
Windows Controls: The Combo Box
 |
Windows Controls: The Combo Box |
Introduction to Combo Boxes
Description
A combo box is a list of items that the user can select from. Like a list box, a combo box is usually made of a list of strings. Unlike a list box, a combo box saves space by using just as much room as a text box control. To show that it is holding a list, a combo box displays a down-pointing arrow on the right side of its text box. In the following screenshot, the Font Effects property page of the Character dialog box of OpenOffice.org presents the Underlining, the Color, the Effects, the Strikethrough, the Relief, and the Font Color combo boxes:

Because a combo box does not (permanently) display its list like a list box, to show its content, the user can click the arrow button. Here is an example:

![]() Application:
Introducing Combo Boxes
Application:
Introducing Combo Boxes
Creating a Combo Box
To support combo boxes, the .NET Framework provides a
class named ComboBox. At design time, to add a combo box to your
application, from the Common Controls section of the Toolbox, you can click
the ComboBox button
![]() and click the form or a container. Like ListBox, the ComboBox
class is derived from the ListControl class. Therefore, to
programmatically create a combo box, declare a variable of type ComboBox,
allocate its memory with the new operator and add it to the Controls
collection of its container. Here is an example:
and click the form or a container. Like ListBox, the ComboBox
class is derived from the ListControl class. Therefore, to
programmatically create a combo box, declare a variable of type ComboBox,
allocate its memory with the new operator and add it to the Controls
collection of its container. Here is an example:
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class Exercise : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
Label lblTitle;
ComboBox cbxAcademicDisciplines;
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
lblTitle = new Label();
lblTitle.Text = "Academic Disciplines";
lblTitle.Location = new Point(12, 12);
lblTitle.AutoSize = true;
Controls.Add(lblTitle);
cbxAcademicDisciplines = new ComboBox();
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Location = new Point(12, 32);
Controls.Add(cbxAcademicDisciplines);
}
}
public class Program
{
static int Main()
{
System.Windows.Forms.Application.Run(new Exercise());
return 0;
}
}
This would produce:

![]() Application:
Creating Combo Boxes
Application:
Creating Combo Boxes

| Control | Name | Text | TextAlign | ToolTip On ToolTip1 | |
| GroupBox | grpIceCream | ||||
| Label | Order &Date: | ||||
| TextBox | txtOrderDate | Enter a value for a date (MM/DD/YYYY) | |||
| Label |
|
Order &Time: | |||
| TextBox |
|
txtOrderTime | Enter a value for a time (23:59) | ||
| Label |
|
&Flavor: | |||
| ComboBox |
|
cboFlavors | Click the arrow to display a list, then select a flavor from the list | ||
| Label |
|
&Container: | |||
| ComboBox |
|
cboContainers | Click to display the list of containers and select one | ||
| Label |
|
&Ingredient: | |||
| ComboBox |
|
cboIngredients | Display the list of ingredients and select the customer's choice | ||
| Label |
|
&Scoops: | |||
| TextBox |
|
txtScoops | 1 | Right | Enter the number of scoops (1, 2, or 3) to fill the container |
| Button |
|
btnCalculate | C&alculate | ||
| Label |
|
&Order Total: | |||
| TextBox |
|
txtOrderTotal | 0.00 | Right | This displays the total amount of this order |
Characteristics of a Combo Box
Introduction
Like all visual controls, a combo box shares all the basic characteristics of other graphic control: the name, the location, the size, the ability to be enabled or disabled, the ability to hide or show it, the ability to dock or anchor, etc.
Creating the List of Items
Probably the most important aspect of a combo box is the list of items it holds. Like the list box and all other list-based controls, the list of a combo box is held by the Items property of the ComboBox class. To visually create the list of items, you can use the String Collection Editor.
The Items property of the ComboBox class is created from the nested ObjectCollection class. To programmatically create a list of items, you can (continuously) call the ObjectCollection.Add() method. Here is an example:
public class Exercise : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
Label lblTitle;
ComboBox cbxAcademicDisciplines;
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
lblTitle = new Label();
lblTitle.Text = "Academic Disciplines";
lblTitle.Location = new Point(12, 12);
lblTitle.AutoSize = true;
Controls.Add(lblTitle);
cbxAcademicDisciplines = new ComboBox();
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Location = new Point(12, 32);
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Natural sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Mathematics and Computer sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Social sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Humanities");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Professions and Applied sciences");
Controls.Add(cbxAcademicDisciplines);
}
}
This would produce:

To add an array of items, you can call the AddRange() method. To insert an item somewhere inside the list, you can call the Insert() method.
