|

As reviewed in the previous lesson, a data adapter allows
you to retrieve records from a database and make them available to your Windows
Forms Application. To make reading data of a database a little faster, the .NET
Framework provides a class used to read data from a database. For s SQL Server
database, this class is called SqlDataReader
|
 Practical
Learning: Introducing the Data Reader
Practical
Learning: Introducing the Data Reader
|
|
- Start Microsoft Visual Studio .NET or Visual Basic .NET
- Display the Server Explorer. Expand the Servers node, followed by the name
of the computer, followed by SQL Servers, followed by the name of the server
- Right-click the server and click New Database
- Set the New Database Name to CPAS and accept to use Windows NT
Integrated Security
- Click OK
- Under the name of the server in Server Explorer, expand the GCS node
- Right-click the Tables node and click New Table
- Create the table with the following columns (change only the indicated
information; anything that is not mentioned should be ignored and use the
default):
| Column Name |
Data Type |
Length |
Allow Nulls |
Other Properties |
| RepairOrderID |
int |
|
|
Primary Key
Identity: Yes |
| OrderDate |
datetime |
|
Unchecked |
|
| OrderTime |
datetime |
20 |
Unchecked |
|
| CustomerName |
varchar |
|
Unchecked |
|
| Address |
varchar |
|
|
|
| City |
varchar |
|
|
|
| State |
char |
2 |
|
|
| ZIPCode |
varchar |
10 |
|
|
| Make |
varchar |
20 |
Unchecked |
|
| Model |
varchar |
32 |
Unchecked |
|
| CarYear |
smallint |
5 |
Unchecked |
|
| ProblemDescription |
text |
|
Unchecked |
|
| PartName1 |
varchar |
|
|
|
| UnitPrice1 |
decimal |
10 |
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| Quantity1 |
tinyint |
3 |
|
Default Value: 0 |
| SubTotal1 |
decimal |
10 |
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| PartName2 |
varchar |
|
|
|
| UnitPrice2 |
decimal |
10 |
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| Quantity2 |
tinyint |
3 |
|
Default Value: 0 |
| SubTotal2 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| PartName3 |
varchar |
|
|
|
| UnitPrice3 |
decimal |
|
|
Scale: 2 |
| Quantity3 |
tinyint |
|
|
Default Value: 0 |
| SubTotal3 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| PartName4 |
varchar |
|
|
|
| UnitPrice4 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| Quantity4 |
tinyint |
|
|
Default Value: 0 |
| SubTotal4 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| PartName5 |
varchar |
|
|
|
| UnitPrice5 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| Quantity5 |
tinyint |
|
|
Default Value: 0 |
| SubTotal5 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| JobPerformed1 |
varchar |
80 |
|
|
| JobPrice1 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| JobPerformed2 |
varchar |
80 |
|
|
| JobPrice2 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| JobPerformed3 |
varchar |
80 |
|
|
| JobPrice3 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| JobPerformed4 |
varchar |
80 |
|
|
| JobPrice4 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| JobPerformed5 |
varchar |
80 |
|
|
| JobPrice5 |
decimal |
|
|
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| TotalParts |
decimal |
|
Unchecked |
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| TotalLabor |
decimal |
|
Unchecked |
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| TaxRate |
decimal |
|
Unchecked |
Default Value: 7.75
Scale: 2 |
| TaxAmount |
decimal |
|
Unchecked |
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| OrderTotal |
decimal |
|
Unchecked |
Default Value: 0.00
Scale: 2 |
| Recommendations |
text |
|
|
|
- Save the table as RepairOrders and close it
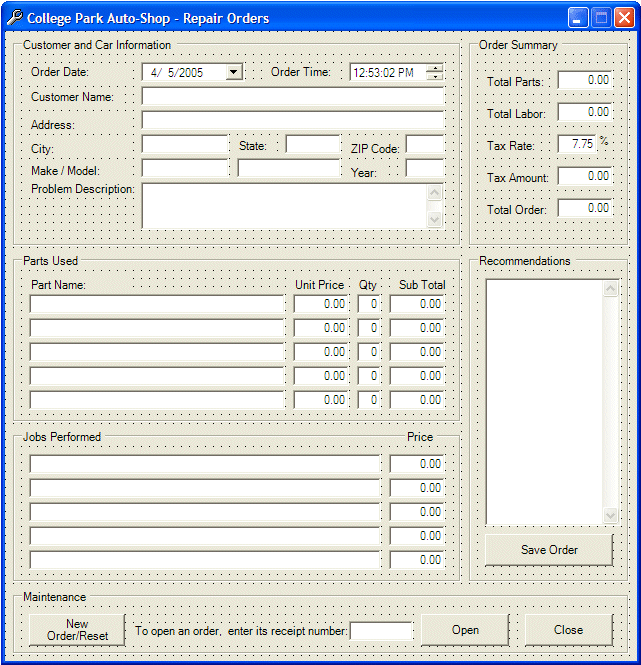
- Create a new Windows Application named CPAS2
- Design the form as follows (you could select (all) and copy the form from
lesson 7, paste it to this form and make the necessary changes):
 |
| Control |
Name |
Text |
Other Properties |
| GroupBox |
|
Customer and Car Information |
|
| Label |
|
First Name: |
|
| TextBox |
txtFirstName |
|
|
| Label |
|
Last Name: |
|
| TextBox |
txtLastName |
|
|
| Label |
|
Address |
|
| TextBox |
txtAddress |
|
|
| Label |
|
City: |
|
| TextBox |
txtCity |
|
|
| Label |
|
State: |
|
| TextBox |
txtState |
|
|
| Label |
|
ZIP Code: |
|
| TextBox |
txtZIPCode |
|
TextAlign: Right |
| Label |
|
Make / Model: |
|
| TextBox |
