|
|

|
Like a real world tree, the branches or nodes of a tree view use a
type of relationship so that they are not completely independent. For
example, a tree view can be based on a list that has a parent item and
other child items that depend on that parent. In real world, if you cut
a branch, the branches and leaves attached to it also disappear. This
scenario is also valid for a tree view.
Most of the time, a tree has only one root but a tree in an
application can have more than one root.
|

|
In a Windows application a tree view is primarily a control
like any other. To use it in your application, you can click the TreeView button
in the Toolbox and click a form or other control in your application. This is
equivalent to programmatically declaring a variable of type TreeView,
using the new operator to instantiate it and adding it to its container's
list of controls through a call to the Controls.Add() method. Here is an
example:
Imports System.Drawing
Imports System.Windows.Forms
Module Exercise
Public Class Starter
Inherits Form
Private tvwCountries As TreeView
Dim components As System.ComponentModel.Container
Public Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
End Sub
End Class
Function Main() As Integer
Dim frmStart As Starter = New Starter
Application.Run(frmStart)
Return 0
End Function
End Module
This would produce:

Using a TreeView variable only adds a rectangular empty
control to your application. The next action you probably take is to add one or
more branches to the tree.
|
 Practical
Learning: Introducing the Tree View Control Practical
Learning: Introducing the Tree View Control
|
|
- Start Microsoft Visual Basic
- Create a new Windows Application named CollegeParkAutoParts2
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click Form1.vb and click Rename
- Type Central.vb and press Enter
- From the Containers section of the Toolbox, click Panel and click the
form
- Set its Dock property to Top
- From the Containers section of the Toolbox, click Panel and click the
form
- Set its Dock property to Bottom
- From the Containers section of the Toolbox, click SplitContainer and
click the middle of the form
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Other Properties |
| Label |
 |
College Park Auto-Parts |
|
BorderStyle: FixedSingle
Font: Times New Roman, 20.25pt, style=Bold
AutoSize: False
TextAlign: MiddleCenter |
| GroupBox |
 |
|
|
Anchor: Top, Bottom, Left, Right |
| TreeView |
 |
|
tvwAutoParts |
Anchor: Top, Bottom, Left, Right |
| GroupBox |
 |
|
|
Anchor: Top, Bottom, Left, Right |
| ListView |
 |
|
lvwAutoParts |
View: Details
Anchor: Top, Bottom, Left, Right |
| Columns |
|
(Name) |
Text |
TextAlign |
Width |
| colPartNumber |
Part # |
|
|
| colPartName |
Part Name |
|
300 |
| colUnitPrice |
Unit Price |
Right |
80 |
| GroupBox |
 |
Selected Parts |
|
|
| Label |
 |
Part # |
|
Anchor: Bottom, Left |
| Label |
 |
Part Name |
|
Anchor: Bottom, Left, Right |
| Label |
 |
Unit Price |
|
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Label |
 |
Qty |
|
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Label |
 |
Sub Total |
|
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartNumber1 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartName1 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtUnitPrice1 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0 |
txtQuantity1 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtSubTotal1 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Button |
 |
Remove |
btnRemove1 |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartNumber2 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartName2 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtUnitPrice2 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0 |
txtQuantity2 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtSubTotal2 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Button |
 |
Remove |
btnRemove2 |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartNumber3 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartName3 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtUnitPrice3 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0 |
txtQuantity3 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtSubTotal3 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Button |
 |
Remove |
btnRemove3 |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartNumber4 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartName4 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtUnitPrice4 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0 |
txtQuantity4 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtSubTotal4 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Button |
 |
Remove |
btnRemove4 |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartNumber5 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartName5 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtUnitPrice5 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0 |
txtQuantity5 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtSubTotal5 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Button |
 |
Remove |
btnRemove5 |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartNumber6 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left |
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtPartName6 |
Anchor: Bottom, Left, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtUnitPrice6 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0 |
txtQuantity6 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtSubTotal6 |
TextAlign: Right
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Button |
 |
Remove |
btnRemove6 |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| GroupBox |
 |
Order Summary |
|
Anchor: Top, Bottom, Left, Right |
| Label |
 |
Total Order: |
|
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
0.00 |
txtTotalOrder |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Button |
 |
Close |
btnClose |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
|
- Execute the application to test it
- Close the form and return to your programming environment
|
Introduction to Creating Tree View Nodes
|
|
To create the nodes of a tree view, Microsoft Visual Studio
provides a convenient dialog box you can use at design time. To display it,
after adding a tree view control to a form, you can click the ellipsis button of
its Nodes field in the Properties window. This would open the TreeNode
Editor:

The primary characteristic of a node is the text it
displays. At design time and in the TreeNode Editor, to create a node, you can
click the Add Root button. When you do this, a node with a default but
incremental name is created. To edit a node's name, first select it in the
Select Node To Edit list, then, on the right side, click Name and enter the
string you wish.
|
Programmatically Creating Nodes
|
|
The branches of a tree view are stored in a property called
Nodes. The Nodes property is an object based on the
TreeNodeCollection class. The TreeNodeCollection class implements the
IList, the ICollection, and the IEnumerable interfaces.
As its name indicates, the Nodes property carries all
of the branches of a tree view. This means that the Nodes property in
fact represents a collection. Each member of this collection is called a node
and it is an object based on the TreeNode class.
At run time, to create a new node, call the
TreeNodeCollection.Add() method which is overloaded with two versions. One
of the versions of this method uses the following syntax:
Public Overridable Function Add(text As String) As TreeNode
This method takes as argument the string that the branch
will display. This method is also the prime candidate to create a root node.
Here is an example of calling it:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add("World")
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
End Sub
This would produce:

|
 Practical
Learning: Creating the Root Node Practical
Learning: Creating the Root Node
|
|
- Right-click the form and click View Code
- In the Class Name combo box, select (Central Events)
- In the Method Name combo box, select Load and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub CentralLoad(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles Me.Load
Dim nodRoot As TreeNode =
tvwAutoParts.Nodes.Add("College Park Auto-Parts")
For i As Integer = Date.Today.Year To 1960 Step -1
nodRoot.Nodes.Add(i)
Next
End Sub
- Execute the application to test the form