If you want the list of items to be sorted, you can change the value of the Sorted property in the Properties window from False (the default) to True. To sort a list programmatically, you can assign a true value to the Sorted property. You can un-sort the list by changing the value of the Sorted property. This property works exactly like its equivalent in the ListBox control.
![]() Practical Learning:
Adding Items to a Combo Box
Practical Learning:
Adding Items to a Combo Box


| Control | Text | Name | |
| GroupBox |
|
Part Selection | |
| Label |
|
Year | |
| Label |
|
Make | |
| Label |
|
Model | |
| Label |
|
Category | |
| ComboBox |
|
cbxCarYears | |
| ComboBox |
|
cbxMakes | |
| ComboBox |
|
cbxModels | |
| ComboBox |
|
cbxCategories | |
| GroupBox |
|
Available Parts | |
| DataGridView |
|
dgvAvailableParts | |
| Button |
|
Close | btnClose |
private void Central_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
for (int i = DateTime.Now.Year; i >= 1960; i--)
this.cbxYears.Items.Add(i);
}Selecting an Item
To select an item from the list, the user can click it. To programmatically select an item, you can assign a string to the Text property of a DropDown or a Simple combo box. Probably the best way to select an item is to specify its index. The items of a combo box are stored in a zero-based list. To select an item, you can assign its position to the SelectedIndex property. In the same way, to find out what item is selected, you can get the value of the SelectedIndex property.
Instead of using of using the index of an item, to select an item using its identity or name, you can use the SelectedItem property. To select an item by its name, assign it to the SelectedItem property.
![]() Practical Learning: Selecting an Item
Practical Learning: Selecting an Item
using System;
namespace CollegeParkAutoParts1
{
public class PartDescription
{
private long ID;
private int yr;
private string mk;
private string mdl;
private string cat;
private string name;
private decimal price;
public PartDescription(long code = 0,
int year = 1960,
string make = "Unknown",
string model = "Unknown",
string type = "Miscellaneous",
string desc = "Anything",
decimal uPrice = 0.00M)
{
this.ID = code ;
this.yr = year;
this.mk = make;
this.mdl = model;
this.cat = type;
this.name = desc;
this.price = uPrice;
}
public long PartNumber
{
get { return ID; }
set { ID = value; }
}
public int CarYear
{
get { return yr; }
set { yr = value; }
}
public string Make
{
get { return mk; }
set { mk = value; }
}
public string Model
{
get { return mdl; }
set { mdl = value; }
}
public string Category
{
get { return cat ; }
set { cat = value; }
}
public string PartName
{
get { return name; }
set { name = value; }
}
public decimal UnitPrice
{
get { return (price < 0) ? 0.00M : price; }
set { price = value; }
}
public override string ToString()
{
return this.PartNumber + " " +
this.CarYear.ToString() + " " +
this.Make + " " +
this.Model + " " +
this.Category + " " +
this.PartName + " " +
this.UnitPrice;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CollegeParkAutoParts1
{
public class PartSelected
{
private long ID;
private string name;
private decimal price;
public PartSelected(long code = 0,
string desc = "Unknown",
decimal uPrice)
{
this.ID = code;
this.name = desc;
this.price = uPrice;
}
public long PartNumber
{
get { return ID; }
set { ID = value; }
}
public string PartName
{
get { return name; }
set { name = value; }
}
public decimal UnitPrice
{
get { return (price < 0) ? 0.00M : price; }
set { price = value; }
}
public override string ToString()
{
return this.PartNumber + " " +
this.PartName + " " +
this.UnitPrice;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CollegeParkAutoParts1
{
public partial class CollegeParkAutoParts : Form
{
List<PartDescription> lstParts = new List<PartDescription>();
BindingSource bsPartsSelected = new BindingSource();
public CollegeParkAutoParts()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void CollegeParkAutoParts_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
for (int i = DateTime.Now.Year; i >= 1960; i--)
this.cbxYears.Items.Add(i);
PartDescription part = null;
part = new PartDescription(447093, 2002, "Ford",
"Escort SE L4 2.0", "Engine Electrical",
"Alternator 75amp Remanufactured; w/ 75 Amp",
205.05M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(203815, 2006, "Dodge",
"Caravan SE L4 2.4", "Cooling System",
"Radiator Cap", 6.65M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(293047, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Thermostat Gasket", 4.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(990468, 2002, "Honda",
"Civic 1.7 EX 4DR", "Exhaust",
