|
Using the Microsoft Access Object Library |
|
 |
The Microsoft Access Object Library is automatically
available when you start a new database or if you open an existing database. To
check its existence, on the main menu of Microsoft Visual Basic, you can click
Tools -> References... In the Available References list of the References
dialog box, you can see that the Microsoft Access Object Library is checked:
|
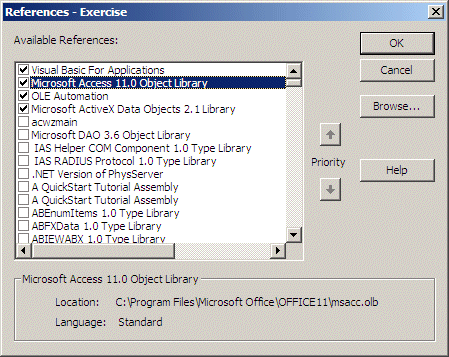
You should not attempt to remove this library.
|
Microsoft Data Access Objects |
|
As introduced in the first lesson, Microsoft Data
Access Objects is a library
published by Microsoft used to create and manage
databases. In previous versions of Microsoft Access, this library was
automatically available. Starting with Microsoft Access 2000, this library
is not loaded by default anymore. If you want to use, you must remember to
"load" it.
Before using DAO, you can first check whether it is
available for your database. If it is not, you can add it. To check it,
from the Microsoft Visual Basic main menu, click Tools -> References...
In the References dialog box, if the check box of the Microsoft DAO item
is not checked, this would indicate that the library is not available for
your database:

If you want to use it, click the Microsoft DAO 3.6
Object Library check box and click OK.
|
Database Creation With DAO |
|
|
In previous lessons, we demonstrated that Microsoft
Access relied on objects and collections. Based on this, the objects used
in DAO are stored in various collections. The main object of the DAO
library is called DAO. The first object of DAO is called DBEngine.
Its main purpose is to give access to the other objects of DAO. For example, to support
the creation of a database, the DBEngne object is equipped with the
CreateDatabase() method. Its syntax is:
|
 |
DBEngine.CreateDatabase(name, locale, options)
Because the DBEngine object is already
recognized in the current database, you can omit it when calling the CreateDatabase()
method.
The first argument can be the name of the database you
want to create. If you provide only the name of the database, it would be
created in the same folder where the action was initiated. For example, if
you are working in a database already and create a new database by
providing a name, the new database would be created in the same folder
where the current database resides. Here is an example:
Private Sub cmdCreate_Click()
CreateDatabase("Exercise.mdb", ...)
End Sub
If you want, you can store the new database in a drive
and folder of your choice. To do this, provide the complete path and the
name of the database as the first argument. This would be done as follows:
Private Sub cmdCreate_Click()
CreateDatabase("C:\Microsoft Access Database Development\Exercise.mdb", ...)
End Sub
The second argument to this method is required and it
specifies the language used for the database. This is also referred to as
the collation. This argument is passed as a constant named value and can
be one of the following:
| Constant |
Language
Group |
| dbLangGeneral |
English, German, French, Portuguese, Italian, and Modern Spanish |
| dbLangArabic |
Arabic |
| dbLangCyrillic |
Russian |
| dbLangCzech |
Czech |
| dbLangDutch |
Dutch |
| dbLangGreek |
Greek |
| dbLangHebrew |
Hebrew |
| dbLangHungarian |
Hungarian |
| dbLangIcelandic |
Icelandic |
| dbLangNordic |
Nordic languages (Microsoft Jet database engine version 1.0 only) |
| dbLangNorwdan |
Norwegian and Danish |
| dbLangPolish |
Polish |
| dbLangSpanish |
Traditional Spanish |
| dbLangSwedfin |
Swedish and Finnish |
| dbLangTurkish |
Turkish |
Here is an example:
Private Sub cmdCreate_Click()
CreateDatabase("Exercise.mdb", dbLangGreek)
End Sub
The third argument of the DBEngine.CreateDatabase()
method is used to pass some options to use when creating the database.
This optional argument can be a constant specified as dbEncrypt, if
you want the database to be encrypted. If you don't pass this constant,
the database would not be encrypted. If you want to
specify the version of Microsoft Jet used in the new database, the options
argument can be one of the following values: dbVersion10, dbVersion11,
dbVersion20, or dbVersion30. If you don't specify one of
these values, the dbVersion30 would be used. If
you want the database to be encrypted and you want to specify the version
of Microsoft Jet used in the new database, combine the dbEncrypt
constant with one of the version values.
|
|
The Database Object of DAO |
|
When the
CreateDatabase() method has finished, it returns a reference to the
database that was created. In fact, you must obtain this reference. The
database is recognized as the Database object of DAO. To get it,
first declare a variable of type Database. Here is an example:
Private Sub cmdGetReferenceToDAO_Click()
Dim db As DAO.Database
End Sub
Because the DAO object is implied, you can omit it in
your declaration and simply use the Database object as type. To get a
reference to the new database, use the SET operator and assign the
returned value of the method to your Database variable. Here is an
example that creates a new database named Exercise.mdb in the current folder:
Private Sub cmdCreate_Click()
Dim db As DAO.Database
Set db = CreateDatabase("Exercise.mdb", dbLangGeneral)
End Sub
|
 Practical
Learning: Creating a Database Using DAO Practical
Learning: Creating a Database Using DAO
|
|
- Start Microsoft Access and, from the resources that accompany this site, open the
Exercise1 database
- On the main menu of Microsoft Access, click Tools -> Macro -> Visual
Basic Editor
- On the main menu of Microsoft Visual Basic, click Tools ->
References...
- In the References dialog box, locate your latest Microsoft DAO Object
Library version and click the check box to its left
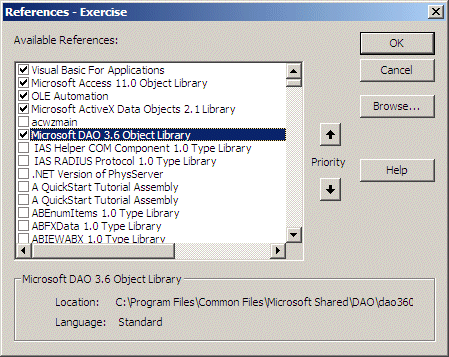
- Click OK
|
|