|
To create a relationship between two tables
- Open the child table in the design view
- Right-click (anywhere in) the table and click Relationships...
If the (necessary) foreign key does not exist, click Add and specify its
name under Identity) on the right side
- Under Selected Relationships, click the foreign key that will hold the
relationship
- On the right side, expand Tables And Columns Specification
- Click its ellipsis button
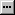
- In the Primary Key Table combo box, select the parent table that
holds the primary data
- Under the parent table, click and select its primary key column
- Under Foreign Key Table, make sure the name of the current table is
set.
Under the name of the child table, click and select the name of the
foreign key column. Here is an example:

- Click OK.
When a relationship has been created, it would show in the Tables And
Column Specification section:

- In the same way, you can create other relationships by clicking Add
and configuring the link.
Once you have finished, click Close
|
 Practical
Learning: Creating Relationships Practical
Learning: Creating Relationships
|
|
- Start Microsoft Visual Basic and create a new Windows Application named
Exercise5
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click Form1.vb and click Rename
- Type Exercise.vb and press Enter twice
- Double-click the middle of the form
- To create a database, including the tables with their primary keys
and their
foreign keys, implement the Load event as follows:
Imports System.Data.SqlClient
Public Class Exercise
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles MyBase.Load
Using conBethesdaCarRental As SqlConnection = _
New SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); " & _
"Integrated Security='SSPI';")
Dim strCreateDatabase As String = "IF EXISTS ( " & _
"SELECT name " & _
"FROM sys.databases " & _
"WHERE name = N'BethesdaCarRental1' " & _
") " & _
"DROP DATABASE BethesdaCarRental1; " & _
"CREATE DATABASE BethesdaCarRental1"
Dim cmdBethesdaCarRental As SqlCommand = _
New SqlCommand(strCreateDatabase, conBethesdaCarRental)
conBethesdaCarRental.Open()
cmdBethesdaCarRental.ExecuteNonQuery()
MsgBox("A database named N'BethesdaCarRental1 has been created")
End Using
Using conBethesdaCarRental As SqlConnection = _
New SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); " & _
"Database='BethesdaCarRental1'; " & _
"Integrated Security='SSPI';")
Dim strCreateTable As String = "CREATE TABLE RentalRates( " & _
"RentalRateID int identity(1, 1) NOT NULL, " & _
"Daily smallmoney, Weekly smallmoney, " & _
"Monthly smallmoney, Weekend smallmoney, " & _
"CONSTRAINT PK_RentalRates PRIMARY KEY (RentalRateID));"
Dim cmdBethesdaCarRental As SqlCommand = _
New SqlCommand(strCreateTable, conBethesdaCarRental)
conBethesdaCarRental.Open()
cmdBethesdaCarRental.ExecuteNonQuery()
MsgBox("A table named RentalRates has been created")
End Using
Using conBethesdaCarRental As SqlConnection = _
New SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); " & _
"Database='BethesdaCarRental1'; " & _
"Integrated Security='SSPI';")
Dim strCreateTable As String = "CREATE TABLE Employees( " & _
"EmployeeID int identity(1, 1) NOT NULL, " & _
"EmployeeNumber nchar(5), " & _
"FirstName varchar(32), " & _
"LastName varchar(32) NOT NULL, " & _
"FullName AS (([LastName]+', ')+[FirstName]), " & _
"Title varchar(80), " & _
"HourlySalary smallmoney, " & _
"CONSTRAINT PK_Employees PRIMARY KEY (EmployeeID));"
Dim cmdBethesdaCarRental As SqlCommand = _
New SqlCommand(strCreateTable, conBethesdaCarRental)
conBethesdaCarRental.Open()
cmdBethesdaCarRental.ExecuteNonQuery()
MsgBox("A table named Employees has been created")
End Using
Using conBethesdaCarRental As SqlConnection = _
New SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); " & _
"Database='BethesdaCarRental1'; " & _
"Integrated Security='SSPI';")
Dim strCreateTable As String = "CREATE TABLE Customers( " & _
"CustomerID int identity(1, 1) NOT NULL, " & _
"DrvLicNumber varchar(50), " & _
"FullName varchar(80), " & _
"Address varchar(100) NOT NULL, " & _
"City varchar(50), " & _
"State varchar(50), " & _
"ZIPCode varchar(20), " & _
"CONSTRAINT PK_Customer PRIMARY KEY (CustomerID));"
Dim cmdBethesdaCarRental As SqlCommand = _
New SqlCommand(strCreateTable, conBethesdaCarRental)
conBethesdaCarRental.Open()
cmdBethesdaCarRental.ExecuteNonQuery()
MsgBox("A table named Customers has been created")
End Using
Using conBethesdaCarRental As SqlConnection = _
New SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); " & _
"Database='BethesdaCarRental1'; " & _
"Integrated Security='SSPI';")
Dim strCreateTable As String = "CREATE TABLE Cars( " & _
"CarID int identity(1, 1) NOT NULL, " & _
"TagNumber varchar(20), " & _
"Make varchar(50), " & _
"Model varchar(50) NOT NULL, " & _
"CarYear smallint, " & _
"Category varchar(50), " & _
"PictureLocation varchar(200), " & _
"CDPlayer bit, " & _
"DVDPlayer bit, " & _
"Available bit, " & _
"CONSTRAINT PK_Car PRIMARY KEY (CarID));"
Dim cmdBethesdaCarRental As SqlCommand = _
New SqlCommand(strCreateTable, conBethesdaCarRental)
conBethesdaCarRental.Open()
cmdBethesdaCarRental.ExecuteNonQuery()
MsgBox("A table named Cars has been created")
End Using
Using conBethesdaCarRental As SqlConnection = _
New SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); " & _
"Database='BethesdaCarRental1'; " & _
"Integrated Security='SSPI';")
Dim strCreateTable As String = "CREATE TABLE RentalOrders( " & _
"RentalOrderID int identity(1, 1) NOT NULL, " & _
"DateProcessed datetime, " & _
"EmployeeID int Constraint " & _
"FK_Employees References " & _
"Employees(EmployeeID) NOT NULL, " & _
"EmployeeName varchar(80), " & _
"CustomerID int Constraint " & _
"FK_Customers References " & _
"Customers(CustomerID) NOT NULL, " & _
"CustomerName varchar(80), " & _
"CustomerAddress varchar(100), " & _
"CustomerCity varchar(50), " & _
"CustomerState varchar(50), " & _
"CustomerZIPCode varchar(20), " & _
"CarID int Constraint " & _
"FK_Cars References Cars(CarID) NOT NULL, " & _
"CarMake varchar(50), " & _
"CarModel varchar(50), " & _
"CarYear smallint, " & _
"CarCondition varchar(50), " & _
"TankLevel varchar(40), " & _
"MileageStart int, " & _
"MileageEnd int, " & _
"RentStartDate datetime, " & _
"RendependDate datetime, " & _
"Days int, " & _
"RateApplied money, " & _
"SubTotal money, " & _
"TaxRate decimal(6, 2), " & _
"TaxAmount money, " & _
"OrderTotal money, " & _
"OrderStatus varchar(50), " & _
"CONSTRAINT PK_RentalOrder " & _
"PRIMARY KEY (RentalOrderID));"
Dim cmdBethesdaCarRental As SqlCommand = _
New SqlCommand(strCreateTable, conBethesdaCarRental)
conBethesdaCarRental.Open()
cmdBethesdaCarRental.ExecuteNonQuery()
MsgBox("A table named RentalOrder has been created")
End Using
End Sub
End Class
|
- Execute the application
- Close the form and return to your programming environment
- In the source file, delete the whole content of the Load event
- In the Server Explorer, right-click the Data Connections node and
click Add Connection
- In the Server Name combo box of the Add Connection dialog box, type
(local) or select the name of the server
- In the Select Or Enter A Database Name combo box, select
BethesdaCarRental1 and click Test Connection
- Click OK twice
A diagram is a window that visually displays the
relationships among the tables of a database. To create a diagram:
- In the Object Explorer in Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio or
in the Server Explorer in Microsoft Visual Studio, in the database node, you can click Database
Diagrams
- A dialog box will inform you that this database does not have a
diagram. Read the message and click Yes
- Right-click Database Diagrams and click New Database Diagram
- In the Add Table dialog box, click each table and click the Add.
Alternatively, you can double-click a table to add it
- In the Add Table dialog box, you can click
Close.
On the toolbar, you can click the Zoom button and select a larger or
smaller value.
To move a table, you can drag its title bar. Here is an example:

- To establish a relationship, you can click the gray box on the left of
any column from the parent table and drop it on any column in the
child table. A better way is to click gray box of the primary key
column from the parent table, drag that box then drop it on the
foreign key column of the child table. Here is an example:

- A Tables and Columns dialog box would come up. It would display the
column that was dragged and the column on which you dropped.
If you had selected just any column, it would show but it may not be
the one you wanted to drag; that is, it may not be the actual column
that is supposed to manage the relationship.
Regardless, under Primary Key Table, you should select the parent
table
- Under the parent table, select its primary column
- Under Foreign Table, select the foreign key column. Here is an
example:

- Once you are ready, click OK. A link would be created between the
tables

- In the same way, you can create other relationships.
When you have finished, you can save and close the database
|
 Practical
Learning: Creating a Diagram Practical
Learning: Creating a Diagram
|
|
- In the Server Explorer, expand the BethesdaCarRental1 node and click
the + button of the Database
Diagrams node
- A dialog box will inform you that this database does not have a
diagram.
Read the message and click Yes
- Right-click Database Diagrams and click Add New Diagram
- In the Add Table dialog box, click Employees and click Add
- Double-click Cars to add it
- In the same way, add the Customers and the RentalOrders tables
- On the Add Table dialog box, click Close.
Notice that, based on how we created the database and its objects, the
relationships have been created already
- To save the diagram, on the Standard toolbar, click Save
- Set its name to dgmBethesdaCarRental and click OK
- Close the window
On a typical database, information comes and goes. For a
car rental company, car information is created and deleted on a regular basis.
When information about a car is deleted, there is concern about the rental
orders related to
that car. Referential integrity allows you to manage these aspects of a
database. You need to make sure that when data is deleted from a parent table, the
child tables are notified and their related records are deleted also. When
information is changed on a parent table, the related information is changed in
the child tables.
To manage referential integrity, you use the Foreign Key
Relationships dialog box. You can access it from the design view of a table or
from the diagram window.
|
 Practical
Learning: Managing Referential Integrity Practical
Learning: Managing Referential Integrity
|
|
- In the Server Explorer, expand the Tables node under
BethesdaCarRental1.
Right-click RentalOrders and click Open Table Definition
- Right-click in the table and click Relationships
- Under Selected Relationships, click FK_Customers. In the right
section, expand INSERT And UPDATE Specification
- Click Delete Rule. In its combo box, select Cascade
- Click Update Rule. In its combo box, select Cascade:

- In the same way, specify the following
| Foreign Key |
Delete Rule |
Update Rule |
| FK_Cars |
Cascade |
Cascade |
| FK_Customers |
Cascade |
Cascade |
| FK_Employees |
Cascade |
Cascade |
- Click Close
- Save and close the table
|
|