"Bolt & Spring Kit (Manifold outlet, Muffler Inlet)",
85.75M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(304158, 1996, "Buick",
"Regal Custom V6 3.8", "Fuel Injection",
"Fuel Injector", 82.75M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(807245, 2004, "Acura",
"MDX 3.5 4WD", "Driveshaft & Axle",
"CV Boot Clamp 7 x 750mm; 1 Large + 1 Small Clamp",
1.60M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(203485, 2001, "Ford",
"Taurus LX V6 3.0", "Fuel Injection",
"Oxygen Sensor OE Style 4Wire; Front; 2 Required",
52.65M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(248759, 1999, "Jeep",
"Wrangler Sahara", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter AirSoft Panel", 7.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(202848, 1998, "Honda",
"Accord 2.3 LX 4DR", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter", 12.55M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(932759, 2006, "Kia",
"Rio 1.6DOHC16V 4-DR", "Cooling System",
"Thermostat", 14.45M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(304975, 2000, "Honda",
"Civic 1.6 EX 4DR", "Suspension",
"Ball Joint; Front Lower; 2 per car", 40.55M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(208450, 2003, "Chevrolet",
"Monte Carlo LS V6 3.4", "Fuel Injection",
"Oxygen Sensor OE connector; Rear", 65.55M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(209480, 2002, "Ford",
"Focus SE DOHC L4 2.0", "Steering",
"Steering Rack Remanufactured", 170.85M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(203495, 2004, "Honda",
"Civic 1.7 EX 4DR", "Climate Control",
"A/C Clutch; OE compressor = Sanden", 184.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(203480, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter", 12.65M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(109379, 2005, "Volvo",
"S40 2.5L T5 AWD", "Fuel Delivery",
"Fuel Filter; Early Design; Outer Diameter = 55mm",
30.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(935794, 2002, "Ford",
"Escape XLS 4WD", "Brake",
"Brake Caliper Remanufactured; Front Right",
65.55M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(203485, 2006, "BMW",
"325i", "Climate Control",
"AC High Pressure Side Switch",
49.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(204875, 1996, "Chevrolet",
"Monte Carlo Z34 V6 3.4", "Fuel Delivery",
"Fuel Filter", 8.05M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(937485, 2007, "Toyota",
"Camry V6", "Air Intake", "Air Filter", 12.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(294759, 2001, "Ford",
"Escape XLT 4WD", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter Panel", 7.25M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(297495, 2003, "Honda",
"Civic 1.7 EX 4DR", "Brake",
"Brake Caliper Reman; w/ ProAct Pads; Front Right",
82.55M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(794735, 2006, "BMW",
"325i", "Climate Control",
"Cabin Air/Pollen Filter; With Activated Carbon",
28.05M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(937485, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Body Electrical",
"Halogen SilverStar; 12V 65W; inner-high beam",
22.85M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(492745, 2005, "Ford",
"Focus ZX3 L4 2.0", "Air Intake",
"Fuel Injection Perf Kit", 342.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(937005, 2004, "Acura",
"MDX 3.5 4WD", "Driveshaft & Axle",
"CV Boot Clamp 7 x 750mm; For Large End of Boot; inner boot",
1.60M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(293749, 2004, "Acura",
"MDX 3.5 4WD", "Driveshaft & Axle",
"Axle Nut 24mm x 1;5; rear ",
2.35M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(920495, 2006, "BMW",
"325i", "Climate Control",
"Adjustable Telescoping Mirror", 7.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(204075, 2004, "Acura",
"MDX 3.5 4WD", "Driveshaft & Axle",
"Wheel Bearing; Rear; 1 per wheel",
70.15M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(979304, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Thermostat Housing", 20.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(300456, 2004, "Acura",
"MDX 3.5 4WD", "Driveshaft & Axle",
"Wheel Bearing; Front; 1 per wheel", 66.65M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(404860, 2001, "Ford",
"Taurus LX V6 3.0", "Suspension",
"Shock Absorber GR2; Rear; Wagon only",
39.40M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(585688, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Brake",
"Climate Control", 10.65M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(739759, 2001, "Ford",
"Taurus LX V6 3.0", "Suspension",
"Shock Absorber GasaJust; Rear; Wagon only", 30.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(927495, 2005, "Volvo",
