|
 Practical
Learning: Introducing Databases Practical
Learning: Introducing Databases
|
|
- Start Microsoft Visual Basic and create a Windows Forms Application named YugoNationalBank1
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click Form1.vb and click Rename
- Type Central.vb and press Enter
Before creating an array, you must decide what type of
values each element of the array would be. A simple array can be made of
primitive types of values. Here is an example:
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
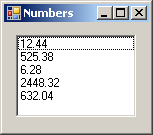
Dim Numbers() As Double = { 12.44, 525.38, 6.28, 2448.32, 632.04 }
End Sub
Once the array has been created, you can access each one of
its elements using the () operator. Here is an example:
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
Dim Numbers() As Double = { 12.44, 525.38, 6.28, 2448.32, 632.04 }
For i As Integer = 0 To 4
lbxNumbers.Items.Add(Numbers(i))
Next
End Sub
An array can also be made of elements that are each a
composite type. That is, each element can be of a class type. Of course, you
must have a class first. You can use one of the many built-in classes of the
.NET Framework or you can create your own class. Here is an example:
Public Class Person
Public PersonID As Integer
Public FirstName As String
Public LastName As String
Public Gender As String
Public Sub New()
End Sub
Public Sub New(ByVal ID As Integer, ByVal FName As String, _
ByVal LName As String, ByVal Gdr As String)
PersonID = ID
FirstName = FName
LastName = LName
Gender = Gdr
End Sub
End Class
After creating the class, you can then use it as the type of
the array. Here is an example:
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
Dim People(7) As Person
People(0) = New Person(72947, "Paulette", _
"Cranston", "Female")
People(1) = New Person(70854, "Harry", _
"Kumar", "Male")
People(2) = New Person(27947, "Jules", _
"Davidson", "Male")
People(3) = New Person(62835, "Leslie", _
"Harrington", "Unknown")
People(4) = New Person(92958, "Ernest", _
"Colson", "Male")
People(5) = New Person(91749, "Patricia", _
"Katts", "Female")
People(6) = New Person(29749, "Patrice", _
"Abanda", "Unknown")
People(7) = New Person(24739, "Frank", _
"Thomasson", "Male")
For i As Integer = 0 To 7
Dim lviPerson As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(People(i).FirstName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).LastName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).Gender)
lvwPeople.Items.Add(lviPerson)
Next
End Sub

To assist you with creating or managing arrays, the .NET
Framework provides the Array class. Every array you create is derived
from this class. As a result, all arrays of your program share many
characteristics and they get their foundation from the Array class, which
include its properties and methods. Once you declare an array variable, it
automatically has access to the members of the Array class. For example, instead
of counting the number of elements in an array, you can access the Length
property of the array variable. Here is an example:
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
Dim Numbers() As Integer = {20, 5, 83405, 734, 5}
For i As Integer = 0 To Numbers.Length - 1
lbxNumbers.Items.Add(Numbers(i))
Next
End Sub
In traditional languages, when you declare an array
variable, you must specify the number of elements that the array will contain.
You must do this especially if you declare the variable without initializing the
array. Here is an example:
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
dim People(4) as Person
End Sub
After declaring the variable, before using the array, you
must initialize it. Otherwise you would receive an error. When initializing the
array, you can only initialize it with the number of elements you had specified.
To illustrate this, consider the following program:
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
Dim People(4) As Person
People(0) = New Person(72947, "Paulette", _
"Cranston", "Female")
People(1) = New Person(70854, "Harry", _
"Kumar", "Male")
People(2) = New Person(27947, "Jules", _
"Davidson", "Male")
People(3) = New Person(62835, "Leslie", _
"Harrington", "Unknown")
People(4) = New Person(92958, "Ernest", _
"Colson", "Male")
For i As Integer = 0 To People.Length - 1
Dim lviPerson As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(People(i).FirstName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).LastName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).Gender)
lvwPeople.Items.Add(lviPerson)
Next
End Sub
Notice that the variable is declared to hold only 4 elements
but the user tries to access a 5th one. This would produce an IndexOutOfRangeExcception
exception:

One of the most valuable features of the Array class
is that it allows an array to be "resizable". That is, if you find out
that an array has a size smaller than the number of elements you want to add to
it, you can increase its capacity. To support this, the Array class is equipped
with the static Resize() method. Its syntax is:
Public Shared Sub Resize(Of T) (ByRef array As T(), newSize As Integer)
As you can see, this is a generic method that takes two
arguments. The first argument is the name of the array variable that you want to
resize. It must be passed by reference. The second argument is the new size you
want the array to have. Here is an example of calling this method:
Public Class Exercise
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
Dim People(4) As Person
People(0) = New Person(72947, "Paulette", _
"Cranston", "Female")
People(1) = New Person(70854, "Harry", _
"Kumar", "Male")
People(2) = New Person(27947, "Jules", _
"Davidson", "Male")
People(3) = New Person(62835, "Leslie", _
"Harrington", "Unknown")
People(4) = New Person(92958, "Ernest", _
"Colson", "Male")
Array.Resize(Of Person)(People, 8)
People(5) = New Person(91749, "Patricia", _
"Katts", "Female")
People(6) = New Person(29749, "Patrice", _
"Abanda", "Unknown")
People(7) = New Person(24739, "Frank", _
"Thomasson", "Male")
For i As Integer = 0 To People.Length - 1
Dim lviPerson As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(People(i).FirstName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).LastName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).Gender)
lvwPeople.Items.Add(lviPerson)
Next
End Sub
End Class
The advantage of this approach is that you can access the
array from any member of the same class or even from another file of the same
program.