txtMake |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtModel |
|
|
| Label |
|
Year: |
|
| TextBox |
txtCarYear |
|
TextAlign: Right |
| Label |
|
Problem Description: |
|
| TextBox |
txtProblem |
|
|
| GroupBox |
|
Parts Used |
|
| Label |
|
Part Name |
|
| Label |
|
Unit Price |
|
| Label |
|
Qty |
|
| Label |
|
Sub Total |
|
| TextBox |
txtPartName1 |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtPartUnitPrice1 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartQuantity1 |
0 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartSubTotal1 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartName2 |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtPartUnitPrice2 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartQuantity2 |
0 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartSubTotal2 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartName3 |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtPartUnitPrice3 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartQuantity3 |
0 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartSubTotal3 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartName4 |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtPartUnitPrice4 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartQuantity4 |
0 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartSubTotal4 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartName5 |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtPartUnitPrice5 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartQuantity5 |
0 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtPartSubTotal5 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| GroupBox |
|
Jobs Performed |
|
| Label |
|
Job Description |
|
| Label |
|
Price |
|
| TextBox |
txtJobDescription1 |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtJobPrice1 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtJobDescription2 |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtJobPrice2 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtJobDescription3 |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtJobPrice3 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtJobDescription4 |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtJobPrice4 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| TextBox |
txtJobDescription5 |
|
|
| TextBox |
txtJobPrice5 |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| GroupBox |
|
Order Summary |
|
| Button |
btnResetOrder |
Reset Order |
|
| Button |
btnCalculateOrder |
Calculate Order |
|
| Label |
|
Total Parts: |
|
| TextBox |
txtTotalParts |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| Label |
|
Total Labor: |
|
| Text |
txtTotalLabor |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| Label |
|
Tax Rate: |
|
| TextBox |
txtTaxRate |
7.75 |
TextAlign: Right |
| Label |
|
% |
|
| Label |
|
Tax Amount: |
|
| TextBox |
txtTaxAmount |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| Label |
|
Total Order: |
|
| TextBox |
txtTotalOrder |
0.00 |
TextAlign: Right |
| Button |
btnSaveOrder |
Save this Order and Start New Order |
|
| Button |
btnOpenOrder |
Open an Existing Order |
|
| Label |
|
Recommendations |
|
| TextBox |
txtRecommendations |
|
Multiline: True
ScrollBars: Vertical |
|
- Double-click the New Order/Reset button and implement its Click event as
follows:
Private Sub btnReset_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnReset.Click
dtpOrderDate.Value = DateTime.Today
dtpOrderTime.Value = DateTime.Now
txtCustomerName.Text = ""
txtAddress.Text = ""
txtCity.Text = ""
txtState.Text = ""
txtZIPCode.Text = ""
txtMake.Text = ""
txtModel.Text = ""
txtCarYear.Text = ""
txtProblem.Text = ""
txtPartName1.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice1.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity1.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal1.Text = "0.00"
txtPartName2.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice2.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity2.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal2.Text = "0.00"
txtPartName3.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice3.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity3.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal3.Text = "0.00"
