
Although not part of their primary role, forms provide a quick means of printing data, especially in the absence of desired reports. There are various issues related to printing forms, including printing all records or just some of them.
You can print a form without opening it. Once you know the form you would like to print, locate its name in the Navigation Pane and use the same steps reviewed for a table.
When a form is opened, you have the option of printing all of its records or the selected one. In the Form View, to print just one record, navigate to the record you would like to print, click the Form Selection bar to select the record and proceed to print.
![]() Practical
Learning: Printing Forms
Practical
Learning: Printing Forms

Reports Fundamentals
A report provides an object used to print a database's records. Although you can print tables or forms, reports are customized to be printer friendly. They can perform and display calculations. Once again, Microsoft Access provides wizards to quickly create reports.
Microsoft Access can help you quickly create a report using one of the pre-designed layouts. This is done using the Report Wizard. The Report Wizard is available from the Reports section of the Create category of the Ribbon.
![]() Practical
Learning: Using the Report Wizard
Practical
Learning: Using the Report Wizard






|
Report Printing |
The report is the favorite object used to print data. As done with the other objects, you can print a report whether it is opened or not. Before printing a report, you must first select or open it. If you want to print a report without opening it, in the Navigation Pane, locate the desired report and click it to select it. Then, proceed from the Office Button as we reviewed for the table and the form. In the same way, you can first open the report from the Navigation Pane and use the Print menu from the Office Button the same way we described for the other objects.
![]() Practical
Learning: Printing a Report
Practical
Learning: Printing a Report
Lesson Summary
|
Exercises |
Yugo National Bank
| Account Type ID | Account Type | Description |
| 1 | Checking | |
| 2 | Saving | |
| 3 | CD |
Watts A loan
World Statistics