Introduction to Microsoft Visual Studio
 |
Introduction to Microsoft Visual Studio |
|
Introduction to Our Lessons |
|
C# and Our Lessons |
|
C#, pronounced c sharp, is a programming language that can be used to give instructions to a computer. The instructions can be written from a text editor such as Notepad. Another way is to use a programming environment that is equipped with many tools that make it easy to work on projects, to create the necessary files, and to distribute a completed application. |
|
Many programming environments are available. Probably the most popular programming environment you can use to write C# instructions is Microsoft Visual Studio. This is commercial application available for purchase from Microsoft. If your primary goal is to learn the C# language, Microsoft provides a free programming studio you can use: Microsoft Visual C# 2010 Express. To follow our lessons, you can use Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 or Microsoft Visual C# 2010 Express. To get Microsoft Visual C# 2010 Express, get to the Microsoft web site and click the Visual Studio Express link. |
To launch Microsoft Visual C# 2010 Express, you can click Start -> (All) Programs -> Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 Express -> Microsoft Visual C# 2010 Express: To launch Microsoft Visual Studio 2010, you can click Start -> (All) Programs -> Microsoft Visual Studio 2010.
The top section of Microsoft Visual Studio displays the main menu divided in categories such as File or Edit. The main menu is used like the menu of a normal application. Under the main menu, there is a toolbar. Normally, when the studio is launched, it displays the Standard toolbar as its default. Some additional toolbars will display in response to an action from you. Still, you can display other toolbars if you want. To do this:
Toolbars are used the same way they are in other applications. Microsoft Visual Studio's menus and toolbars can be customized. You can customize a menu category on the main menu by adding a menu item to it. You can customize a toolbar by adding a button to it. To start, right-click anything on the main menu or on any toolbar and click Customize... For example, imagine you want to add an item named Start Without Debugging to the left side of the Start button:
To do this:
In the same way, you can customize any toolbar and any menu category.
The Start Page is the main body of Microsoft Visual Studio or Microsoft Visual C# Express when it has been launched. It starts on top with a tab labeled Start Page. The main body of Microsoft Visual C# Express displays Microsoft Visual C# 2010 Express. The left section shows two labels: New Project... and Open Project... When some projects have been previously created or used, their names appear under Open Project... When you work on a project, the Start Page is usually in the background but it is represented by a tab. At any time, to display the Start Page:
When you start or open a project, the studio makes some
windows available. These are the most regularly used windows. If you think
that one of them is not regularly used in your types of assignments, you can
remove it from the screen. To hide a window, you can click its Close button
All of the windows you can use are listed in the View menu. Therefore, if a window is not displaying, you can click View on the main menu and click a window of your choice.
When working on a project, you will use a set of windows that each accomplishes a specific purpose. Some windows are represented by an icon but hide the rest of the body. To display such a window, you can position the mouse on it. This would expand the window: 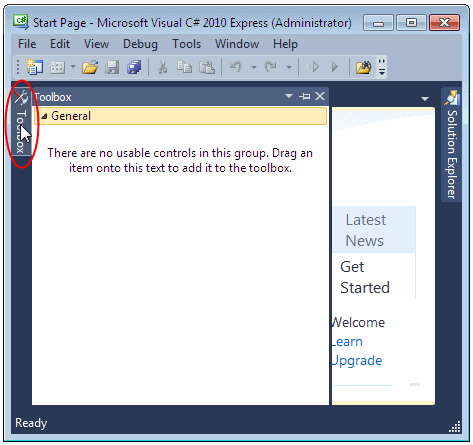 If you expand a window, it would display a title bar with three buttons. One of the button is called Auto Hide:  If you expand a window but find out you don't need it any more, you can just move the mouse away. The window would return to its previous state. Based on this functionality, if you are working with a window and move the mouse away, it would retract. If you need it again, you would have to reopen it using the same technique. If you are going to work with a certain window for a while, you can keep it open even if you move the mouse away. To do this, you can click the Auto Hide button. If clicked, the Auto Hide button changes from pointing left to pointing down:
By default, the studio installs some windows to the left and some others to the right of the screen. You can change this arrangement if you want. To do this, expand a window, then click its title bar and start dragging. While you are dragging, to assist you with a new position, the studio displays five boxes:
To position a window on one side of the studio, drag its title bar to the box that represents that side. When you get to a side, a transparent blue rectangle would be drawn to indicate the possible position. Drop the window to either the most left guiding box to position it to the left of the screen, or to the most right guiding box to position it to the right of the screen. Here is an example:
or
To position a window to the top or the bottom side of the studio, drag its title bar to either the most top guiding box to position it to the top of the studio or to the most bottom guiding box to position it to the bottom of the studio. Here is an example:
To make two windows share an area, you can position one above or below an existing window. Of course, you must first have a window as reference. Then, drag the second window to the existing window. Drop it in the top or the bottom guiding box of the middle big box. This
Becomes
Most of the windows you will use are positioned on one side of the screen. If you want, you can have a window that stays on top of other windows but is not "glued" to one side. Such a window is said to float. To float a window, drag its title bar and release it somewhere in the middle of the screen but not on a guiding box. When a window is floating, it displays a Maximize button
If a window is currently floating and you want to dock it, right-click its title bar and click Dock:
If a window is currently docked and you want to float it, right-click its title bar and click Float.
You can make two or more windows share one side of the screen or to share an area. To do this, first expand and dock the window that you will use as the base (or reference). Then, drag the title bar of the window that will share the area to its target until the bottom part of the base window shows a highlighted and a non highlighted area:
Then release the mouse:
To remove a window that shares an area, drag its tab away:
To position a window to the left or the right of an existing window, first drag the second window to where the existing window is. Then click the left (or the right, depending on the side you want) guiding box of the multiple-box. This
becomes this
In the same way, you can make two or more windows share the same area.
You can make a window display its tab in the top section of the Code Editor and share the area with it. There are two ways yon do it:
This
becomes this
If a window is already represented with a tab on top of the Code Editor, you can drag the second window and drop it to the left or of the right tab of the existing window.
|
|
|
||
| Home | Copyright © 2010-2016, FunctionX | Next |
|
|
||