txtPartName4.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice4.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity4.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal4.Text = "0.00"
txtPartName5.Text = ""
txtUnitPrice5.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity5.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal5.Text = "0.00"
txtJobPerformed1.Text = ""
txtJobPrice1.Text = "0.00"
txtJobPerformed2.Text = ""
txtJobPrice2.Text = "0.00"
txtJobPerformed3.Text = ""
txtJobPrice3.Text = "0.00"
txtJobPerformed4.Text = ""
txtJobPrice4.Text = "0.00"
txtJobPerformed5.Text = ""
txtJobPrice5.Text = "0.00"
txtTotalParts.Text = "0.00"
txtTotalLabor.Text = "0.00"
txtTaxRate.Text = "7.75"
txtTaxAmount.Text = "0.00"
txtTotalOrder.Text = "0.00"
txtRecommendations.Text = ""
txtCustomerName.Focus()
End Sub
|
- Under the above event, implement the follow sub procedure:
Private Sub CalculateOrder()
Dim part1UnitPrice As Decimal
Dim part1SubTotal As Decimal
Dim part2UnitPrice As Decimal
Dim part2SubTotal As Decimal
Dim part3UnitPrice As Decimal
Dim part3SubTotal As Decimal
Dim part4UnitPrice As Decimal
Dim part4SubTotal As Decimal
Dim part5UnitPrice As Decimal
Dim part5SubTotal As Decimal
Dim totalParts As Decimal
Dim part1Quantity As Integer = 0
Dim part2Quantity As Integer = 0
Dim part3Quantity As Integer = 0
Dim part4Quantity As Integer = 0
Dim part5Quantity As Integer = 0
Dim job1Price As Decimal = 0.0
Dim job2Price As Decimal = 0.0
Dim job3Price As Decimal = 0.0
Dim job4Price As Decimal = 0.0
Dim job5Price As Decimal = 0.0
Dim totalLabor As Decimal
Dim taxRate As Decimal
Dim taxAmount As Decimal
Dim totalOrder As Decimal
' Don't charge a part unless it is clearly identified
If txtPartName1.Text = "" Then
txtUnitPrice1.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity1.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal1.Text = "0.00"
part1UnitPrice = 0.0
Else
Try
part1UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice1.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Unit Price")
txtUnitPrice1.Text = "0.00"
txtUnitPrice1.Focus()
End Try
Try
part1Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity1.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Quantity")
txtQuantity1.Text = "0"
txtQuantity1.Focus()
End Try
End If
If txtPartName2.Text = "" Then
txtUnitPrice2.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity2.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal2.Text = "0.00"
part2UnitPrice = 0.0
Else
Try
part2UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice2.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Unit Price")
txtUnitPrice2.Text = "0.00"
txtUnitPrice2.Focus()
End Try
Try
part2Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity2.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Quantity")
txtQuantity2.Text = "0"
txtQuantity2.Focus()
End Try
End If
If txtPartName3.Text = "" Then
txtUnitPrice3.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity3.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal3.Text = "0.00"
part3UnitPrice = 0.0
Else
Try
part3UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice3.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Unit Price")
txtUnitPrice3.Text = "0.00"
txtUnitPrice3.Focus()
End Try
Try
part3Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity3.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Quantity")
txtQuantity3.Text = "0"
txtQuantity3.Focus()
End Try
End If
If txtPartName4.Text = "" Then
txtUnitPrice4.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity4.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal4.Text = "0.00"
part4UnitPrice = 0.0
Else
Try
part4UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice4.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Unit Price")
txtUnitPrice4.Text = "0.00"
txtUnitPrice4.Focus()
End Try
Try
part4Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity4.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Quantity")
txtQuantity4.Text = "0"
txtQuantity4.Focus()
End Try
End If
If txtPartName5.Text = "" Then
txtUnitPrice5.Text = "0.00"
txtQuantity5.Text = "0"
txtSubTotal5.Text = "0.00"
part5UnitPrice = 0.0
Else
Try
part5UnitPrice = CDbl(txtUnitPrice5.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Unit Price")
txtUnitPrice5.Text = "0.00"
txtUnitPrice5.Focus()
End Try
Try
part5Quantity = CInt(txtQuantity5.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Quantity")