"S40 2.5L T5 AWD", "Engine Mechanical",
"Timing Belt Idler Pulley Original Equipment INA",
65.55M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(979374, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Thermostat Gasket", 4.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(542347, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Brake",
"Brake Pad Set ProACT Ceramic w/Shims; Front", 80.05M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(683064, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Radiator Hose; Upper", 103.75M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(248759, 1999, "Jeep",
"Wrangler Sahara", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter", 50.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(973974, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Air Intake",
"Air Mass Meter; W/o Housing; Meter/sensor only",
134.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(285800, 2001, "Ford",
"Escape XLT 4WD", "Transmission", "AT Filter", 34.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(207495, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Body Electrical",
"Headlight Bulb; 12V 65W; inner-high beam", 9.35M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(566676, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Auxiliary Fan Switch", 42.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(304950, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Body Electrical",
"Headlight Bulb; 12V 51W; outer", 7.85M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(797394, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Water Flange Gasket", 0.85M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(910203, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Suspension",
"Strut Mount Inc; Sleeve; Rear Right", 80.85M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(790794, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Radiator Hose; Lower", 9.45M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(970394, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Suspension",
"Coil Spring Insulator; Front Lower", 14.55M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(290840, 2005, "Volvo",
"S40 2.5L T5 AWD", "Engine Mechanical",
"Rod Bearing Set 1 per Rod; Standard; Reqs. 5-per Engine",
26.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(209704, 2007, "Toyota",
"Corolla", "Body Electrical",
"Wiper Blade Excel+; Front Right", 7.25M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(200368, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Radiator Drain Plug incl; gasket", 3.15M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(200970, 2005, "Volvo",
"S40 2.5L T5 AWD", "Engine Mechanical",
"Reference Sensor; Flywheel Engine Speed", 62.05M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(542347, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter", 50.25M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(927045, 2001, "Ford",
"Escape XLT 4WD", "Air Intake",
"Air Filter", 62.95M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(990659, 2000, "Toyota",
"RAV4 2WD/4-DOOR", "Cooling System",
"Radiator OE Plastic tank", 136.85M);
lstParts.Add(part);
part = new PartDescription(440574, 2007, "Buick",
"Lacrosse CXS V6 3.6", "Suspension",
"Strut Mount Inc; Sleeve; Rear Left", 80.80M);
}
}
}
private void cbxYears_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
cbxMakes.Text = "";
cbxMakes.Items.Clear();
cbxModels.Text = "";
cbxModels.Items.Clear();
cbxCategories.Text = "";
cbxCategories.Items.Clear();
foreach (PartDescription part in lstParts)
if (part.CarYear == int.Parse(cbxYears.Text))
if (cbxMakes.FindString(part.Make) == -1)
cbxMakes.Items.Add(part.Make);
}
private void cbxMakes_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
cbxModels.Text = "";
cbxModels.Items.Clear();
cbxCategories.Text = "";
cbxCategories.Items.Clear();
foreach (PartDescription part in lstParts)
if ((part.CarYear == int.Parse(cbxYears.Text)) &&
(part.Make == cbxMakes.Text))
if (cbxModels.FindString(part.Model) == -1)
cbxModels.Items.Add(part.Model);
}
private void cbxModels_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
foreach (PartDescription part in lstParts)
if ((part.CarYear == int.Parse(cbxCarYears.Text)) &&
(part.Make == cbxMakes.Text) &&
(part.Model == cbxModels.Text))
if (cbxCategories.FindString(part.Category) == -1)
cbxCategories.Items.Add(part.Category);
}
private void cbxCategories_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Check each record in the list of parts
foreach (PartDescription part in lstParts)
{
// If/When you find a record that matches
// the values of the combo boxes . . .
