|
The similarities of both types are:
- A directory or a file can be created. One of the restrictions is that
two files cannot have the same name inside of the same directory. Two
directories cannot have the same name inside of the same parent directory.
- A directory or a file can be renamed. If a directory is renamed, the
"path" of its file(s) changes
- A directory or a file can be deleted. If a directory is deleted, its
files are deleted also
- A directory or a file can be moved. If a directory moves, it "carries"
all of its files to the new location
- A directory or a file can be copied. A file can be copied from one
directory to another. If a directory is copied to a new location, all of its
files are also copied to the new location
|
 Practical
Learning: Introducing Directories Practical
Learning: Introducing Directories
|
|
- Create a new Windows Application, named WattsALoan2
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click Form1.vb and click Rename
- Type WattsALoan.vb and press Enter
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Name |
Text |
| Label |
|
If this is a new loan, enter a new account
number and the name of the customer who is requesting the
loan |
| Label |
|
To open a previously prepared loan, enter
its account number and press Tab |
| Label |
|
Acnt #: |
| Label |
|
Customer Name: |
| Label |
|
Customer: |
| TextBox |
txtAccountNumber |
|
| TextBox |
txtCustomerName |
|
| Label |
|
Empl #: |
| Label |
|
Employee Name: |
| Label |
|
Prepared By: |
| TextBox |
txtEmployeeNumber |
|
| TextBox |
txtEmployeeName |
|
| Button |
btnNewEmployee |
|
| Button |
btnNewCustomer |
|
| Label |
|
Loan Amount: |
| TextBox |
txtLoanAmount |
|
| Label |
|
Interest Rate: |
| TextBox |
txtInterestRate |
|
| Label |
|
% |
| Label |
|
Periods |
| TextBox |
|
txtPeriods |
| Button |
btnCalculate |
Calculate |
| Label |
|
Monthly Payment: |
| TextBox |
txtMonthlyPayment |
|
| Button |
btnClose |
Close |
|
- Double-click the Calculate button and implement its event as follows:
Imports System.IO
Public Class WattsALoan
Private Sub btnCalculate_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnCalculate.Click
Dim LoanAmount As Double
Dim InterestRate As Double
Dim Periods As Double
Dim MonthlyPayment As Double
Try
LoanAmount = CDbl(txtLoanAmount.Text)
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Invalid Loan Amount")
End Try
Try
InterestRate = CDbl(txtInterestRate.Text)
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Invalid Interest Rate")
End Try
Try
Periods = CDbl(txtPeriods.Text)
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox("Invalid Periods Value")
End Try
MonthlyPayment = Pmt(InterestRate / 12 / 100, _
Periods, -LoanAmount, 0, _
DueDate.BegOfPeriod)
txtMonthlyPayment.Text = FormatCurrency(MonthlyPayment)
End Sub
End Class
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnClose
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnClose.Click
End
End Sub
|
- To create a new form, on the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows
Form...
- In the Templates list, make sure Windows Form is selected.
Set the Name to NewEmployee and click Add
- Design the form as follows:
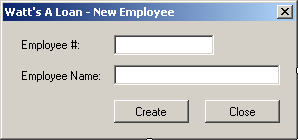 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
| Label |
Employee #: |
|
| TextBox |
|
txtEmployeeNumber |
| Label |
Employee Name: |
|
| TextBox |
|
txtEmployeeName |
| Button |
Create |
btnCreate |
| Button |
Close |
btnClose |
|
- Double-click the Close button
- Implement the event as follows:
Imports System.IO
Public Class NewEmployee
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnClose.Click
Close()
End Sub
End Class
|
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click WattsALoan.vb and click View Code
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnNewEmployee
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub btnNewEmployee_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnNewEmployee.Click
Dim FormEmployee As NewEmployee = New NewEmployee()
FormEmployee.ShowDialog()
End Sub
|
- Save the file
Before using a directory, you must first have it. You can
use an existing directory if the operating system or someone else had already
created one. You can also create a new directory. Directories are created and
managed by various classes but the fundamental class is called Directory.
Directory is a static class. All of its methods are static, which means
you will never need to declare an instance of the Directory class in
order to use it.
Besides the Directory class, additional operations of
folders and sub-folders can be performed using the DirectoryInfo class.