As done previously, you can create an array in a method. A
disadvantage of this approach is that the array can be accessed from only the
method (or event) in which it is created. As an alternative, you can declare an
array as a member of a class. Here is an example:
Public Class Exercise
Dim People() As Person
End Class
The advantage of this approach is that you can access the
array from any member of the same class or even from another file of the same
program. After declaring the variable, you can initialize it. You can do this in
a constructor or in an event that would be fired before any other event that
would use the array. This type of initialization is usually done in a Load
event of a form. After initializing the array, you can then access in another
method or another event of the form. Here is an example:
Public Class Exercise
Dim People(7) As Person
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
People(0) = New Person(72947, "Paulette", _
"Cranston", "Female")
People(1) = New Person(70854, "Harry", _
"Kumar", "Male")
People(2) = New Person(27947, "Jules", _
"Davidson", "Male")
People(3) = New Person(62835, "Leslie", _
"Harrington", "Unknown")
People(4) = New Person(92958, "Ernest", _
"Colson", "Male")
People(5) = New Person(91749, "Patricia", _
"Katts", "Female")
People(6) = New Person(29749, "Patrice", _
"Abanda", "Unknown")
People(7) = New Person(24739, "Frank", _
"Thomasson", "Male")
For i As Integer = 0 To People.Length - 1
Dim lviPerson As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(People(i).FirstName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).LastName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).Gender)
lvwPeople.Items.Add(lviPerson)
Next
End Sub
End Class
An array can be passed as argument to a method. Here is an
example:
Public Class Exercise
Private Sub ArrayInitializer(ByVal People() As Person)
End Sub
End Class
In the method, you can use the array as you see fit. For
example you can assign values to the elements of the array. When calling a
method that is passed an array, you can pass the argument by reference so it
would come back with new values. Here are examples:
Public Class Exercise
Private Sub ArrayInitializer(ByVal People() As Person)
People(0) = New Person(72947, "Paulette", _
"Cranston", "Female")
People(1) = New Person(70854, "Harry", _
"Kumar", "Male")
People(2) = New Person(27947, "Jules", _
"Davidson", "Male")
People(3) = New Person(62835, "Leslie", _
"Harrington", "Unknown")
People(4) = New Person(92958, "Ernest", _
"Colson", "Male")
People(5) = New Person(91749, "Patricia", _
"Katts", "Female")
People(6) = New Person(29749, "Patrice", _
"Abanda", "Unknown")
People(7) = New Person(24739, "Frank", _
"Thomasson", "Male")
End Sub
Private Sub ShowPeople(ByVal People() As Person)
For i As Integer = 0 To People.Length - 1
Dim lviPerson As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(People(i).FirstName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).LastName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).Gender)
lvwPeople.Items.Add(lviPerson)
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Dim Persons(7) As Person
ArrayInitializer(Persons)
ShowPeople(Persons)
End Sub
End Class
A method can be created to return an array. When creating
the method, on the right side of the name of the method, type the name of the type
of value the method would return. In the method,
create and initialize an array. Before exiting the method, you must return the
array. Here is an example:
Public Class Exercise
Private Function ArrayInitializer() As Person()
Dim People(7) As Person
People(0) = New Person(72947, "Paulette", _
"Cranston", "Female")
People(1) = New Person(70854, "Harry", _
"Kumar", "Male")
People(2) = New Person(27947, "Jules", _
"Davidson", "Male")
People(3) = New Person(62835, "Leslie", _
"Harrington", "Unknown")
People(4) = New Person(92958, "Ernest", _
"Colson", "Male")
People(5) = New Person(91749, "Patricia", _
"Katts", "Female")
People(6) = New Person(29749, "Patrice", _
"Abanda", "Unknown")
People(7) = New Person(24739, "Frank", _
"Thomasson", "Male")
Return People
End Function
Private Sub ShowPeople(ByVal People() As Person)
For i As Integer = 0 To People.Length - 1
Dim lviPerson As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(People(i).FirstName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).LastName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).Gender)
lvwPeople.Items.Add(lviPerson)
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Dim Persons(7) As Person
Persons = ArrayInitializer()
ShowPeople(Persons)
End Sub
End Class
|
 Practical
Learning: Creating an Array Practical
Learning: Creating an Array
|
|
- To create a new class, on the main menu, click Project -> Add Class...
