|
SQL Data Source Fundamentals |
|
|
|
To use or manipulate the values of a database on a web site,
you can use an intermediate object named a data source. For a relational
database that uses SQL, you can use the SQL data source. To support it, the
.NET Framework provides a class named SQLDataSource.
|
If you are using either Microsoft Visual Studio or Microsoft
Visual Web Developer to create your web site, the SQLDataSource class is
represented in the Toolbox by a SQLDataSource button in the Data section.
Therefore, to create a data source, drag this object and drop it on your form.
To configure it, you can click the arrow button on its right side and click Con
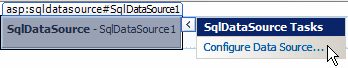
This would open the Configure Data Source wizard:
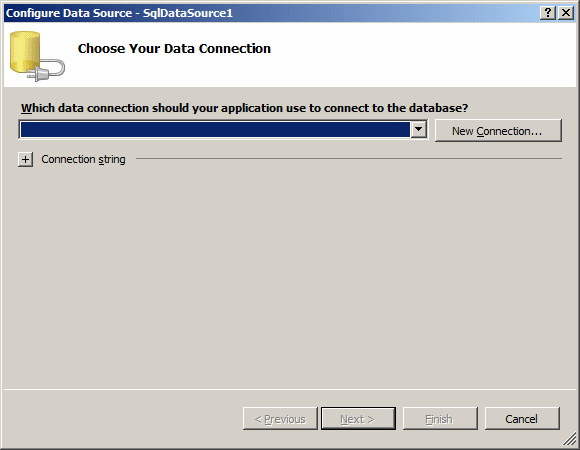
The SQL data source can be used on various types of
databases, including
Microsoft Access.
In
the first page of the wizard, click the New Connection button. This would open
the Add Connection dialog box:

In the Add Connection dialog box, click the
Change... button. In the Choose Data Source dialog box, click Microsoft Access
Database File:
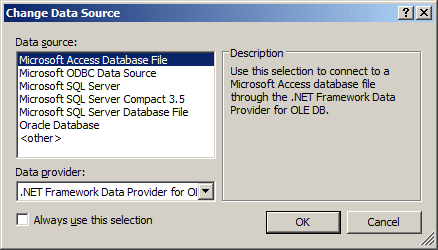
Click OK. This would open the Add Connection dialog box
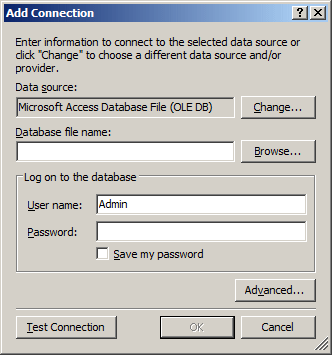
In the Data Source text box, make sure Microsoft Access Database File (OLE DB)
is specified. In the database File Name text box, enter the name or path of
the database including its extension. Otherwise, click the Browse button to
locate it and select it:
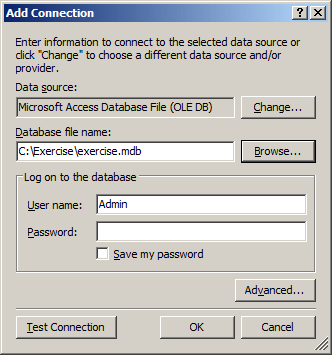
If necessary, specify the authentication
credentials in the Log on to the Database section. Once you are ready, click
Test Connection and click OK
. You would get back to the
first page of the wizard where you would click next.
|
Creating a SQL Data Source |
|
The SQLDataSource is used as a control. Therefore, to
manually initiate it, create an <asp:SQLDataSource> tag in your form. Like every
control, the tag should have an ID and a runat attribute. Here is an
example:
<%@ Page Language="C#" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Exercise</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="frmExercise" runat="server">
<asp:SQLDataSource id="sdsExercise" runat="server"></asp:SQLDataSource>
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
Characteristics of a SQL Data Source |
|
A web configuration file is a document that specifies how to
use some details of a web site. If you use Microsoft Visual Studio or Microsoft
Visual Web Developer to create your web site, a web configuration file would be
generated for you.
The content of a web configuration document resembles that
of an XML file. As an
XML-like file, it starts with <?xml version="1.0"?>. The root of the
document is the <configuration> tag. Here is an example of starting a web
configuration file:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
</configuration>
After creating the file, you must save it in the root
directory (or folder) of your project. Save the file with the name web.config.
One of the roles of a web configuration file is to provide a connection string.
This specifies how a database would be accessed. A connection string is a value made of different
sections that each uses the
formula key=value. To create the connection string, in your
web configuration file, include a <connectionStrings> tag:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
<connectionStrings></connectionStrings>
</configuration>
As you can see from its name, the <connectionStrings>
(plural) tag holds a collection of values.
When creating a connection string, you must give it a name
so you can refer to it later. If you are using the Configuration Data Source
dialog box, in the second page of the wizard, enter the name of the connection
string:
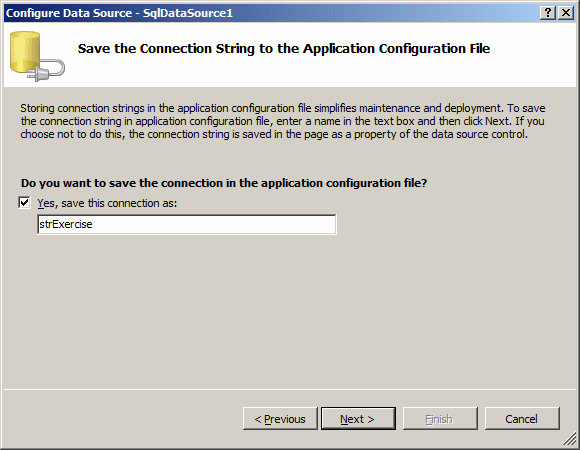
After specifying the name, click Next.
If you are manually creating the configuration file, to specify the name, create an <add>
tag equipped with an attribute named name. Assign the desired name to the
attribute. Here is an example:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
<connectionStrings>
<add name="strExercise"></add>
</connectionStrings>
</configuration>
Besides the name, you must add an attribute
named connectionstring to the <add> tag. Assign the values of the
connection string to this attribute. Here is an example for a Microsoft SQL
Server database:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
<connectionStrings>
<add name="strExercise"
connectionString="Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=C:\Exercise\exercise.mdb"></add>
</connectionStrings>
</configuration>
Besides the name and the connection string, you must also
specify the data provider. To support this, the <add> attribute is
equipped with an attribute named providerName. Use providerName="System.Data.OleDb".
This would be done as follows:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
<connectionStrings>
<add name="strExercise"
connectionString="Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=C:\Exercise\exercise.mdb"
providerName="System.Data.OleDb"></add>
</add>
</connectionStrings>
</configuration>
A web configuration file can contain more information than
this.