To create a directory, you can call the CreateDirectory()
method of the Directory class. This method is available in two versions.
One of the versions uses the following syntax:
Public Shared Function CreateDirectory(path As String) As DirectoryInfo
This method takes as argument the (complete) path of the
desired directory. Here is an example:
E:\Programs\Business Orders\Customer Information
When this method is called:
- It first checks the parent drive, in this case E.
If the drive doesn't exist, because this method cannot create a drive, the
compiler would throw a DirectoryNotFoundException exception
- If the drive (in this case E) exists, the compiler moves to the first
directory part of the path; in this case this would be the Programs folder
in the E drive.
If the folder doesn't exist, the compiler would create it. If that first
director doesn't exist, this means that the other directory(ies), if any,
under the first don't exist. So, the compiler would create it/them
- If the first directory exists and if there is no other directory under
that directory, the compiler would stop and would not do anything further.
- If the directory exists and there is a sub-directory specified under it,
the compiler would check the existence of that directory.
If the sub-directory exists, the compiler would not do anything further and
would stop.
If the sub-directory doesn't exist, the compiler would create it
- The compiler would repeat step 4 until the end of the specified path
The Directory.CreateDirectory() method returns a
DirectoryInfo object that you can use as you see fit.
|
 Practical
Learning: Creating a Directory Practical
Learning: Creating a Directory
|
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select (WattsALoan Events)
- In the Method Name combo box, select Load and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub WattsALoan_Load(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles Me.Load
Dim Folder As String
Dim EmployeeWriter As StreamWriter
Dim Filename As String = "Employees.wal"
Dim EmployeeInformation As FileInfo = _
My.Computer.FileSystem.GetFileInfo(Filename)
Folder = "C:\Watts A Loan"
If Not Directory.Exists(Folder) Then
Directory.CreateDirectory(Folder)
Dim strFilename As String = Folder & "\Employees.wal"
Dim fiEmployees As FileInfo = New FileInfo(strFilename)
' If the employees file was not created already,
' then create it
If Not EmployeeInformation.Exists Then
EmployeeWriter = EmployeeInformation.CreateText()
' And create a John Doe employee
Try
EmployeeWriter.WriteLine("00-000")
EmployeeWriter.WriteLine("John Doe")
Finally
EmployeeWriter.Close()
End Try
End If
End If
End Sub
|
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click NewEmployee and click View Code
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnCreate
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub btnCreate_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnCreate.Click
Dim Filename As String = "C:\Watts A Loan\Employees.wal"
Dim EmployeeInformation As FileInfo
Dim EmployeeWriter As StreamWriter
EmployeeInformation = My.Computer.FileSystem.GetFileInfo(Filename)
' Normally, we should have the file already but just in case...
If Not EmployeeInformation.Exists Then
EmployeeWriter = EmployeeInformation.CreateText()
Else ' If the file exists already, then we will only add to it
EmployeeWriter = EmployeeInformation.AppendText()
End If
Try
EmployeeWriter.WriteLine(txtEmployeeNumber.Text)
EmployeeWriter.WriteLine(txtEmployeeName.Text)
Finally
EmployeeWriter.Close()
End Try
txtEmployeeNumber.Text = ""
txtEmployeeName.Text = ""
txtEmployeeNumber.Focus()
End Sub
|
- Click the WattsALoan.vb [Design] tab
|
Checking for a Directory Existence
|
|
Before using or creating a directory, you can first check if
it exists. This is because, if a directory already exists in the location where
you want to create it, you would be prevented from creating one with the same
name. In the same way, if you just decide to directly use a directory that
doesn't exist, the operation you want to perform may fail because the directory
would not be found.
To check whether a directory exists or not, you can call the
Directory.Exists() Boolean static method. Its syntax is:
Public Shared Function Exists(path As String) As Boolean
This method receives the (complete) path of the directory.
If the path exists, the method returns true. If the directory doesn't exist, the
method returns false.
One of the most routine operations performed in a directory
consists of looking for a file. Microsoft Windows operating systems and the
user's intuition have different ways of addressing this issue. The .NET
Framework also provides its own means of performing this operation, through
various techniques. You can start by checking the sub-directories and files
inside of a main directory.