- Set the name to Employee and press Enter
- Complete the file as follows:
Public Class Employee
Public EmployeeNumber As Integer
Public FirstName As String
Public LastName As String
Public Title As String
Public CanCreateNewAccount As Boolean
Public HourlySalary As Double
Public ReadOnly Property FullName() As String
Get
Return LastName & ", " & FirstName
End Get
End Property
End Class
|
- To create a form that will be used to displays the employees information, on the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows
Form
- Set the name to Employees and press Enter
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Other Properties |
| ListView |
 |
|
lvwEmployees |
FullRowSelect: True
GridLines: True
View: Details |
| Columns |
| (Name) |
Text |
TextAlign |
Width |
| colIndex |
# |
|
20 |
| colEmployeeNumber |
Empl # |
|
50 |
| colFirstName |
First Name |
|
65 |
| colLastName |
Last Name |
|
65 |
| colFullName |
Full Name |
|
95 |
| colTitle |
Title |
|
145 |
| colHourlySalary |
Salary |
Right |
50 |
|
| Button |
 |
Close |
btnClose |
|
|
- To create a new class, on the main menu, click Project -> Add Class...
- Set the name to Customer and press Enter
- Complete the file as follows:
Public Enum AccountStatus
Active
Suspended
Closed
End Enum
Public Class Customer
Public CreatedBy As String
Public DateCreated As DateTime
Public CustomerName As String
Public AccountNumber As String
Public AccountType As String
Public Status As AccountStatus
End Class
|
- To create a form that will show the customers information, on the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows
Form
- Set the name to Customers and press Enter
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Other Properties |
| ListView |
 |
|
lvwCustomers |
FullRowSelect: True
GridLines: True
View: Details |
| Columns |
| (Name) |
Text |
TextAlign |
Width |
| colIndex |
# |
|
20 |
| colCreatedBy |
Created By |
|
100 |
| colDateCreated |
Date Created |
Center |
75 |
| colCustomerName |
Customer Name |
|
120 |
| colAccountNumber |
Account # |
Center |
80 |
| colAccountType |
Account Type |
|
80 |
| coloAccountStatus |
Status |
|
50 |
|
| Button |
 |
Close |
btnClose |
|
|
- Double-click the Close button and implement its event as follows:
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnClose.Click
Close()
End Sub
|
- To create a new class, on the main menu, click Project -> Add Class...
- Set the name to AccountTransaction and press Enter
- Complete the file as follows:
Public Enum TransactionTypes
Deposit
Withdrawal
Transfer
MonthlyCharge
MoneyOrder
Overdraft
TransactionFee
End Enum
Public Class AccountTransaction
Public TransactionDate As DateTime
Public ProcessedBy As Integer
Public ProcessedFor As String
Public TransactionType As TransactionTypes
Public DepositAmount As Double
Public WithdrawalAmount As Double
Public ChargeAmount As Double
End Class
|
- To create a new form that will show the transactions done on the customers
accounts, on the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows
Form
- Set the name to CustomersTransactions and press Enter
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Other Properties |
| ListView |
 |
|
lvwTransactions |
FullRowSelect: True
GridLines: True
View: Details |
| Columns |
| (Name) |
Text |
TextAlign |
Width |
| colIndex |
# |
|
25 |
| colTransactionDate |
Trans Date |
Center |
80 |
| colProcessedBy |
Processed By |
Center |
80 |
| colProcessedFor |
Processed For |
Center |
90 |
| colTransactionType |
Trans Type |
|
90 |
| colDepositAmount |
Deposit |
Right |
|
| colWithdrawalAmount |
Withdrawal |
Right |
65 |
| colChargeAmount |
Charge |
Right |
50 |
|
| Button |
 |
Close |
btnClose |
|
|
- Double-click the Close button and implement its event as follows:
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnClose.Click
Close()
End Sub
|
- To create a new class, on the main menu, click Project -> Add Class...
- Set the name to AccountsRecords and press Enter
- Complete the file as follows:
Public Class AccountsRecords
Public Shared Function GetEmployees() As Employee()
Dim StaffMembers(6) As Employee
StaffMembers(0) = New Employee
StaffMembers(0).EmployeeNumber = 74228
StaffMembers(0).FirstName = "Chrissie"
StaffMembers(0).LastName = "Nomads"
StaffMembers(0).Title = "General Manager"
StaffMembers(0).CanCreateNewAccount = True
StaffMembers(0).HourlySalary = 40.25
StaffMembers(1) = New Employee
StaffMembers(1).EmployeeNumber = 27905
StaffMembers(1).FirstName = "Calvin"
StaffMembers(1).LastName = "Braxton"
StaffMembers(1).Title = "Public Relations Manager"
StaffMembers(1).CanCreateNewAccount = False
StaffMembers(1).HourlySalary = 25.95
StaffMembers(2) = New Employee()
StaffMembers(2).EmployeeNumber = 94805
StaffMembers(2).FirstName = "Emilie"
StaffMembers(2).LastName = "Pastore"
StaffMembers(2).Title = "Branch Manager"
StaffMembers(2).CanCreateNewAccount = True
StaffMembers(2).HourlySalary = 32.55
StaffMembers(3) = New Employee()
StaffMembers(3).EmployeeNumber = 39850
StaffMembers(3).FirstName = "Walter"
StaffMembers(3).LastName = "Lemme"
StaffMembers(3).Title = "Accounts Manager"
StaffMembers(3).CanCreateNewAccount = True
StaffMembers(3).HourlySalary = 28.35
StaffMembers(4) = New Employee()
StaffMembers(4).EmployeeNumber = 70594
StaffMembers(4).FirstName = "Cecile"
StaffMembers(4).LastName = "Richards"
StaffMembers(4).Title = "Accounts Representative"
StaffMembers(4).CanCreateNewAccount = False
StaffMembers(4).HourlySalary = 18.15
StaffMembers(5) = New Employee()
StaffMembers(5).EmployeeNumber = 85285
StaffMembers(5).FirstName = "Joan"
StaffMembers(5).LastName = "Verrion"
StaffMembers(5).Title = "Accounts Representative"
StaffMembers(5).CanCreateNewAccount = False
StaffMembers(5).HourlySalary = 14.85
StaffMembers(6) = New Employee()
StaffMembers(6).EmployeeNumber = 94852
StaffMembers(6).FirstName = "Donald"
StaffMembers(6).LastName = "Waters"
StaffMembers(6).Title = "Accounts Representative"
StaffMembers(6).CanCreateNewAccount = False
StaffMembers(6).HourlySalary = 16.45
Return StaffMembers