if ((part.CarYear == int.Parse(cbxYears.Text)) &&
(part.Make == cbxMakes.Text) &&
(part.Model == cbxModels.Text) &&
(part.Category == cbxCategories.Text))
{
// . . . get the values from that part and create a selected part
PartSelected selected = new PartSelected(part.PartNumber,
part.PartName,
part.UnitPrice);
// Store that part in the binding source
bsPartsSelected.Add(selected);
}
}
// Empty the data grid view
for (int i = 0; i < dgvAvailableParts.Rows.Count - 2; i++ )
dgvAvailableParts.Rows.RemoveAt(i);
// Display the selected item(s) in the data grid view
dgvAvailableParts.DataSource = bsPartsSelected;
}
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}Finding a String in the Combo Box
Instead of simply selecting an item from a combo box, the user may want to find out if a certain string exists in the list. To support this operation, the ComboBox class is equipped with a method named FindString that is overloaded with two versions. One of the syntaxes of this method is:
public int FindString(string s);
This method takes as argument the string to find in the combo box. If the item is found in the list, the method returns its position. If the list does not have that string, the method return -1. The above syntax of the method would look through the whole list. If you want the search to start at a specific index, you can use the following version of the FindString() method:
public int FindString(string s, int startIndex);
This version takes as the first argument a string. Instead of start looking for it from the beginning of the list, this method starts at the index specified by the startIndex value.
The FindString() method performs its operation without regards to case. This means that it would perform the same search for BlindMan, Blindman, blindMan, or BLINDMAN and would produce the same result for them. If you want the case of the characters to be taken into consideration, use the FindStringExact() method that also is overloaded with two versions. The syntax of the first version is:
public int FindStringExact(string s);
This method proceeds like the FindString() method by starting to look for the string from the beginning of the list. If you want to specify from where to start looking for the string, you should use the following version:
public int FindStringExact(string s, int startIndex);
The Styles of a Combo Box
Like most graphical controls, a combo box appears as a 3-D object with raised borders. As an alternative, you can display it as a flat object. To assist you with this choice, the ComboBox class provides the FlatStyle property. The FlatStyle property is based on the FlatStyle enumeration. Its members are:
private void InitializeComponent()
{
SuspendLayout();
lblTitle = new Label();
lblTitle.Text = "Academic Disciplines";
lblTitle.Location = new Point(12, 12);
lblTitle.AutoSize = true;
Controls.Add(lblTitle);
cbxAcademicDisciplines = new ComboBox();
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Location = new Point(12, 32);
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Width = 232;
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Natural Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Mathematics and Computer Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Social Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Humanities");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Professions and Applied Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.FlatStyle = FlatStyle.Standard;
Controls.Add(cbxAcademicDisciplines);
}
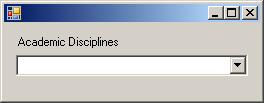
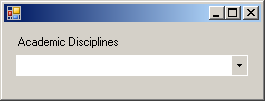
cbxAcademicDisciplines.FlatStyle = FlatStyle.Popup; |
 |
cbxAcademicDisciplines.FlatStyle = FlatStyle.Flat; |
 |
The Drop Down Style
In our introduction to the combo box, we saw that it appeared like a text box with a down-pointing button on its right side. In reality, that was the description of just one type of combo box. There are three styles of combo boxes, although all allow the user to make only one selection. These styles are controlled by the DropDownStyle property, which is based on the ComboBoxStyle enumeration.
