|
|
For your databases, you can create expressions that represent a combination of values,
variables, and operators. To support expressions, Transact-SQL provides
operators other than, or in addition to, those we saw in Lesson 2.
|
 |
A comparison is a Boolean operation that produces a
true or a false result, depending on the values on which the comparison
is performed. A comparison is performed between two values of the same
type; for example, you can compare two numbers, two characters, or the
names of two cities. To support comparisons, Transact-SQL provides all
necessary operators.
To compare two values for equality, use the = operator. Its formula is:
Value1 = Value2
|
The equality operation is used to find out whether two
values are the same. From the above formula, the SQL interpreter would compare
Value1 and Value2. If Value1 and Value2 are
the same, the comparison produces a TRUE result. If they are different, the comparison renders
FALSE.
The equality operation can be illustrated as follows:

|
 Practical Learning:
Introducing Variables Practical Learning:
Introducing Variables
|
|
- All Computers: Start the computer and log in using your domain account
- Server: Launch Microsoft SQL Server. In the Server Name combo box, make sure the name of the computer is selected.
In the Authentication combo box, make sure Windows Authentication is
selected. Make
sure the account you are using is selected in the User Name combo box. Click Connect
- Each Student:
- Start Microsoft SQL Server
- In the Server Name combo box, select the
name of the server or type it
- In the Authentication combo box, select SQL Server Authentication
- In the User Name combo box, type the name of the domain, followed
by \, and followed by the login name you were given
- In the Password combo box, type your password
- Click Connect
- All Computers: On the Standard toolbar, click the New Query button

As opposed to equality, to find out if two values are
not equal, use the <> operator. Its formula is:
Value1 <> Value2
The <> is a binary operator (like all logical
operators) proposed by the international standard (ISO). It is used to compare two values. The values can come from
two variables as in Variable1 <> Variable2. Upon comparing the
values, if both hold different values, the comparison produces a TRUE. Otherwise, the comparison renders
FALSE or a null value.
It can be illustrated as follows:

Notice that the Not Equal operator <> is the opposite
to the Equality operator =.
Besides the <> operator of the ISO SQL, Transact-SQL also
supports the C language inequal operator, which is represented as !=. It
essentially performs the same role as <> and can be used in the same
circumstances.
To find out whether one value is lower than another,
use the < operator. Its formula is:
Value1 < Value2
The value held by Value1 is compared to that of
Value2. As it would be done with other operations, the comparison can be
made between two variables, as in Variable1 < Variable2. If the value
held by Value1 is lower than that of Value2, the comparison produces
a true or positive result.
The Less Than operator "<" can be
illustrated as follows:

The Equality and the Less Than operators can be combined to compare
two values. This allows you to know if two values are the same or if the
first is less than the second. The operator used is <= and its formula is:
Value1 <= Value2
If both Value1 and Value2 are the same, the result is
true or positive. If the left operand, in this case Value1, holds a
value lower than the second operand, in this case Value2, the
result is still true. If the value of Value1 is strictly higher than that
of Value, the comparison produces a FALSE result.
A <= operation can be illustrated as follows:

To find out if one value is strictly greater than
another, you can use the > operator. Its formula is:
Value1 > Value2
Both operands, in this case Value1 and Value2, can be
variables or the left operand can be a variable while the right operand is
a constant. If the value on the left of the > operator is greater than
the value on the right side or a constant, the comparison produces a true
or positive value. Otherwise, the comparison renders false or null.
The > operator can be illustrated as follows:

Notice that the > operator is the opposite to <=.
|
Greater Than or Equal To >= |
|
The greater than and the equality operators can be
combined to produce an operator as follows: >=. This is the
"greater than or equal to" operator. Its formula is:
Value1 >= Value2
The comparison is performed on both operands: Value1 and
Value2. If the value of Value1 and that of Value2 are the same, the
comparison produces a true or positive value. If the value of the left
operand is greater than that of the right operand, the comparison
produces true or positive also. If the value of the left operand is
strictly less than the value of the right operand, the comparison produces
a false or null result. This can be illustrated as follows:

Notice that the >= operator is the opposite to <.
Transact-SQL supports an operator represented as !>. This
means that a value is not greater than the indicated value. In most cases, this
is equivalent to the Less Than Or Equal To operator "<=".
Transact-SQL supports one more comparison operator
represented as !<. It is used to find out whether one of the operands is less
than the other. This operator is equivalent to >=.
 |
A condition statement is an expression you formulate to
evaluate it. Most of the time, the statement is written so that, when
evaluated, it can produce a result of true or false, then, depending on the
outcome, you can take action. A condition is usually written as simple as
possible to make it clear to you and the SQL interpreter. Although the
interpreter never gets confused, if you create a difficult statement, you may
receive an unpredictable result.
In the next few sections, we will review the keywords and
formulas that Transact-SQL provides to help you formulate clear expressions.
Expressions usually start with a keyword, followed by the expression itself.
After the expression, you can tell the interpreter what to do. The statement may
appear as follows:
Keyword Expression
Statement
|
With the above formula, we will always let you know what
keyword you can use, why, and when. After the expression, you can write the
statement in one line. This is the statement that would be executed if/when the Expression
of our formula is satisfied. In most cases, you will need more than one line of
code to specify the Statement.
As it happens, the interpreter considers
whatever comes after the Statement as a unit but only the line immediately after
the Expression. To indicate that your Statement covers more than
one line, start it with the BEGIN keyword. Then you must use the END
keyword to indicate where the Statement ends. In this case, the formula
of a conditional statement would appear as follows:
Keyword Expression
BEGIN
Statement Line 1
Statement Line 2
Statement Line n
END
You can still use the BEGIN...END combination even if
your Statement covers only one line:
Keyword Expression
BEGIN
Statement
END
Using the BEGIN...END combination makes your code
easier to read because it clearly indicates the start and end of the Statement.
Probably the primary comparison you can perform on a
statement is to find out whether it is true. This operation is performed using
an IF statement in Transact-SQL. Its basic formula is:
IF Condition
Statement
When creating an IF statement, first make sure you provide a
Condition expression that can be evaluated to produce true or false. To
create this Condition, you can use variables and the logical comparison
operator reviewed above.
When the interpreter executes this statement, it first
examines the Condition to evaluate it to a true result. If the Condition
produces true, then the interpreter executes the Statement.
|
 Practical
Learning: Checking a Condition Practical
Learning: Checking a Condition
|
|
From here to the end of this lesson, all instructions
are intended for All Computers:
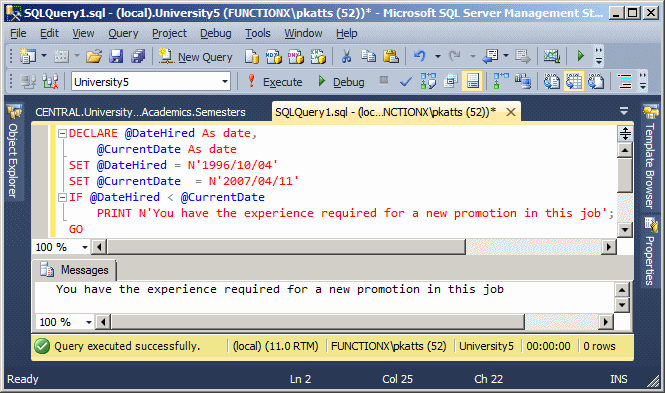
- In the Query window, type the following:
DECLARE @DateHired As datetime2,
@CurrentDate As datetime2
SET @DateHired = N'1996/10/04'
SET @CurrentDate = N'2007/04/11'
IF @DateHired < @CurrentDate
PRINT N'You have the experience required for a new promotion in this job';
- To execute the statement, press F5.
This would produce:
The IF condition we used above is appropriate
when you only need to know if an expression is true. There is nothing to
do in other alternatives.
|
 Practical
Learning: Creating an IF...ELSE Condition Practical
Learning: Creating an IF...ELSE Condition
|
|
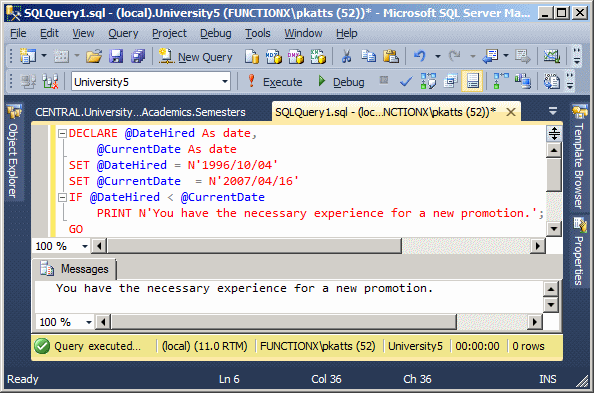
- Click inside the top section of the Query window and press Ctrl + A
to select everything
- Type the following:
DECLARE @DateHired As datetime2,
@CurrentDate As datetime2
SET @DateHired = N'1996/10/04'
SET @CurrentDate = N'2007/04/16'
IF @DateHired > @CurrentDate
PRINT 'You have the experience required for a new promotion'
GO
- To execute, press F5. This would produce:
Notice that, in case the expression to examine
produces a false result, there is nothing to do. Sometimes this will
happen.
The CASE keyword is used as a conditional operator
that considers a value, examines it, and acts on an option depending on the
value. The formula of the CASE statement is:
CASE Expression
WHEN Value1 THEN Result
WHEN Value2 THEN Result
WHEN Value_n THEN Result
END
In the following example, a letter that represents a student
is provided. If the letter is m or M, a string is created as Male. If the value
is provided as f or F, a string is created as Female.