End Function
Public Shared Function GetCustomers() As Customer()
Dim Clients(4) As Customer
Clients(0) = New Customer
Clients(0).CreatedBy = "Lemme, Walter"
Clients(0).DateCreated = New DateTime(2007, 1, 16)
Clients(0).CustomerName = "Louis George Berholdt"
Clients(0).AccountNumber = "95-722947-93"
Clients(0).AccountType = "Checking"
Clients(0).Status = AccountStatus.Active
Clients(1) = New Customer()
Clients(1).CreatedBy = "Pastore, Emilie"
Clients(1).DateCreated = New DateTime(2007, 1, 18)
Clients(1).CustomerName = "William Foster"
Clients(1).AccountNumber = "62-384638-48"
Clients(1).AccountType = " Checking"
Clients(1).Status = AccountStatus.Active
Clients(2) = New Customer()
Clients(2).CreatedBy = "Lemme, Walter"
Clients(2).DateCreated = New DateTime(2007, 1, 18)
Clients(2).CustomerName = "Catherine Hoods"
Clients(2).AccountNumber = "92-318284-75"
Clients(2).AccountType = "Checking"
Clients(2).Status = AccountStatus.Active
Clients(3) = New Customer()
Clients(3).CreatedBy = "Lemme, Walter"
Clients(3).DateCreated = New DateTime(2007, 3, 26)
Clients(3).CustomerName = "Harriett Cranston"
Clients(3).AccountNumber = "17-490040-83"
Clients(3).AccountType = "Saving"
Clients(3).Status = AccountStatus.Active
Clients(4) = New Customer()
Clients(4).CreatedBy = "Nomads, Chrissie"
Clients(4).DateCreated = New DateTime(2007, 4, 4)
Clients(4).CustomerName = "Janice Bonnie Weiss"
Clients(4).AccountNumber = "58-405048-15"
Clients(4).AccountType = "Checking"
Clients(4).Status = AccountStatus.Active
Return Clients
End Function
Public Shared Function GetTransactions() As AccountTransaction()
Dim Transactions(28) As AccountTransaction
Transactions(0) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(0).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 16)
Transactions(0).ProcessedBy = 39850
Transactions(0).ProcessedFor = "95-722947-93"
Transactions(0).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Deposit
Transactions(0).DepositAmount = 325.5
Transactions(1) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(1).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 18)
Transactions(1).ProcessedBy = 94805
Transactions(1).ProcessedFor = "62-384638-48"
Transactions(1).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Deposit
Transactions(1).DepositAmount = 550.0
Transactions(2) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(2).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 18)
Transactions(2).ProcessedBy = 39850
Transactions(2).ProcessedFor = "92-318284-75"
Transactions(2).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Deposit
Transactions(2).DepositAmount = 975.35
Transactions(3) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(3).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 22)
Transactions(3).ProcessedBy = 94852
Transactions(3).ProcessedFor = "95-722947-93"
Transactions(3).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Withdrawal
Transactions(3).WithdrawalAmount = 100.0
Transactions(4) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(4).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 22)
Transactions(4).ProcessedBy = 70594
Transactions(4).ProcessedFor = "62-384638-48"
Transactions(4).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Withdrawal
Transactions(4).WithdrawalAmount = 122.48
Transactions(5) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(5).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 22)
Transactions(5).ProcessedBy = 94852
Transactions(5).ProcessedFor = "92-318284-75"
Transactions(5).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Withdrawal
Transactions(5).WithdrawalAmount = 214.86
Transactions(6) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(6).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 22)
Transactions(6).ProcessedBy = 85285
Transactions(6).ProcessedFor = "62-384638-48"
Transactions(6).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Withdrawal
Transactions(6).WithdrawalAmount = 140.0
Transactions(7) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(7).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 24)
Transactions(7).ProcessedBy = 85285
Transactions(7).ProcessedFor = "95-722947-93"
Transactions(7).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MoneyOrder
Transactions(7).WithdrawalAmount = 116.24
Transactions(8) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(8).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 24)
Transactions(8).ProcessedFor = "95-722947-93"
Transactions(8).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.TransactionFee
Transactions(8).ChargeAmount = 1.45
Transactions(9) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(9).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 30)
Transactions(9).ProcessedBy = 70594
Transactions(9).ProcessedFor = "62-384638-48"
Transactions(9).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Withdrawal
Transactions(9).WithdrawalAmount = 40.0
Transactions(10) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(10).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 30)
Transactions(10).ProcessedFor = "95-722947-93"
Transactions(10).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MonthlyCharge
Transactions(10).ChargeAmount = 6.0
Transactions(11) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(11).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 30)
Transactions(11).ProcessedFor = "92-318284-75"
Transactions(11).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MonthlyCharge
Transactions(11).ChargeAmount = 6.0
Transactions(12) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(12).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 1, 30)
Transactions(12).ProcessedFor = "62-384638-48"
Transactions(12).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MonthlyCharge
Transactions(12).ChargeAmount = 6.0
Transactions(13) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(13).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 2, 6)
Transactions(13).ProcessedBy = 85285
Transactions(13).ProcessedFor = "92-318284-75"