- Close the form and return to your programming environment
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add Class...
- Set the name to PartDescription and press Enter
- To create a class that can holds a structured item of a list, change the
class as follows:
Public Class PartDescription
' These members will be used to define a car part
Private ID As Long
Private yr As Integer
Private mk As String
Private mdl As String
Private cat As String
Private name As String
Private price As Double
Public Sub New()
ID = 0
yr = 1960
mk = ""
mdl = ""
name = "Unknown"
price = 0.0
End Sub
Public Sub New(ByVal code As Long, ByVal year As Integer,
ByVal make As String, ByVal model As String,
ByVal type As String, ByVal desc As String,
ByVal UPrice As Double)
ID = code
yr = year
mk = make
mdl = model
cat = type
name = desc
price = UPrice
End Sub
Public Property PartNumber() As Long
Get
Return ID
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Long)
ID = value
End Set
End Property
Public Property CarYear() As Integer
Get
Return yr
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Integer)
yr = value
End Set
End Property
Public Property Make() As String
Get
Return mk
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
mk = value
End Set
End Property
Public Property Model() As String
Get
Return mdl
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
mdl = value
End Set
End Property
Public Property Category() As String
Get
Return cat
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
cat = value
End Set
End Property
Public Property PartName() As String
Get
Return name
End Get
Set(ByVal value As String)
name = value
End Set
End Property
Public Property UnitPrice() As Double
Get
Return price
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
price = value
End Set
End Property
Public Overrides Function ToString() As String
Return PartNumber & " " &
CarYear.ToString() & " " &
Make & " " &
Model & " " &
Category & " " &
PartName & " " &
UnitPrice
End Function
End Class
The other version of the TreeNodeCollection.Add()
method uses the following syntax:
Public Overridable Function Add(node As TreeNode) As Integer
This method takes as argument a TreeNode object. In
other words, it expects a complete or semi-complete branch already defined
somehow.
The TreeNode class is equipped with various
constructors you can use to instantiate it. Its default constructor allows you
to create a node without primarily giving its details. Another TreeNode
constructor has the following syntax:
Public Sub New(text As String)
This constructor takes as argument the string that the node
will display. Here is an example of using it and adding its newly create node to
the tree view:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
Dim nodElement As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World")
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodElement)
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
End Sub
We mentioned that the primary characteristic of a node is
the text it displays. The text of a node is stored in a property of the
TreeNode class and is called Text. This allows you either to specify
the string of a node or to retrieve it when needed. Here is an example of
setting it:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
Dim nodElement As TreeNode = New TreeNode
nodElement.Text = "World"
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodElement)
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
End Sub
Just as we called the TreeNodeCollection.Add() method
to create a branch, you can call it as many times as necessary to create
additional branches. Here is an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add("World")
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add("Jupiter")
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add("Neptune")
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add("Uranus")
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
End Sub
This would produce:

Alternatively, if you have many branches to add to the tree,
you can first create them as an array of TreeNode values, then called the
TreeNodeCollection.AddRange() method. The syntax of this method is:
public virtual void AddRange(TreeNode() nodes)
This method takes as argument an array of TreeNode
objects. Here is an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
Dim nodPlanets() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("World"),
New TreeNode("Jupiter"),
New TreeNode("Neptune"),
New TreeNode("Uranus")
}
tvwCountries.Nodes.AddRange(nodPlanets)
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
End Sub
At design time and in the TreeNode Editor, to create a child
node for an existing item, first select it in the Select Node To Edit list, then
click the Add Child button. This causes a child node to be created for the
selected item. To edit its name, first click it and change the string in the
Label text box.
At run time, to create a child node, first get a reference
to the node that will be used as its parent. One way you can get this reference
is to obtain the returned value of the first version of the
TreeNodeCollection.Add() method. As its syntax indicates, this method
returns a TreeNode object.
We have used the default constructor of the TreeNode
class and the constructor that takes as argument a string. The TreeNode
class provides another constructor whose syntax is:
Public Sub New(text As String, children As TreeNode())
The first argument of this method is the string that the new
node this constructor creates will display. The second argument is a collection
of the child nodes of this branch. The collection is passed as an array. Based
on this, you use this constructor to create a new node including its children.
After creating the new node, you can pass it to the TreeNodeCollection.Add()
method as we did earlier. Here is an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Africa"),
New TreeNode("America"),
New TreeNode("Asia"),
New TreeNode("Europe")
}
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
End Sub
This would produce

Using the same approach, you can create as many branches and
their child nodes as you wish. Here is an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
' Create a list of some African countries and
' store them in an array named nodAfricans
Dim nodAfricans() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Senegal"),
New TreeNode("Botswana"),
New TreeNode("Ghana"),
New TreeNode("Morocco")
}
' Create a list of some American countries and
' store them in an array named nodAmericans
Dim nodAmericans() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Canada"),
New TreeNode("Jamaica"),
New TreeNode("Colombia")
}
' Create a list of some European countries and
' store them in an array named nodEuropeans
Dim nodEuropeans() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Italy"),
New TreeNode("Greece"),
New TreeNode("Spain"),
New TreeNode("England")
}
' Create a list of continents, independently
Dim nodAfrica As TreeNode = New TreeNode("Africa", nodAfricans)
Dim nodAmerica As TreeNode = New TreeNode("America", nodAmericans)
Dim nodAsia As TreeNode = New TreeNode("Asia")
Dim nodEurope As TreeNode = New TreeNode("Europe", nodEuropeans)
' Store the list of continents in an array named nodContinents
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode =
{nodAfrica, nodAmerica, nodAsia, nodEurope}
' Create a branch named nodWorld and store the list of
' continents as its child
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
' Finally, add the nodWorld branch to the tree view
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
End Sub
This would produce:

|
 Practical
Learning: Creating Child Nodes Practical
Learning: Creating Child Nodes
|
|
- Access the Central.vb code file and change it as follows:
Private parts(55) As PartDescription
Private Sub CentralLoad(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles Me.Load
Dim nodRoot As TreeNode = tvwAutoParts.Nodes.Add("College Park Auto-Parts")
' This is simply used to initialize the whole array with empty parts
' This is just to make sure that each member of the array is defined
For i As Integer = Date.Today.Year To 1960 Step -1
nodRoot.Nodes.Add(i)
Next
parts(0) = New PartDescription(447093, 2002, "Ford",
"Escort SE L4 2.0", "Engine Electrical",
"Alternator 75amp Remanufactured; w/ 75 Amp",
205.05)
parts(1) = New PartDescription(203815, 2006, "Dodge",
"Caravan SE L4 2.4", "Cooling System",
"Radiator Cap", 6.65)
parts(2) = New PartDescription(293047, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Thermostat Gasket", 4.95)
parts(3) = New PartDescription(990468, 2002, "Honda",
"Civic 1.7 EX 4DR", "Exhaust",
"Bolt & Spring Kit (Manifold outlet, Muffler Inlet)",
85.75)
parts(4) = New PartDescription(304158, 1996, "Buick",
"Regal Custom V6 3.8", "Fuel Injection",
"Fuel Injector", 82.75)
parts(5) = New PartDescription(807245, 2004, "Acura",
"MDX 3.5 4WD", "Driveshaft & Axle",
"CV Boot Clamp 7 x 750mm; 1 Large + 1 Small Clamp",
1.6)
parts(6) = New PartDescription(203485, 2001, "Ford",
"Taurus LX V6 3.0", "Fuel Injection",
"Oxygen Sensor OE Style 4Wire; Front; 2 Required",
52.65)
parts(7) = New PartDescription(248759, 1999, "Jeep",
"Wrangler Sahara", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter AirSoft Panel", 7.95)
parts(8) = New PartDescription(202848, 1998, "Honda",
"Accord 2.3 LX 4DR", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter", 12.55)
parts(10) = New PartDescription(932759, 2006, "Kia",
"Rio 1.6DOHC16V 4-DR", "Cooling System",
"Thermostat", 14.45)
parts(11) = New PartDescription(304975, 2000, "Honda",
"Civic 1.6 EX 4DR", "Suspension",
"Ball Joint; Front Lower; 2 per car", 40.55)
parts(12) = New PartDescription(208450, 2003, "Chevrolet",
"Monte Carlo LS V6 3.4", "Fuel Injection",
"Oxygen Sensor OE connector; Rear", 65.55)
parts(13) = New PartDescription(209480, 2002, "Ford",
"Focus SE DOHC L4 2.0", "Steering",
"Steering Rack Remanufactured", 170.85)
parts(9) = New PartDescription(203495, 2004, "Honda",
"Civic 1.7 EX 4DR", "Climate Control",
"A/C Clutch; OE compressor = Sanden", 184.95)
parts(14) = New PartDescription(203480, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter", 12.65)
parts(15) = New PartDescription(109379, 2005, "Volvo",
"S40 2.5L T5 AWD", "Fuel Delivery",
"Fuel Filter; Early Design; Outer Diameter = 55mm",
30.95)
parts(16) = New PartDescription(935794, 2002, "Ford",
"Escape XLS 4WD", "Brake",
"Brake Caliper Remanufactured; Front Right",
65.55)
parts(17) = New PartDescription(203485, 2006, "BMW",
"325i", "Climate Control",
"AC High Pressure Side Switch",
49.95)
parts(18) = New PartDescription(204875, 1996, "Chevrolet",
"Monte Carlo Z34 V6 3.4", "Fuel Delivery",
"Fuel Filter", 8.05)
parts(19) = New PartDescription(937485, 2007, "Toyota",
"Camry V6", "Air Intake", "Air Filter", 12.95)
parts(20) = New PartDescription(294759, 2001, "Ford",
"Escape XLT 4WD", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter Panel", 7.25)
parts(21) = New PartDescription(297495, 2003, "Honda",
"Civic 1.7 EX 4DR", "Brake",
"Brake Caliper Reman; w/ ProAct Pads; Front Right",
82.55)
parts(22) = New PartDescription(794735, 2006, "BMW",
"325i", "Climate Control",
"Cabin Air/Pollen Filter; With Activated Carbon",
28.05)
parts(23) = New PartDescription(937485, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Body Electrical",
"Halogen SilverStar; 12V 65W; inner-high beam",
22.85)
parts(24) = New PartDescription(492745, 2005, "Ford",
"Focus ZX3 L4 2.0", "Air Intake",
"Fuel Injection Perf Kit", 342.95)
parts(25) = New PartDescription(937005, 2004, "Acura",
"MDX 3.5 4WD", "Driveshaft & Axle",
"CV Boot Clamp 7 x 750mm; For Large End of Boot; inner boot",
1.6)
parts(26) = New PartDescription(293749, 2004, "Acura",
"MDX 3.5 4WD", "Driveshaft & Axle",
"Axle Nut 24mm x 1;5; rear ", 2.35)
parts(27) = New PartDescription(920495, 2006, "BMW",
"325i", "Climate Control",
"Adjustable Telescoping Mirror", 7.95)
parts(28) = New PartDescription(204075, 2004, "Acura",
"MDX 3.5 4WD", "Driveshaft & Axle",
"Wheel Bearing; Rear; 1 per wheel", 70.15)
parts(29) = New PartDescription(979304, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Thermostat Housing", 20.95)
parts(30) = New PartDescription(300456, 2004, "Acura",
"MDX 3.5 4WD", "Driveshaft & Axle",
"Wheel Bearing; Front; 1 per wheel",
66.65)
parts(31) = New PartDescription(404860, 2001, "Ford",
"Taurus LX V6 3.0", "Suspension",
"Shock Absorber GR2; Rear; Wagon only",
39.4)
parts(32) = New PartDescription(585688, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Brake",
"Climate Control", 10.65)
parts(33) = New PartDescription(739759, 2001, "Ford",
"Taurus LX V6 3.0", "Suspension",
"Shock Absorber GasaJust; Rear; Wagon only",
30.95)
parts(34) = New PartDescription(927495, 2005, "Volvo",
"S40 2.5L T5 AWD", "Engine Mechanical",
"Timing Belt Idler Pulley Original Equipment INA",
65.55)
parts(40) = New PartDescription(979374, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Thermostat Gasket", 4.95)
parts(35) = New PartDescription(542347, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Brake",
"Brake Pad Set ProACT Ceramic w/Shims; Front", 80.05)
parts(36) = New PartDescription(683064, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Radiator Hose; Upper", 103.75)
parts(37) = New PartDescription(248759, 1999, "Jeep",
"Wrangler Sahara", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter", 50.95)
parts(38) = New PartDescription(973974, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Air Intake",
"Air Mass Meter; W/o Housing; Meter/sensor only",
134.95)
parts(39) = New PartDescription(285800, 2001, "Ford",
"Escape XLT 4WD", "Transmission",
"AT Filter", 34.95)
parts(41) = New PartDescription(207495, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Body Electrical",
"Headlight Bulb; 12V 65W; inner-high beam", 9.35)
parts(42) = New PartDescription(566676, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Auxiliary Fan Switch", 42.95)
parts(43) = New PartDescription(304950, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Body Electrical",
"Headlight Bulb; 12V 51W; outer", 7.85)
parts(44) = New PartDescription(797394, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Water Flange Gasket", 0.85)
parts(45) = New PartDescription(910203, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Suspension",
"Strut Mount Inc; Sleeve; Rear Right", 80.85)
parts(46) = New PartDescription(790794, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Radiator Hose; Lower", 9.45)
parts(47) = New PartDescription(970394, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Suspension",
"Coil Spring Insulator; Front Lower", 14.55)
parts(48) = New PartDescription(290840, 2005, "Volvo",
"S40 2.5L T5 AWD", "Engine Mechanical",
"Rod Bearing Set 1 per Rod; Standard; Reqs. 5-per Engine",
26.95)
parts(49) = New PartDescription(209704, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Body Electrical",
"Wiper Blade Excel+; Front Right", 7.25)
parts(50) = New PartDescription(200368, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Radiator Drain Plug incl; gasket", 3.15)
parts(51) = New PartDescription(200970, 2005, "Volvo",
"S40 2.5L T5 AWD", "Engine Mechanical",
"Reference Sensor; Flywheel Engine Speed",
62.05)
parts(52) = New PartDescription(542347, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter", 50.25)
parts(53) = New PartDescription(927045, 2001, "Ford",
"Escape XLT 4WD", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter", 62.95)
parts(54) = New PartDescription(990659, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Radiator OE Plastic tank", 136.85)
parts(55) = New PartDescription(440574, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Suspension",
"Strut Mount Inc; Sleeve; Rear Left",
80.8)
' Showing the makes nodes
' Showing the makes nodes
For Each nodYear As TreeNode In nodRoot.Nodes
Dim lstMakes As ArrayList = New ArrayList()
For Each part As PartDescription In parts
If nodYear.Text = part.CarYear.ToString() Then
If Not lstMakes.Contains(part.Make) Then
lstMakes.Add(part.Make)
End If
End If
Next
For Each strMake As String In lstMakes
nodYear.Nodes.Add(strMake)
Next
Next
' Showing the models nodes
For Each nodYear As TreeNode In nodRoot.Nodes
For Each nodMake As TreeNode In nodYear.Nodes
Dim lstModels As ArrayList = New ArrayList()
For Each part As PartDescription In parts
If nodYear.Text = part.CarYear.ToString() And
(nodMake.Text = part.Make) Then
If Not lstModels.Contains(part.Model) Then
lstModels.Add(part.Model)
End If
End If
Next
For Each strModel As String In lstModels
nodMake.Nodes.Add(strModel)
Next
Next
Next
' Showing the categories nodes
For Each nodYear As TreeNode In nodRoot.Nodes
For Each nodMake As TreeNode In nodYear.Nodes
For Each nodModel As TreeNode In nodMake.Nodes
Dim lstCategories As ArrayList = New ArrayList()
For Each part As PartDescription In parts
If (nodYear.Text = part.CarYear.ToString()) And
(nodMake.Text = part.Make) And
(nodModel.Text = part.Model) Then
If Not lstCategories.Contains(part.Category) Then
lstCategories.Add(part.Category)
End If
End If
Next
For Each strCategory As String In lstCategories
nodModel.Nodes.Add(strCategory)
Next
Next
Next
Next
End Sub
- Save the file
|
The Number of Child Nodes
|
|
The number of nodes in the TreeNode objects is stored
in the TreeNodeCollection.Count property. To get the current number of
nodes in the tree view, you can call the TreeView.GetNodeCount() method.
Its syntax is:
Public Function GetNodeCount(includeSubTrees As Boolean) As Integer
Here is an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
. . . No Change
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
Dim NodeCount As Integer = tvwCountries.GetNodeCount(True)
Text = CStr(NodeCount)
End Sub
This would produce:

If you create a node and add it to a branch that already
contains another node, the new node is referred to as a sibling to the existing
child node.
In our introduction, we saw that a node, any node, could
have as many nodes as you judge necessary. To support this, the TreeNode
class is equipped with a property called Nodes, which, like that of the
TreeView class, is based on the TreeNodeCollection class. This
allows you to refer to the list of children of the node that this Nodes
property belongs to. With this information, you can further create or manipulate
child nodes of any node as you wish.
Besides looking at a node, probably the primary action a
user performs on a tree is to select an item. To select a node in the tree, the
user can click it. To programmatically select a node, assign its reference to
the TreeView.SelectedNode property. Here is an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
Dim nodAfrica As TreeNode = New TreeNode("Africa")
Dim nodAmerica As TreeNode = New TreeNode("America")
Dim nodEurope As TreeNode = New TreeNode("Europe")
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode = {nodAfrica, nodAmerica, nodEurope}
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
tvwCountries.SelectedNode = nodAmerica
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
End Sub
After selecting a node, the tree view indicates the item
selected by highlighting it. In the following picture, the America node is
selected:

To programmatically find out what item is selected in the
tree, get the value of the TreeView.SelectedNode Boolean property. If no
node is selected, this property produces null. Alternatively, you can check the
value of a node's TreeNode.IsSelected Boolean property to find out if it
is currently selected.
After locating a node, the user may want to change its text.
To change the string of a node, it must be put to edit mode. To do this, you can
call the TreeNode.BeginEdit() method. Its syntax is:
Public Sub BeginEdit
When a node is in edit mode, the caret blinks in its edit
box section. The user can then type a new string or edit the existing string.
After setting the (new) string, the user can press Enter or may click somewhere.
At this time, you need to indicate that the user has finished this operation. To
do this, you can call the TreeNode.EndEdit() method. Its syntax is:
Public Sub EndEdit(cancel As Boolean)
Just before this method, you can check the content of the
string that was added or edited. This allows you to accept or reject the change.
The argument to the EndEdit() method allows you to validate or cancel the
editing action.
As mentioned already, the nodes of a tree view are stored in
a collection of type TreeNodeCollection. Every time you create a new
node, it occupies a position inside the tree. Each node is represented by the
Item indexed property of this collection. The first node of the tree has an
index of 0.
When you call the TreeNodeCollection.Add() method to
create a node, the new branch is added at the end of the list of its siblings.
If you want, you can add a new child somewhere in the tree. To do this, you
would call the TreeNodeCollection.Insert() method. Its syntax is:
Public Overridable Sub Insert(index As Integer, node As TreeNode)
The first argument to this method is the index that the new
node will occupy when created. The second argument is a reference to the new
node to be created. Here is an example of using it:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Africa"),
New TreeNode("America"),
New TreeNode("Asia"),
New TreeNode("Europe")
}
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Insert(1, New TreeNode("Neptune"))
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
End Sub
This would produce:

Another technique you can use to locate a node consists of
using some coordinates. To do this, you can call the TreeView.GetNodeAt()
method that is overloaded with two versions whose syntaxes are:
Public Function GetNodeAt(x As Integer, y As Integer) As TreeNode
Public Function GetNodeAt(pt As Point) As TreeNode
To use this method, you must know either the Point
location or the x and y coordinates of the node. If you provide valid arguments
to this method, it returns a reference to the TreeNode located at the
argument. Here is an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Africa"),
New TreeNode("America"),
New TreeNode("Asia"),
New TreeNode("Europe")
}
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
tvwCountries.ExpandAll()
Dim nodBranch As TreeNode = tvwCountries.GetNodeAt(22, 48)
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
Text = nodBranch.Text
End Sub
This would produce:

After creating a tree, to get a reference to the first child
node, you can retrieve the TreeNode.FirstNode property. You would use
code as follows:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Africa"),
New TreeNode("America"),
New TreeNode("Asia"),
New TreeNode("Europe")
}
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
dim nodFirst as TreeNode = tvwCountries.Nodes(0).FirstNode
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
Text = nodFirst.Text
End Sub
To get a reference to the last child node, retrieve the
TreeNode.LastNode property. You would use code as follows:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Africa"),
New TreeNode("America"),
New TreeNode("Asia"),
New TreeNode("Europe")
}
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
Dim nodLast As TreeNode = tvwCountries.Nodes(0).FirstNode
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
Text = nodLast.Text
End Sub
To get a reference to the sibling above a node, if any, you
can retrieve its TreeNode.PrevNode property. To get a reference to the
sibling below a node, if any, you can retrieve its TreeNode.NextNode
property.
To find whether a tree view contains a certain node, you can
call the TreeNodeCollection.Contains() method. Its syntax is:
Public Function Contains(node As TreeNode) As Boolean
This method expects as argument a reference to the node to
look for. If the tree contains that node, the method returns true. If the node
is not found, this method returns false.
|
 Practical
Learning: Using the Selected Node Practical
Learning: Using the Selected Node
|
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select tvwAutoParts
- In the Method Name combo box, select NodeMouseClick
- Implement the event as follows:
Private Sub tvwAutoPartsNodeMouseClick(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.TreeNodeMouseClickEventArgs)
Handles tvwAutoParts.NodeMouseClick
Dim nodClicked As TreeNode = e.Node
If nodClicked.Level = 4 Then lvwAutoParts.Items.Clear()
Try
Try
For Each part As PartDescription In parts
If (part.Category = nodClicked.Text) And
(part.Model = nodClicked.Parent.Text) And
(part.Make = nodClicked.Parent.Parent.Text) And
(part.CarYear.ToString() =
nodClicked.Parent.Parent.Parent.Text) Then
Dim lviAutoPart As ListViewItem =
New ListViewItem(part.PartNumber.ToString())
lviAutoPart.SubItems.Add(part.PartName)
lviAutoPart.SubItems.Add(part.UnitPrice.ToString())
lvwAutoParts.Items.Add(lviAutoPart)
End If
Next
Catch ex As NullReferenceException
End Try
Catch ex As NullReferenceException
End Try
End Sub
- Under the above End Sub line, create the following procedure:
Private Sub CalculateOrder()
' Calculate the current total order and update the order
Dim SubTotal1 As Double
Dim SubTotal2 As Double
Dim SubTotal3 As Double
Dim SubTotal4 As Double
Dim SubTotal5 As Double
Dim SubTotal6 As Double
Dim OrderTotal As Double
' Retrieve the value of each sub total
Try
SubTotal1 = CDbl(txtSubTotal1.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
Try
SubTotal2 = CDbl(txtSubTotal2.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
Try
SubTotal3 = CDbl(txtSubTotal3.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
Try
SubTotal4 = CDbl(txtSubTotal4.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
Try
SubTotal5 = CDbl(txtSubTotal5.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
Try
SubTotal6 = CDbl(txtSubTotal6.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
' Calculate the total value of the sub totals
OrderTotal = SubTotal1 + SubTotal2 + SubTotal3 +
SubTotal4 + SubTotal5 + SubTotal6
' Display the total order in the appropriate text box
txtTotalOrder.Text = CStr(OrderTotal)
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select lvwAutoParts
- In the Method Name combo box, select DoubleClick and implement the event
as follows:
Private Sub lvwAutoPartsDoubleClick(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles lvwAutoParts.DoubleClick
Dim lviAutoPart As ListViewItem = lvwAutoParts.SelectedItems(0)
If lvwAutoParts.SelectedItems.Count = 0 Or
lvwAutoParts.SelectedItems.Count > 1 Then
End If
If txtPartNumber1.Text = "" Then
txtPartNumber1.Text = lviAutoPart.Text
txtPartName1.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(1).Text
txtUnitPrice1.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(2).Text
txtQuantity1.Text = "1"
txtSubTotal1.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(2).Text
txtQuantity1.Focus()
' If the previous Part # text box is not empty,
' then use the next one
ElseIf txtPartNumber2.Text = "" Then
txtPartNumber2.Text = lviAutoPart.Text
txtPartName2.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(1).Text
txtUnitPrice2.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(2).Text
txtQuantity2.Text = "1"
txtSubTotal2.Text = txtUnitPrice2.Text
txtQuantity2.Focus()
ElseIf txtPartNumber3.Text = "" Then
txtPartNumber3.Text = lviAutoPart.Text
txtPartName3.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(1).Text
txtUnitPrice3.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(2).Text
txtQuantity3.Text = "1"
txtSubTotal3.Text = txtUnitPrice3.Text
txtQuantity3.Focus()
ElseIf txtPartNumber4.Text = "" Then
txtPartNumber4.Text = lviAutoPart.Text
txtPartName4.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(1).Text
txtUnitPrice4.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(2).Text
txtQuantity4.Text = "1"
txtSubTotal4.Text = txtUnitPrice4.Text
txtQuantity4.Focus()
ElseIf txtPartNumber5.Text = "" Then
txtPartNumber5.Text = lviAutoPart.Text
txtPartName5.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(1).Text
txtUnitPrice5.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(2).Text
txtQuantity5.Text = "1"
txtSubTotal5.Text = txtUnitPrice5.Text
txtQuantity5.Focus()
ElseIf txtPartNumber6.Text = "" Then
txtPartNumber6.Text = lviAutoPart.Text
txtPartName6.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(1).Text
txtUnitPrice6.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems(2).Text
txtQuantity6.Text = "1"
txtSubTotal6.Text = txtUnitPrice6.Text
txtQuantity6.Focus()
' If all Part # text boxes are filled, don't do anything
Else
Exit Sub
End If
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity1
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity1Leave(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles txtQuantity1.Leave
Dim Quantity As Integer
Dim UnitPrice As Double, SubTotal As Double
' Get the quantity of the current item
Try
Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity1.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
' Get the unit price of the current item
Try
UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice1.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
' Calculate the current sub total
SubTotal = Quantity * UnitPrice
' Display the new sub total in the corresponding text box
txtSubTotal1.Text = SubTotal.ToString()
' Update the order
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity2
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity2Leave(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles txtQuantity2.Leave
Dim Quantity As Integer
Dim UnitPrice As Double, SubTotal As Double
Try
Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity2.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
Try
UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice2.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
SubTotal = Quantity * UnitPrice
txtSubTotal2.Text = SubTotal.ToString()
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity3
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity3Leave(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles txtQuantity3.Leave
Dim Quantity As Integer
Dim UnitPrice As Double, SubTotal As Double
Try
Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity3.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
Try
UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice3.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
SubTotal = Quantity * UnitPrice
txtSubTotal3.Text = SubTotal.ToString()
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity4
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity4Leave(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles txtQuantity4.Leave
Dim Quantity As Integer
Dim UnitPrice As Double, SubTotal As Double
Try
Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity4.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
Try
UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice4.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
SubTotal = Quantity * UnitPrice
txtSubTotal4.Text = SubTotal.ToString()
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity5
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity5Leave(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles txtQuantity5.Leave
Dim Quantity As Integer
Dim UnitPrice As Double, SubTotal As Double
Try
Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity5.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
Try
UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice5.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
SubTotal = Quantity * UnitPrice
txtSubTotal5.Text = SubTotal.ToString()
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity6
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity6Leave(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles txtQuantity6.Leave
Dim Quantity As Integer
Dim UnitPrice As Double, SubTotal As Double
Try
Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity6.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
Try
UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice6.Text)
Catch
MsgBox("Invalid Value")
End Try
SubTotal = Quantity * UnitPrice
txtSubTotal6.Text = SubTotal.ToString()
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnRemove1
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub btnRemove1Click(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles btnRemove1.Click
txtPartNumber1.Text = ""
txtPartName1.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice1.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity1.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal1.Text = "0.00"
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnRemove2
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub btnRemove2Click(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles btnRemove2.Click
txtPartNumber2.Text = ""
txtPartName2.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice2.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity2.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal2.Text = "0.00"
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnRemove3
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub btnRemove3Click(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles btnRemove3.Click
txtPartNumber3.Text = ""
txtPartName3.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice3.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity3.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal3.Text = "0.00"
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnRemove4
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub btnRemove4Click(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles btnRemove4.Click
txtPartNumber4.Text = ""
txtPartName4.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice4.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity4.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal4.Text = "0.00"
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnRemove5
- Double-click the fifth Remove button and implement its event as follows:
Private Sub btnRemove5Click(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles btnRemove5.Click
txtPartNumber5.Text = ""
txtPartName5.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice5.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity5.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal5.Text = "0.00"
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnRemove6
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub btnRemove6Click(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles btnRemove6.Click
txtPartNumber6.Text = ""
txtPartName6.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice6.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity6.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal6.Text = "0.00"
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnClose
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub btnCloseClick(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles btnClose.Click
End
End Sub
- Execute the application to test it