One of the types of combo boxes is referred to as Drop Down and is created by setting the DropDownStyle property to DropDown. Here is an example:
private void InitializeComponent()
{
lblTitle = new Label();
lblTitle.Text = "Academic Disciplines";
lblTitle.Location = new Point(12, 12);
lblTitle.AutoSize = true;
Controls.Add(lblTitle);
cbxAcademicDisciplines = new ComboBox();
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Location = new Point(12, 32);
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Natural sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Mathematics and Computer sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Social sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Humanities");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Professions and Applied sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.DropDownStyle = ComboBoxStyle.DropDown;
Controls.Add(cbxAcademicDisciplines);
}
This type is made of a text box on the left side and a down-pointing arrowed button on the right side. Depending on how the control was created, when it comes up, it may not display anything:

Normally, if you want a DropDown style of combo box to display a string when the control comes up, you can either enter a value in the Text property or assign a string to the ComboBox.Text property. Here is an example:
private void InitializeComponent()
{
lblTitle = new Label();
lblTitle.Text = "Academic Disciplines";
lblTitle.Location = new Point(12, 12);
lblTitle.AutoSize = true;
Controls.Add(lblTitle);
cbxAcademicDisciplines = new ComboBox();
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Location = new Point(12, 32);
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Natural sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Mathematics and Computer sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Social sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Humanities");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Professions and Applied sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.DropDownStyle = ComboBoxStyle.DropDown;
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Text = "Social sciences";
Controls.Add(cbxAcademicDisciplines);
}
This would produce:

The string you give to the Text property does not have to be one of the items of the list.
To use the combo box, the user can click its down pointing arrow. At any time, to find out whether the list is displaying, you can check the value of the DroppedDown Boolean property. In the same way, to drop the list, you can programmatically set the combo box' DroppedDown property to true.
Once the list is displaying, if the user clicks that arrow, a list would appear (or expand). If the string assigned to the Text property is one of the items in the list, it would display in the text box side of the control and it would be selected in the list. Here is an example:
private void InitializeComponent()
{
lblTitle = new Label();
lblTitle.Text = "Academic Disciplines";
lblTitle.Location = new Point(12, 12);
lblTitle.AutoSize = true;
Controls.Add(lblTitle);
cbxAcademicDisciplines = new ComboBox();
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Location = new Point(12, 32);
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Natural Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Mathematics and Computer Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Social Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Humanities");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Professions and Applied Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.DropDownStyle = ComboBoxStyle.DropDown;
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Text = "Social Sciences";
Controls.Add(cbxAcademicDisciplines);
}
This would produce:

If the string assigned to the Text property is not one of the items in the list, it would still appear selected in the text box side of the control:
Here is an example:
private void InitializeComponent()
{
lblTitle = new Label();
lblTitle.Text = "Academic Disciplines";
lblTitle.Location = new Point(12, 12);
lblTitle.AutoSize = true;
Controls.Add(lblTitle);
cbxAcademicDisciplines = new ComboBox();
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Location = new Point(12, 32);
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Natural Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Mathematics and Computer Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Social Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Humanities");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Items.Add("Professions and Applied Sciences");
cbxAcademicDisciplines.DropDownStyle = ComboBoxStyle.DropDown;
cbxAcademicDisciplines.Text = "Arts & Sciences";
Controls.Add(cbxAcademicDisciplines);
}
This would produce:

When the list displays, either because the user clicked the arrow button, pressed Alt + the down arrow key or because you decided to display it, the control fires a DropDown event, which is of type EventArgs.
If the user sees an item that he or she wants or was asked to select, he or she can click it. After an item has been clicked, two things happen: 1. the list retracts (or collapses) like a plastic; 2. the item that was clicked fills the text part and becomes the new selection:
 |
 |
On the other hand, after displaying the list, if the user doesn't want to select anything from the list, he or she can click the arrow again or click anywhere away from the list. The list would collapse and the text part would get back to the previous text.
One of the major characteristics of a DropDown style of combo box, as compared to the type we will see next, is that, if the user knows for sure that the item he or she is looking for is in the list, he can first delete the string in the text box part of the control, then start typing. For example, if the list contains a string such as Social Sciences , the user can delete the text part, and start typing so. If there is only one item that starts with s, the user can then click the arrow twice and the item would be selected. Imagine the list contains such items as Jules and Julienne, if the user types the first common letters of these item and double-click the arrow, the first item that has these letters would be selected. This means that, if the user wants to other item to be selected, he or she should type the letters beyond the common ones. In the case of Jules and Julienne, if the user wants Julienne to be selected from an incomplete string, he or she can type juli and click the arrowed button twice.