Transactions(13).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Withdrawal
Transactions(13).WithdrawalAmount = 42.35
Transactions(14) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(14).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 2, 6)
Transactions(14).ProcessedBy = 70594
Transactions(14).ProcessedFor = "95-722947-93"
Transactions(14).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Withdrawal
Transactions(14).WithdrawalAmount = 115.0
Transactions(15) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(15).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 2, 6)
Transactions(15).ProcessedBy = 94852
Transactions(15).ProcessedFor = "62-384638-48"
Transactions(15).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Withdrawal
Transactions(15).WithdrawalAmount = 64.14
Transactions(16) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(16).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 2, 28)
Transactions(16).ProcessedFor = "95-722947-93"
Transactions(16).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MonthlyCharge
Transactions(16).ChargeAmount = 6.0
Transactions(17) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(17).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 2, 28)
Transactions(17).ProcessedFor = "95-722947-93"
Transactions(17).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Overdraft
Transactions(17).WithdrawalAmount = 35.0
Transactions(18) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(18).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 2, 28)
Transactions(18).ProcessedFor = "62-384638-48"
Transactions(18).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MonthlyCharge
Transactions(18).ChargeAmount = 6.0
Transactions(19) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(19).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 2, 28)
Transactions(19).ProcessedFor = "92-318284-75"
Transactions(19).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MonthlyCharge
Transactions(19).ChargeAmount = 6.0
Transactions(20) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(20).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 3, 15)
Transactions(20).ProcessedBy = 70594
Transactions(20).ProcessedFor = "95-722947-93"
Transactions(20).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Withdrawal
Transactions(20).WithdrawalAmount = 200.0
Transactions(21) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(21).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 3, 26)
Transactions(21).ProcessedBy = 39850
Transactions(21).ProcessedFor = "17-490040-83"
Transactions(21).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Deposit
Transactions(21).DepositAmount = 1000.0
Transactions(22) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(22).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 4, 4)
Transactions(22).ProcessedBy = 74228
Transactions(22).ProcessedFor = "58-405048-15"
Transactions(22).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Deposit
Transactions(22).DepositAmount = 126.85
Transactions(23) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(23).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 4, 6)
Transactions(23).ProcessedBy = 85285
Transactions(23).ProcessedFor = "92-318284-75"
Transactions(23).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Deposit
Transactions(23).DepositAmount = 250.0
Transactions(24) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(24).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 4, 6)
Transactions(24).ProcessedBy = 70594
Transactions(24).ProcessedFor = "62-384638-48"
Transactions(24).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Deposit
Transactions(24).DepositAmount = 400.0
Transactions(25) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(25).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 4, 12)
Transactions(25).ProcessedBy = 94852
Transactions(25).ProcessedFor = "95-722947-93"
Transactions(25).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.Deposit
Transactions(25).DepositAmount = 100.0
Transactions(25) = New AccountTransaction()
Transactions(25).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 4, 30)
Transactions(25).ProcessedFor = "58-405048-15"
Transactions(25).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MonthlyCharge
Transactions(25).ChargeAmount = 6.0
Transactions(26) = New AccountTransaction
Transactions(26).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 4, 30)
Transactions(26).ProcessedFor = "62-384638-48"
Transactions(26).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MonthlyCharge
Transactions(26).ChargeAmount = 6.0
Transactions(27) = New AccountTransaction()
Transactions(27).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 4, 30)
Transactions(27).ProcessedFor = "92-318284-75"
Transactions(27).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MonthlyCharge
Transactions(27).ChargeAmount = 6.0
Transactions(28) = New AccountTransaction()
Transactions(28).TransactionDate = New DateTime(2007, 4, 30)
Transactions(28).ProcessedFor = "17-490040-83"
Transactions(28).TransactionType = TransactionTypes.MonthlyCharge
Transactions(28).ChargeAmount = 6.0
Return Transactions
End Function
End Class
|
- Access the Central form and a button to it
- Change the properties of the button as follows:
(Name): btnEmployees
Text: Employees
- Double-click the Employees button and implement its event as follows:
Private Sub btnEmployees_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnEmployees.Click
Dim i As Integer
Dim frmEmployees As Employees = New Employees
Dim StaffMembers() As Employee = AccountsRecords.GetEmployees()
frmEmployees.lvwEmployees.Items.Clear()
i = 1
For Each empl As Employee In StaffMembers
Dim lviEmployee As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(i)
lviEmployee.SubItems.Add(CStr(empl.EmployeeNumber))
lviEmployee.SubItems.Add(empl.FirstName)
lviEmployee.SubItems.Add(empl.LastName)
lviEmployee.SubItems.Add(empl.FullName)
lviEmployee.SubItems.Add(empl.Title)