txtQuantity5.Text = "0"
txtQuantity5.Focus()
End Try
End If
' Don't bill the customer for a job that is not specified
If txtJobPerformed1.Text = "" Then
txtJobPrice1.Text = "0.00"
job1Price = 0.0
Else
Try
job1Price = CDbl(txtJobPrice1.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
msgbox("Invalid Job Price")
txtJobPrice1.Text = "0.00"
txtJobPrice1.Focus()
End Try
End If
If txtJobPerformed2.Text = "" Then
txtJobPrice2.Text = "0.00"
job2Price = 0.0
Else
Try
job2Price = CDbl(txtJobPrice2.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
MsgBox("Invalid Job Price")
txtJobPrice2.Text = "0.00"
txtJobPrice2.Focus()
End Try
End If
If txtJobPerformed3.Text = "" Then
txtJobPrice3.Text = "0.00"
job3Price = 0.0
Else
Try
job3Price = CDbl(txtJobPrice3.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
MsgBox("Invalid Job Price")
txtJobPrice3.Text = "0.00"
txtJobPrice3.Focus()
End Try
End If
If txtJobPerformed4.Text = "" Then
txtJobPrice4.Text = "0.00"
job4Price = 0.0
Else
Try
job4Price = CDbl(txtJobPrice4.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
MsgBox("Invalid Job Price")
txtJobPrice4.Text = "0.00"
txtJobPrice4.Focus()
End Try
End If
If txtJobPerformed5.Text = "" Then
txtJobPrice5.Text = "0.00"
job5Price = 0.0
Else
Try
job5Price = CDbl(txtJobPrice5.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
MsgBox("Invalid Job Price")
txtJobPrice5.Text = "0.00"
txtJobPrice5.Focus()
End Try
End If
part1SubTotal = part1UnitPrice * part1Quantity
part2SubTotal = part2UnitPrice * part2Quantity
part3SubTotal = part3UnitPrice * part3Quantity
part4SubTotal = part4UnitPrice * part4Quantity
part5SubTotal = part5UnitPrice * part5Quantity
txtSubTotal1.Text = part1SubTotal.ToString("F")
txtSubTotal2.Text = part2SubTotal.ToString("F")
txtSubTotal3.Text = part3SubTotal.ToString("F")
txtSubTotal4.Text = part4SubTotal.ToString("F")
txtSubTotal5.Text = part5SubTotal.ToString("F")
totalParts = part1SubTotal + part2SubTotal + part3SubTotal + _
part4SubTotal + part5SubTotal
totalLabor = job1Price + job2Price + job3Price + _
job4Price + job5Price
Try
taxRate = CDbl(txtTaxRate.Text)
Catch ex As FormatException
MsgBox("Invalid Tax Rate")
txtTaxRate.Text = "7.75"
txtTaxRate.Focus()
End Try
Dim totalPartsAndLabor As Decimal = totalParts + totalLabor
taxAmount = totalPartsAndLabor * taxRate / 100
totalOrder = totalPartsAndLabor + taxAmount
txtTotalParts.Text = totalParts.ToString("F")
txtTotalLabor.Text = totalLabor.ToString("F")
txtTaxAmount.Text = taxAmount.ToString("F")
txtTotalOrder.Text = totalOrder.ToString("F")
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity1
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave
and implement it as follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity1_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtQuantity1.Leave
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity2
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement it
as follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity2_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtQuantity2.Leave
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity3
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement it
as follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity3_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtQuantity3.Leave
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity4
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement it
as follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity4_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtQuantity4.Leave
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtQuantity5
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement it
as follows:
Private Sub txtQuantity5_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtQuantity5.Leave
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtJobPrice1
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement it as follows:
Private Sub txtJobPrice1_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtJobPrice1.Leave
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtJobPrice2
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement it
as follows:
Private Sub txtJobPrice2_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtJobPrice2.Leave
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtJobPrice3
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement it