To look for files in a directory, the DirectoryInfo
class can assist you with its GetFiles() method, which is overloaded with
three versions.
|
 Practical
Learning: Using Directories and Files Practical
Learning: Using Directories and Files
|
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtAccountNumber
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub txtAccountNumber_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtAccountNumber.Leave
Dim Filename As String
Dim LoanPath As String
Dim FileFullname As String
Dim ListOfLoans() As FileInfo
Dim LoanReader As StreamReader
Dim LoanFolder As DirectoryInfo
Dim LoanInformation As FileInfo
Dim Found As Boolean
Found = False
LoanPath = "C:\Watts A Loan"
LoanFolder = New DirectoryInfo(LoanPath)
ListOfLoans = LoanFolder.GetFiles("*", _
SearchOption.AllDirectories)
Filename = txtAccountNumber.Text & ".wal"
FileFullname = LoanPath & "none.wal"
For Each fle As FileInfo In ListOfLoans
If fle.Name = Filename Then
Found = True
FileFullname = fle.FullName
End If
Next
If Found = True Then
LoanInformation = My.Computer.FileSystem.GetFileInfo(Filename)
LoanReader = LoanInformation.OpenText
Try
txtAccountNumber.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtCustomerName.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtEmployeeNumber.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtEmployeeName.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtLoanAmount.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtInterestRate.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtPeriods.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtMonthlyPayment.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
Finally
LoanReader.Close()
End Try
End If
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtEmployeeNumber
- In the Method Name combo box, select click Leave and implement the event
as follows:
Private Sub txtAccountNumber_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtAccountNumber.Leave
Dim Filename As String
Dim LoanPath As String
Dim FileFullname As String
Dim ListOfLoans() As FileInfo
Dim LoanReader As StreamReader
Dim LoanFolder As DirectoryInfo
Dim LoanInformation As FileInfo
Dim Found As Boolean
Found = False
LoanPath = "C:\Watts A Loan"
LoanFolder = New DirectoryInfo(LoanPath)
ListOfLoans = LoanFolder.GetFiles("*", _
SearchOption.AllDirectories)
Filename = txtAccountNumber.Text & ".wal"
FileFullname = LoanPath & "none.wal"
For Each fle As FileInfo In ListOfLoans
If fle.Name = Filename Then
Found = True
FileFullname = fle.FullName
End If
Next
If Found = True Then
LoanInformation = My.Computer.FileSystem.GetFileInfo(FileFullname)
MsgBox(LoanInformation.FullName)
LoanReader = LoanInformation.OpenText
Try
txtAccountNumber.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtCustomerName.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtEmployeeNumber.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtEmployeeName.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtLoanAmount.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtInterestRate.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtPeriods.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
txtMonthlyPayment.Text = LoanReader.ReadLine
Finally
LoanReader.Close()
End Try
End If
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select btn Save
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement the event as
follows:
Private Sub btnSave_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnSave.Click
Dim LoanPath As String
Dim LoanWriter As StreamWriter
LoanPath = "C:\Watts A Loan\" & txtAccountNumber.Text & ".wal"
LoanWriter = My.Computer.FileSystem.OpenTextFileWriter(LoanPath, False)
Try
LoanWriter.WriteLine(txtAccountNumber.Text)
LoanWriter.WriteLine(txtCustomerName.Text)
LoanWriter.WriteLine(txtEmployeeNumber.Text)
LoanWriter.WriteLine(txtEmployeeName.Text)
LoanWriter.WriteLine(txtLoanAmount.Text)
LoanWriter.WriteLine(txtInterestRate.Text)
LoanWriter.WriteLine(txtPeriods.Text)
LoanWriter.WriteLine(txtMonthlyPayment.Text)
txtAccountNumber.Text = ""
txtCustomerName.Text = ""
txtEmployeeNumber.Text = ""
txtEmployeeName.Text = ""
txtLoanAmount.Text = ""
txtInterestRate.Text = ""
txtPeriods.Text = ""
txtMonthlyPayment.Text = ""
txtAccountNumber.Focus()
Finally
LoanWriter.Close()
End Try
End Sub
|
- Execute the application to test it
- First create a few employees as follows:
| Employee # |
Employee Name |
| 42-806 |
Patricia Katts |
| 75-148 |
Helene Mukoko |
| 36-222 |
Frank Leandro |
| 42-808 |
Gertrude Monay |
- Process a few loans
- Close the application
|
|