lviEmployee.SubItems.Add(empl.HourlySalary.ToString("F"))
frmEmployees.lvwEmployees.Items.Add(lviEmployee)
i = i + 1
Next
frmEmployees.ShowDialog()
End Sub
|
- Return to the Central form and a button to it
- Change the properties of the button as follows:
(Name): btnCustomers
Text: Customers
- Double-click the Employees button and implement its event as follows:
Private Sub btnCustomers_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnCustomers.Click
Dim i As Integer
Dim frmCustomers As Customers = New Customers
Dim Clients() As Customer = AccountsRecords.GetCustomers()
frmCustomers.lvwCustomers.Items.Clear()
i = 1
For Each client As Customer In Clients
Dim lviCustomer As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(i)
lviCustomer.SubItems.Add(client.CreatedBy)
lviCustomer.SubItems.Add(client.DateCreated.ToShortDateString())
lviCustomer.SubItems.Add(client.CustomerName)
lviCustomer.SubItems.Add(client.AccountNumber)
lviCustomer.SubItems.Add(client.AccountType)
lviCustomer.SubItems.Add(client.Status.ToString())
frmCustomers.lvwCustomers.Items.Add(lviCustomer)
i = i + 1
Next
frmCustomers.ShowDialog()
End Sub
|
- Return to the Central form and a button to it
- Change the properties of the button as follows:
(Name): btnTransactions
Text: Transactions
- Double-click the Employees button and implement its event as follows:
Private Sub btnTransactions_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnTransactions.Click
Dim i As Integer
Dim frmTransactions As CustomersTransactions = _
New CustomersTransactions
Dim Transactions() As AccountTransaction = _
AccountsRecords.GetTransactions()
frmTransactions.lvwTransactions.Items.Clear()
i = 1
For Each ActTrans As AccountTransaction In Transactions
Dim lviTransactions As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(i)
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add( _
ActTrans.TransactionDate.ToString("dd-MMM-yyyy"))
If ActTrans.ProcessedBy = 0 Then
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add("")
Else
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add(ActTrans.ProcessedBy)
End If
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add(ActTrans.ProcessedFor)
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add(ActTrans.TransactionType.ToString())
If ActTrans.DepositAmount = 0 Then
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add("")
Else
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add( _
ActTrans.DepositAmount.ToString("F"))
End If
If ActTrans.WithdrawalAmount = 0 Then
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add("")
Else
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add( _
ActTrans.WithdrawalAmount.ToString("F"))
End If
If ActTrans.ChargeAmount = 0 Then
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add("")
Else
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add( _
ActTrans.ChargeAmount.ToString("F"))
End If
frmTransactions.lvwTransactions.Items.Add(lviTransactions)
i = i + 1
Next
frmTransactions.ShowDialog()
End Sub
|
- Execute the application to see the results
- Close the forms and return to your programming environment
Because an array is primarily a series of objects or
values, there are various pieces of information you would get interested to get
from it. Typical operations include:
- Adding elements to the array
- Re-arranging the list or the order of elements in the array.
- Finding out whether the array contains a certain element
- If the array contains a certain element, what index that element has
Although you can write your own routines to perform these
operations, the Array class provides most of the methods you would need to get
the necessary information.
|
 Practical
Learning: Introducing Operations on Arrays Practical
Learning: Introducing Operations on Arrays
|
|
- To create a new form, on the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows
Form
- Set the name to CustomerTransactions and press Enter
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Other Properties |
| Label |
 |
View Transactions For: |
|
|
| MaskedTextBox |
 |
|
txtAccountNumber |
Mask: 00-000000-00 |
| Button |
 |
Find |
btnFind |
|
| ListView |
 |
|
lvwCustomers |
FullRowSelect: True
GridLines: True
View: Details |
| Columns |
| (Name) |
Text |
TextAlign |
Width |
| colIndex |
# |
|
25 |
| colTransactionDate |
Trans Date |
Center |
80 |
| colProcessedBy |
Processed By |
Center |
80 |
| colTransactionType |
Trans Type |
|
90 |
| colDeposit |
Deposit |
Right |
|
| colWithdrawal |
Withdrawal |
Right |
65 |
| colChargeAmount |
Charge |
Right |
50 |
|
| Button |
 |
Close |
btnClose |
|
|
- Save all
|
Adding an Element to an Array |
|
We have seen that, using the () operator, you can add a new
element to an array. Still, to support this operation, the Array class is
equipped with the SetValue() method that is overloaded with various
versions. Here is an example that adds an element to the third position of the
array:
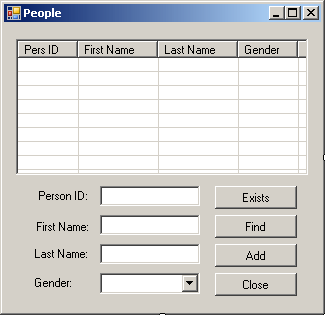
Public Class Exercise
Dim People(7) As Person
Private Sub ArrayInitializer()
For i As Integer = 0 To 7
People(i) = New Person
People(i).PersonID = 0
People(i).FirstName = ""
People(i).LastName = ""
People(i).Gender = "Unknown"
Next
End Sub
Private Sub ShowPeople()
lvwPeople.Items.Clear()
For Each Pers As Person In People
Dim lviPerson As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(Pers.FirstName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(Pers.LastName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(Pers.Gender)
lvwPeople.Items.Add(lviPerson)
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
ArrayInitializer()
ShowPeople()
End Sub
Private Sub btnAdd_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnAdd.Click
Dim pers As Person = New Person
pers.PersonID = CInt(txtPersonID.Text)
pers.FirstName = txtFirstName.Text
pers.LastName = txtLastName.Text
pers.Gender = cbxGenders.Text
People.SetValue(pers, 2)
ShowPeople()
End Sub
End Class
When the Array.SetValue() method is called, it
replaces the element at the indicated position.