as follows:
Private Sub txtJobPrice3_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtJobPrice3.Leave
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtJobPrice4
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement it
as follows:
Private Sub txtJobPrice4_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtJobPrice4.Leave
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select txtJobPrice5
- In the Method Name combo box, select Leave and implement it
as follows:
Private Sub txtJobPrice5_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles txtJobPrice5.Leave
CalculateOrder()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnSaveOrder
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement its
Click event as follows:
Private Sub btnSaveOrder_Click(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnSaveOrder.Click
Dim strCustomerName As String = txtCustomerName.Text
If strCustomerName = "" Then
MsgBox("You must provide a name for the customer")
Exit Sub
End If
Dim strOrderDate As String = dtpOrderDate.Value.ToString("d")
Dim strOrderTime As String = dtpOrderTime.Value.ToString("t")
Dim strNewRepairOrder As String = "INSERT INTO RepairOrders(OrderDate, " & _
"OrderTime, CustomerName, Address, " & _
"City, State, ZIPCode, Make, Model, " & _
"CarYear, ProblemDescription, PartName1, " & _
"UnitPrice1, Quantity1, SubTotal1, " & _
"PartName2, UnitPrice2, Quantity2, " & _
"SubTotal2, PartName3, UnitPrice3, " & _
"Quantity3, SubTotal3, PartName4, " & _
"UnitPrice4, Quantity4, SubTotal4, " & _
"PartName5, UnitPrice5, Quantity5, " & _
"SubTotal5, JobPerformed1, JobPrice1, " & _
"JobPerformed2, JobPrice2, JobPerformed3, " & _
"JobPrice3, JobPerformed4, JobPrice4, " & _
"JobPerformed5, JobPrice5, TotalParts, " & _
"TotalLabor, TaxRate, TaxAmount, " & _
"OrderTotal, Recommendations) " & _
"VALUES('" & strOrderDate & "', '" & strOrderTime & _
"', '" & strCustomerName & "', '" & txtAddress.Text & _
"', '" & txtCity.Text & "', '" & txtState.Text & _
"', '" & txtZIPCode.Text & "', '" & txtMake.Text & _
"', '" & txtModel.Text & "', '" & txtCarYear.Text & _
"', '" & txtProblem.Text & "', '" & txtPartName1.Text & _
"', '" & txtUnitPrice1.Text & "', '" & txtQuantity1.Text & _
"', '" & txtSubTotal1.Text & "', '" & txtPartName2.Text & _
"', '" & txtUnitPrice2.Text & "', '" & txtQuantity2.Text & _
"', '" & txtSubTotal2.Text & "', '" & txtPartName3.Text & _
"', '" & txtUnitPrice3.Text & "', '" & txtQuantity3.Text & _
"', '" & txtSubTotal3.Text & "', '" & txtPartName4.Text & _
"', '" & txtUnitPrice4.Text & "', '" & txtQuantity4.Text & _
"', '" & txtSubTotal4.Text & "', '" & txtPartName5.Text & _
"', '" & txtUnitPrice5.Text & "', '" & txtQuantity5.Text & _
"', '" & txtSubTotal5.Text & "', '" & txtJobPerformed1.Text & _
"', '" & txtJobPrice1.Text & "', '" & txtJobPerformed2.Text & _
"', '" & txtJobPrice2.Text & "', '" & txtJobPerformed3.Text & _
"', '" & txtJobPrice3.Text & "', '" & txtJobPerformed4.Text & _
"', '" & txtJobPrice4.Text & "', '" & txtJobPerformed5.Text & _
"', '" & txtJobPrice5.Text & "', '" & txtTotalParts.Text & _
"', '" & txtTotalLabor.Text & "', '" & txtTaxRate.Text & _
"', '" & txtTaxAmount.Text & "', '" & txtTotalOrder.Text & _
"', '" & txtRecommendations.Text & "');"
Dim conDatabase As System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection = New _
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection( _
"Data Source=(local);Database='CPAS';Integrated Security=yes")
Dim cmdDatabase As System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand = New _
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand(strNewRepairOrder, conDatabase)
conDatabase.Open()
cmdDatabase.ExecuteNonQuery()
conDatabase.Close()
End Sub
|
- In the Class Name combo box, select btnClose
- In the Method Name combo box, select Click and implement its Click
event as follows:
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles btnClose.Click
End
End Sub
|
- Execute the application and create a repair order. Here is an example:
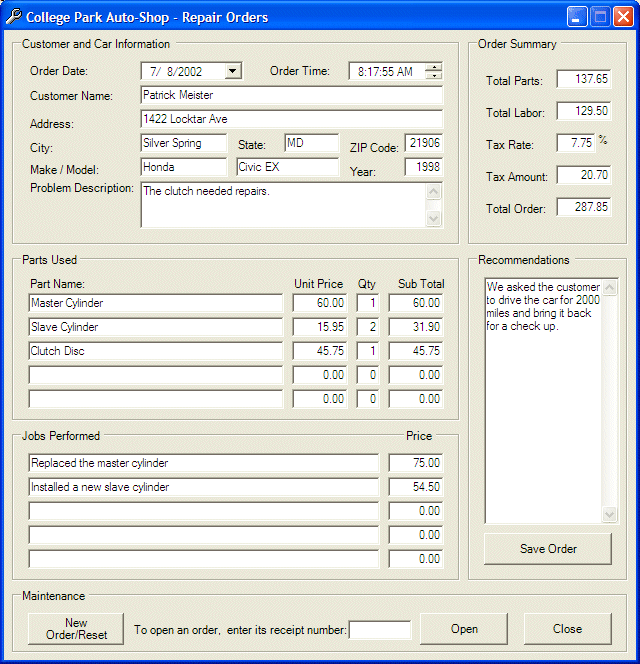
- Save the order
- Close the form and return to your programming environment
The .NET
Framework provides XML-supported classes used to read from, and write to, an XML
file going forth but without back. To support a unidirectional approach to
reading data from a SQL Server database, the .NET Framework provides the SqlDataReader.