- After using it, close the form
When a tree contains a few nodes, the user may want to
delete some of them, for any reason. To delete a node, you can call the
TreeNodeCollection.Remove() method. Its syntax is:
Public Sub Remove(node As TreeNode)
This method expects a reference to the node you want to
delete. Another solution you can use would consist of locating the node by its
index. To do this, you would call the TreeNodeCollection.RemoveAt()
method. Its syntax is:
Public Overridable Sub RemoveAt(index As Integer)
When calling this method, pass the index of the node to be
deleted. If you are already at that node and you want to remove it, you can call
the TreeNode.Remove() method. Its syntax is:
Public Sub Remove
One of the characteristics of a tree in the real world is
that, if you cut a branch, the branches attached to it and their leaves are cut
too. In the same way, if you call any of these Remove() or RemoveAt()
methods to delete a node, its children, if any, would be deleted too.
To remove all nodes of a tree view, you can call the
TreeNodeCollection.Clear() method. Its syntax is:
Public Overridable Sub Clear
This method is used to get rid of all nodes of a tree.
|
Characteristics of a Tree View
|
|
After a node has been added to a tree, it holds a position
relative to its parent and its existence depends on that parent. To keep track
of its "ancestry", each node has a path that can be used to identify its parent
and its grand-parent(s), if any. To know the path of a node from itself to the
root, you can access its TreeNode.FullPath property. This property
produces a string made of sections separated by a specific character identified
as the TreeView.PathSeparator property. By default, this character is the
backslash, following the conventions of the operating system. If you want to use
a different character or string, assign it to the PathSeparator property.
To know what character or string a tree view is using as the separator, you can
retrieve the value of its PathSeparator property.
In order to select an item, the user must click it or
navigate to it using the keyboard. Alternatively, if you want the items to be
underlined when the mouse passes over them, set to true the
TreeView.HotTracking Boolean property. Its default value is false. Here is
an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
tvwCountries.HotTracking = True
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Africa"),
New TreeNode("America"),
New TreeNode("Asia"),
New TreeNode("Europe")
}
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
End Sub
This would produce:

|
The Intermediary Lines of Related Nodes
|
|
As mentioned already, a tree view appears as a list of items
arranged like a tree. This implies a relationship of parent-child among the
items in the control. To indicate this relationship between two nodes, a line is
drawn from one to another. Based on this, a line from a node on top of another
node under it indicates that the one on top is the parent to the one under it.
The presence or absence of the lines among related nodes is
controlled by the TreeView.ShowLines Boolean property. By default, this
property is set to true (in the .NET Framework, some other libraries have it set
by default to false). If this property is set to false, the lines between the
nodes would not display. Here is an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
tvwCountries.ShowLines = False
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Africa"),
New TreeNode("America"),
New TreeNode("Asia"),
New TreeNode("Europe")
}
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
End Sub
This would produce:

If you create a tree that has more than one root, a line is
drawn among those root nodes. Here is an example:

The presence or absence of this type of line is controlled
by the TreeView.ShowRootLines Boolean property.
Indentation is the ability for a child node to be aligned to
the right with regards to its parent. The general distance from the left border
of the parent to the left border of the child is partially controlled by the
TreeView.Indent property which is an integer. If the default distance
doesn't suit you, you can change it by assigning a positive number to the
control's Indent property.
When the user clicks an item, that node becomes highlighted
for the length of its string. If you want, you can show the highlighting on the
selected node but from the left to the right borders of the tree view. To do
this, you can set the TreeView.FullRowSelect Boolean property to true.
Its default value is false. For the TreeView.FullRowSelect property to
work, the ShowLines property must be set to false. Here is an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
tvwCountries.HotTracking = True
tvwCountries.ShowLines = False
tvwCountries.FullRowSelect = True
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Africa"),
New TreeNode("America"),
New TreeNode("Asia"),
New TreeNode("Europe")
}
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
End Sub
This would produce:

|
Hiding Selection After Losing Focus
|
|
We saw that, to select an item, the user can click it. If
the user clicks another control, the node that was selected in the tree view
loses its highlighting because the control has lost focus. When the focus moves
to another control, if you want the selected node of the tree view to preserve
its highlighting, set to false the TreeView.HideSelection Boolean
property. Its default value is true.
At this time, we have seen that some nodes have children and
some don't. When a node has at least one child, the node indicates this by
displaying a + button. If the user clicks the + button, the node expands,
displays a list of its children, and the button becomes -. The presence or
absence of the + and - buttons is controlled by the TreeView.ShowPlusMinus
Boolean property. By default, this property is set to true. If you don't want
the parent nodes to display the + or - button, set this property to false.
|
Expanding and Collapsing Tree Nodes
|
|
When a node displays a + button and the user clicks that
button, the node displays its child(ren). This action is referred to as
expanding the node. To programmatically expand a node, call its
TreeNode.Expand() method. Its syntax is:
Public Sub Expand
This method only expands the node that calls it but if its
children have their own children, they are not expanded. To expand a node
and its children that have nodes, you can call its TreeNode.ExpandAll()
method. Its syntax is:
Public Sub ExpandAll
To find out if a node is expanded, check the value of its
TreeNode.IsExpanded property.
To expand other nodes of the tree view, the user can
continue clicking each node that has a + button as necessary. To
programmatically expand all nodes of a tree view, call its
TreeView.ExpandAll() method. Its syntax is:
Public Sub ExpandAll
If a node is displaying a - button, it indicates that it is
showing the list of its children. To hide the list, the user can click the -
button. This action is referred to as collapsing the node. To programmatically
collapse a node, call its TreeNode.Collapse() method whose syntax is:
Public Sub ExpandAll
The user can do this for each node that is expanded. To
programmatically collapse all nodes of a tree view, call its
TreeView.CollapseAll() method. Its syntax is:
Public Sub CollapseAll
|
Tree Nodes and Check Boxes
|
|
Besides the strings (and some small pictures as we will see
later), the nodes of a tree view can display a check box on their left side. The
presence or absence of the check box is controlled by the CheckBoxes
Boolean property whose default value is false. If you want to display the check
boxes, set this property to true. Here is an example:
Public Sub InitializeComponent()
Text = "Countries Statistics"
Size = New Size(242, 280)
tvwCountries = New TreeView()
tvwCountries.Location = New Point(12, 12)
tvwCountries.Width = 210
tvwCountries.Height = 230
tvwCountries.CheckBoxes = True
Controls.Add(tvwCountries)
Dim nodContinents() As TreeNode =
{
New TreeNode("Africa"),
New TreeNode("America"),
New TreeNode("Asia"),
New TreeNode("Europe")
}
Dim nodWorld As TreeNode = New TreeNode("World", nodContinents)
tvwCountries.Nodes.Add(nodWorld)
End Sub
This would produce:

If you equip the nodes with check boxes, the user can click
an item to select it independently of the check box. The user can also click the
check box, which would place a check mark in the box. To programmatically check
the box, you can assign a true value to the node's Checked property.
When a check mark has been placed in a node's check box, the
tree view fires an AfterCheck event, which is handled by the
TreeViewEventHandler delegate. The AfterCheck event is carried by the
TreeViewEventArgs class. One of properties of this class is called
Action, which specifies why or how the event occurred. The Action
property is in fact a value based on the TreeViewAction enumerator. Its
members are:
ByKeyboard: This indicates that the event was fired
by pressing a key
ByMouse: This indicates that the event was fired
based on an action on the mouse
Collapse: This indicates that event was fired when
the tree collapsed
Expand: This indicates that the event was fired when
the tree expanded
Unknown: None of the above reasons caused the event,
but the event was fired
The other property of the TreeViewEventArgs class is
called Node. This member is of type TreeNode. It carries a
reference to the node that fired the event, whether it was clicked, checked,
expanded, or collapsed.
To programmatically find out if a node is checked, check the
value of its Checked property.
Each of the nodes we have used so far displayed a simple
piece of text. To enhance the appearance of a node, besides its text, you can
display a small icon to the left of its string. To do this, you must first
create an ImageList control and assign it to the TreeView.ImageList
property.
When creating a node, if you plan to display an icon next to
it, you can use the following constructor of the TreeNode class:
Public Sub New (
text As String,
imageIndex As Integer,
selectedImageIndex As Integer
)
This constructor allows you to specify the text that the
node will display, the index of the picture it will use in the ImageList
property, and the picture it will display when it is selected.
If you are creating a node with its children and you want to
specify its pictures, use the following constructor of the TreeNode
class:
Public Sub New (
text As String,
imageIndex As Integer,
selectedImageIndex As Integer,
children As TreeNode()
)
Just as done previously, after defining the TreeNode
object, you can add it to the tree by passing it to the
TreeNodeCollection.Add() method. In the same way, you can create an array of
TreeNode objects and pass it to the TreeNodeCollection.AddRange()
method.
|
 Practical
Learning: Associating Icons With Nodes Practical
Learning: Associating Icons With Nodes
|
|
- Display the Central form.
To create an icon, on the main menu, click Project -> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click Icon File
- Set the Name to cpap1 and click Add
- Right-click the white area and click Delete Image Type
- Design the 16x16, 16 colors version of the icon as follows:
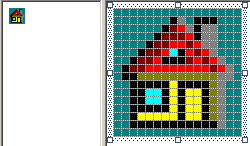
- On the main menu, click File -> Save cpap1.ico
- On the main menu, click File -> Close
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click Icon File
- Set the Name to cpap2 and click Add
- Right-click the white area and click Delete Image Type
- Design the 16x16, 16 colors version of the icon as follows:
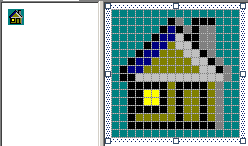
- On the main menu, click File -> Save cpap2.ico
- On the main menu, click File -> Close
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click Icon File
- Set the Name to year1 and click Add
- Right-click the white area and click Delete Image Type
- Design the 16x16, 16 colors version of the icon as follows:
- On the main menu, click File -> Save make2.ico
- On the main menu, click File -> Close
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click Icon File
- Set the Name to year2 and click Add
- Right-click the white area and click Delete Image Type
- Design the 16x16, 16 colors version of the icon as follows:
- On the main menu, click File -> Save year2.ico
- On the main menu, click File -> Close
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click Icon File
- Set the Name to make1 and click Add
- Right-click the white area and click Delete Image Type
- Design the 16x16, 16 colors version of the icon as follows:

- On the main menu, click File -> Save make1.ico
- On the main menu, click File -> Close
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click Icon File
- Set the Name to make2 and click Add
- Right-click the white area and click Delete Image Type
- Design the 16x16, 16 colors version of the icon as follows:
- On the main menu, click File -> Save make2.ico
- On the main menu, click File -> Close
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click Icon File
- Set the Name to model1 and click Add
- Right-click the white area and click Delete Image Type
- Design the 16x16, 16 colors version of the icon as follows:
- On the main menu, click File -> Save model1.ico
- On the main menu, click File -> Close
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click Icon File
- Set the Name to model2 and click Add
- Right-click the white area and click Delete Image Type
- Design the 16x16, 16 colors version of the icon as follows:

- On the main menu, click File -> Save model2.ico
- On the main menu, click File -> Close
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click Icon File
- Set the Name to category1 and click Add
- Right-click the white area and click Delete Image Type
- Design the 16x16, 16 colors version of the icon as follows:
- On the main menu, click File -> Save category1.ico
- On the main menu, click File -> Close
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click Icon File
- Set the Name to category2 and click Add
- Right-click the white area and click Delete Image Type
- Design the 16x16, 16 colors version of the icon as follows:
- On the main menu, click File -> Save category2.ico
- On the main menu, click File -> Close
- Display the form.
In the Toolbox, click ImageList and click the form
- In the Properties window, click (Name) and type imgAutoParts
- Click the ellipsis button of the Images field
- In Image Collection Editor, click Add
- Locate the folder that contains the icons you created and display it in
the Look In combo box
- Select cpap1.ico and click Open
- In the same way, add the other pictures in the following order:
cpap2.ico, year1.ico, year2.ico, make1.ico, make2.ico, model1.ico,
model2.ico, category1.ico, and category1.ico
- Click OK
- On the form, click the tree view
- In the Properties window, click ImageList, then click the arrow of its
combo box and select imgAutoParts
- Access the Central.vb source file and change the code of the Load event
as follows:
Private Sub CentralLoad(ByVal sender As Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Handles Me.Load
Dim nodRoot As TreeNode =
tvwAutoParts.Nodes.Add("College Park Auto-Parts",
"College Park Auto-Parts", 0, 1)
' This is simply used to initialize the whole array with empty parts
' This is just to make sure that each member of the array is defined
For i As Integer = Date.Today.Year To 1960 Step -1
nodRoot.Nodes.Add(CStr(i), CStr(i), 2, 3)
Next
' Expand the root node
tvwAutoParts.ExpandAll()
. . . No Change
' Showing the makes nodes
For Each nodYear As TreeNode In nodRoot.Nodes
Dim lstMakes As ArrayList = New ArrayList()
For Each part As PartDescription In parts
If nodYear.Text = part.CarYear.ToString() Then
If Not lstMakes.Contains(part.Make) Then
lstMakes.Add(part.Make)
End If
End If
Next
For Each strMake As String In lstMakes
nodYear.Nodes.Add(strMake, strMake, 4, 5)
Next
Next
' Showing the models nodes
For Each nodYear As TreeNode In nodRoot.Nodes
For Each nodMake As TreeNode In nodYear.Nodes
Dim lstModels As ArrayList = New ArrayList()
For Each part As PartDescription In parts
If nodYear.Text = part.CarYear.ToString() And
(nodMake.Text = part.Make) Then
If Not lstModels.Contains(part.Model) Then
lstModels.Add(part.Model)
End If
End If
Next
For Each strModel As String In lstModels
nodMake.Nodes.Add(strModel, strModel, 6, 7)
Next
Next
Next
' Showing the categories nodes
For Each nodYear As TreeNode In nodRoot.Nodes
For Each nodMake As TreeNode In nodYear.Nodes
For Each nodModel As TreeNode In nodMake.Nodes
Dim lstCategories As ArrayList = New ArrayList()
For Each part As PartDescription In parts
If (nodYear.Text = part.CarYear.ToString()) And
(nodMake.Text = part.Make) And
(nodModel.Text = part.Model) Then
If Not lstCategories.Contains(part.Category) Then
lstCategories.Add(part.Category)
End If
End If
Next
For Each strCategory As String In lstCategories
nodModel.Nodes.Add(strCategory, strCategory, 8, 9)
Next
Next
Next
Next
End Sub
- Execute the application to test it

- Close the form and return to your programming environment
|
|