|
Getting an Element From an Array |
|
The reverse of adding an item to an array is to retrieve
one. To support this operation, the Array
class is equipped with the GetValue() method that comes in various
versions. Here is an example of calling it:
Public Class Exercise
Dim People(7) As Person
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
People(0) = New Person(72947, "Paulette", _
"Cranston", "Female")
People(1) = New Person(70854, "Harry", _
"Kumar", "Male")
People(2) = New Person(27947, "Jules", _
"Davidson", "Male")
People(3) = New Person(62835, "Leslie", _
"Harrington", "Unknown")
People(4) = New Person(92958, "Ernest", _
"Colson", "Male")
People(5) = New Person(91749, "Patricia", _
"Katts", "Female")
People(6) = New Person(29749, "Patrice", _
"Abanda", "Unknown")
People(7) = New Person(24739, "Frank", _
"Thomasson", "Male")
For i As Integer = 0 To People.Length - 1
Dim lviPerson As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(People(i).FirstName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).LastName)
lviPerson.SubItems.Add(People(i).Gender)
lvwPeople.Items.Add(lviPerson)
Next
End Sub
Private Sub lvwPeople_ItemSelectionChanged(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.ListViewItemSelectionChangedEventArgs) _
Handles lvwPeople.ItemSelectionChanged
Dim pers As Person = CType(People.GetValue(e.ItemIndex), Person)
txtPersonID.Text = pers.PersonID
txtFirstName.Text = pers.FirstName
txtLastName.Text = pers.LastName
cbxGenders.Text = pers.Gender
End Sub
End Class
When calling this method, make sure you provide a valid
index, if you do not, you would get an IndexOutOfRangeException
exception.
|
Checking the Existence of an Element |
|
Once some elements have been added to an array, you can try
to locate one. One of the most fundamental means of looking for an item consists
of finding out whether a certain element exists in the array. To support this
operation, the Array class is equipped with the Exists() method whose
syntax is:
Public Shared Function Exists(Of T) ( _
array As T(), _
match As Predicate(Of T) _
) As Boolean
This is a generic method that takes two arguments. The first
is the array on which you will look for the item. The second argument is a
delegate that specifies the criterion to apply. Here is an example:
Public Class Exercise
Dim People(7) As Person
Shared IDToFind As Integer
Private Sub Exercise_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
. . . No Change
End Sub
Private Shared Function IDExists(ByVal p As Person) As Boolean
If p.PersonID = IDToFind Then
Return True
Else
Return False
End If
End Function
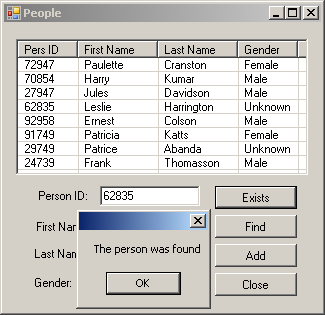
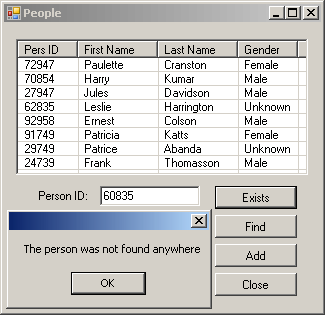
Private Sub btnExists_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnExists.Click
IDToFind = CInt(txtPersonID.Text)
If Array.Exists(People, AddressOf IDExists) Then
MessageBox.Show("The person was found")
Else
MessageBox.Show("The person was not found anywhere")
End If
End Sub
End Class
|
 Practical
Learning: Checking the Existence of an Element Practical
Learning: Checking the Existence of an Element
|
|
- On the Account Transactions form, double-click the Find button and change
the file as follows:
Public Class CustomerTransactions
Shared AccountNumber As String
Private Shared Function AccountNumberExists(ByVal Client As Customer) _
As Boolean
If Client.AccountNumber = AccountNumber Then
Return True
Else
Return False
End If
End Function
Private Sub btnFind_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnFind.Click
AccountNumber = txtAccountNumber.Text
Dim Accounts() As Customer = AccountsRecords.GetCustomers()
If Array.Exists(Accounts, AddressOf AccountNumberExists) Then
MsgBox("Good")
Else
MsgBox("There is no customer with that account number")
End If
End Sub
End Class
|
- Display the Central form and complete its design as follows:
 |
| Button |
Text |
Name |
 |
Employees |
btnEmployees |
 |
Customers |
btnCustomers |
 |
Transactions |
btnTransactions |
 |
Customer Records |
btnCustomerRecords |
 |
Close |
btnClose |
|
- Double-click the Customer Records button and implement its event as
follows:
Private Sub btnCustomerRecords_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnCustomerRecords.Click
Dim CustRecords As CustomerTransactions = New CustomerTransactions
CustRecords.ShowDialog()
End Sub