This class reads data in a top-down direction without referring back to a record
it passed already:
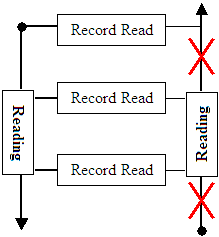
In other words, the SqlDataReader reads the first
record, moves down, reads the second record, moves down, and so on, until it
gets to the last record. Once it has passed a record, it doesn't and cannot
refer back to it.
To create a data reader, you can declare a pointer to SqlDataReader.
This class doesn't have a constructor. This means that, to use it, you must
(directly) specify where it would read its data. To provide data to the reader,
the SqlCommand class is equipped with the ExecuteReader() method
that is overloaded with two versions. The simplest version of this method uses
the following syntax:
Overloads Public Function ExecuteReader() As SqlDataReader
Based on this, before using a data reader, you should first
create a command that would specify how data would be acquired. Once the data is
reader, you can pass it to the data reader by assigning the result of a call to
a SqlCommand.ExecuteReader() method to a SqlDataReader object.
Once data is supplied to the reader, you can access it, one
record at a time, from top to bottom. To access data that the reader acquired,
you can call its Read() method whose syntax is:
Public Overridable Function Read() As Boolean Implements IDataReader.Read
As you can see, the Read() method simply reads a
record and moves on. When reading the records of a table, as mentioned already
many times, the data reader reads one record at a time and moves to the next.
Before moving to the next record, you can access the values stored in the
current record. To help with this, the columns of the table being read are
stored in a collection and each column can be referred to with a numeric index.
The first column has an index of 1. The second column has an index of 2, and so
on. To retrieve the actual data stored in a column, you may need to know the
type of information that column is holding so you can read it accurately.
Depending on the data type that a column was created with,
you can access it as follows:
| If the column holds the following data type |
Use the following method |
System.Data.SqlTypes Equivalent |
| bit |
GetBoolean() |
|
GetSqlBoolean() |
| char, nchar |
GetChar() |
|
GetSqlChar() |
| varchar, nvarchar |
GetString() |
|
GetSqlString() |
| text, ntext |
GetString() |
|
GetSqlString() |
| binary, varbinary |
GetBinary() |
|
GetSqlBinary() |
| decimal |
GetDecimal() |
GetDouble() |
GetSqlDecimal() |
| float |
GetFloat() |
|
GetSqlSingle() |
| int |
GetInt32() |
|
GetSqlInt32() |
| money, smallmoney |
GetDecimal() |
|
GetSqlDecimal() |
| bigint |
GetInt64() |
|
GetSqlInt64() |
| datetime, smalldatetime |
GetDateTime() |
|
GetSqlDateTime() |
| smallint, tinyint |
GetInt16() |
GetByte() |
GetSqlInt16() |
When using one of the Get... or GetSql... methods, the
compiler doesn't perform any conversion. This means that, before sending the
data, you have two responsibilities. First you must convert the value read to
the appropriate (and probably exact) format. For example, if you read a natural
number from a column created with the tinyint data type, even though C++
allows a short to be implicitly converted to an int, the compiler
you use for your application would not perform or assume the conversion: the
value of a column created with tinyint must be read with GetByte()
or GetSqlByte() and trying to use GetInt32() or GetSqlInt32()
would throw an error.
|
|