|
- Return to the Central form and double-click the Close button
- Implement its event as follows:
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnClose.Click
End
End Sub
|
- Execute the application to test it
- Close the forms and return to your programming environment
One of the most valuable operations you can perform on an
array consists of looking for a particular element. To assist you with this, the
Array class is equipped with the Find() method. Its syntax is:
Public Shared Function Find(Of T) ( _
array As T(), _
match As Predicate(Of T) _
) As T
This generic method takes two arguments. The first argument
is the name of the array that holds the elements. The second argument is a
delegate that has the criterion to be used to find the element. Here is an
example:
Private Sub btnFind_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnFind.Click
IDToFind = CInt(txtPersonID.Text)
Dim pers As Person = Array.Find(People, AddressOf IDExists)
If Not pers Is Nothing Then
txtFirstName.Text = pers.FirstName
txtLastName.Text = pers.LastName
cbxGenders.Text = pers.Gender
End If
End Sub
|
 Practical
Learning: Finding an Element Practical
Learning: Finding an Element
|
|
- Access the CustomerTransactions.cs source code and change the Click event
of the Find button as follows:
Private Sub btnFind_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnFind.Click
' AccountNumber = txtAccountNumber.Text
' Dim Accounts() As Customer = AccountsRecords.GetCustomers()
' If Array.Exists(Accounts, AddressOf AccountNumberExists) Then
' MsgBox("Good")
' Else
' MsgBox("There is no customer with that account number")
' End If
Dim TotalDeposits As Double = 0
Dim TotalWithdrawals As Double = 0
Dim TotalCharges As Double = 0
Dim Balance As Double
AccountNumber = txtAccountNumber.Text
Dim Accounts() As Customer = AccountsRecords.GetCustomers()
Dim Trans() As AccountTransaction = _
AccountsRecords.GetTransactions()
Dim AccountFound As Boolean = _
Array.Exists(Accounts, AddressOf AccountNumberExists)
If AccountFound = True Then
Dim i As Integer = 1
lvwTransactions.Items.Clear()
For Each ActTrans As AccountTransaction In Trans
If ActTrans.ProcessedFor = AccountNumber Then
Dim lviTransactions As ListViewItem = New ListViewItem(i)
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add( _
ActTrans.TransactionDate.ToString("dd-MMM-yyyy"))
If ActTrans.ProcessedBy = 0 Then
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add("")
Else
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add(ActTrans.ProcessedBy)
End If
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add( _
ActTrans.TransactionType.ToString())
If ActTrans.DepositAmount = 0 Then
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add("")
Else
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add( _
ActTrans.DepositAmount.ToString("F"))
End If
If ActTrans.WithdrawalAmount = 0 Then
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add("")
Else
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add( _
ActTrans.WithdrawalAmount.ToString("F"))
End If
If ActTrans.ChargeAmount = 0 Then
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add("")
Else
lviTransactions.SubItems.Add( _
ActTrans.ChargeAmount.ToString("F"))
End If
lvwTransactions.Items.Add(lviTransactions)
i = i + 1
End If
Next
For Each lviTransaction As ListViewItem In lvwTransactions.Items
If lviTransaction.SubItems(4).Text <> "" Then
TotalDeposits = TotalDeposits + _
CDbl(lviTransaction.SubItems(4).Text)
End If
If lviTransaction.SubItems(5).Text <> "" Then
TotalWithdrawals = TotalWithdrawals + _
CDbl(lviTransaction.SubItems(5).Text)
End If
If lviTransaction.SubItems(6).Text <> "" Then
TotalCharges = TotalCharges + _
CDbl(lviTransaction.SubItems(6).Text)
End If
Next
Balance = TotalDeposits - (TotalWithdrawals + TotalCharges)
txtTotalDeposits.Text = FormatNumber(TotalDeposits)
txtTotalWithdrawals.Text = FormatNumber(TotalWithdrawals)
txtTotalCharges.Text = FormatNumber(TotalCharges)
txtBalance.Text = FormatNumber(Balance)
Else
MessageBox.Show("There is no customer with that account number")
End If
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnClose
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as follows:
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnClose.Click
Close()
End Sub
|
- Execute the application to test it
|
|