The Drop Down List
Another style of a combo box is gotten by setting the DropDownStyle to DropDownList. This type also is made of a text box on the left and a down-pointing arrowed button on the right side. It also may appear empty when it comes up, depending on how it was created. The biggest difference between a DropDown combo box and a DropDownList combo box is that, with the drop down list, the user can only select from the list: he or she cannot type anything in the text box part of the control.
Once again, to use the control, the user can click its arrow, which causes the list to display. The user can also display the list using the keyboard by pressing Alt + down arrow key after giving focus to the control.
![]() Practical Learning: Applying a Style to a Combo Box
Practical Learning: Applying a Style to a Combo Box



The Simple Combo Box
The last type of combo box is called a simple combo box and is gotten by setting the DropDownStyle to Simple. After setting this value, you must heighten the control to get the desired size. This type of combo box is also made of two parts but they are distinct. The top section of the combo box displays a text box. Immediately under the text box, there is a list box. The following is the Character dialog box of OpenOffice.org. Its Font property page is equipped with the Font, the Typeface, and the Size combo boxes that are of a Simple style:

Notice that the control doesn't display a down-arrow pointing button on the right side of the selected item since the list is available already. To use this combo box, the user can examine the list part. If he or she sees the desired item, he can click it. When an item is clicked, it becomes the string of the top text part. If the user clicks a different item, it would become the new selection, replacing the one that was in the text part. Although this appears as a list box, the user cannot select more than one item.
The most regularly used combo boxes are made of text items. You can also create a combo box that displays colors or pictures. To create such a combo box, you start by changing the value of the DrawMode property that is set to Normal by default. If you want to display items that are not just regular text, you can set this property to either OwnerDrawFixed, which would make all items have the same height, or OwnerDrawVariable, which allows different items to have different sizes.
If the combo box has a DropDownStyle other than Simple, there is typically a fixed number of items that display when the user clicks the control’s arrow. You can control the number of items that displays using the MaxDropDownItems property. By default, this is set to 8. If the list contains a number of items less than the MaxDropDownItems integer value, all of the items would display fine. If the list contains more than the MaxDropDownItems number of items, when the user clicks the arrow, a vertical scroll box would appear. The control would display MaxDropDownItems number of items; to reveal more, the user would have to scroll in the list.
Automatic List Creation
Using an External List
In the next previous sections, we saw how to create a list of items. The .NET Framework provides an alternative. Instead of creating a list from scratch, you can use one that exists already. For example, you can use a list of recently accessed web sites or custom list of your own. To assist you with this, the ComboBox class provides with three techniques.
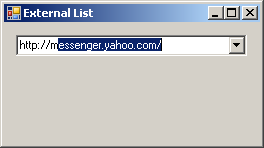
To specify an external list of items to use for the combo box, you have two options. You can use the AutoCompleteSource property, that is based on the AutoCompleteSource enumeration. The members of this enumeration are: None, RecentlyUsedList, FileSystem, FileSystemDirectories, HistoryList, ListItems, AllSystemSources, AllUrl, and CustomSource. Imagine that you want to use the list of web pages you had visited lately. To use that list, you can specify the AutoCompleteSource as HistoryList.
After specifying the source of the list, use the AutoCompleteMode property to specify how the combo box (or rather the text box side of the control) will assist the user. This property is based on the AutoCompleteMode enumeration that has four members. None is the default value. Imagine you had set the value of the AutoCompleteSource property as HistoryList. If you specify AutoCompleteMode as:
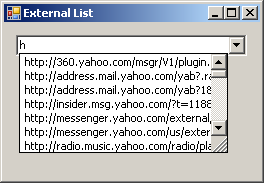
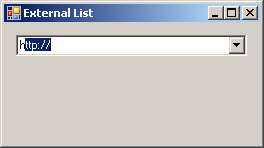 |
 |
 |
|
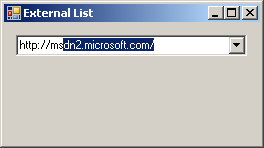
First the user types h and http:// comes up as the first closest match. Then, the user specifies that the address starts with m and the compiler suggests, in alphabetical order, the closest URL with that. Then, the user types ms and finds out that msdn2 is available
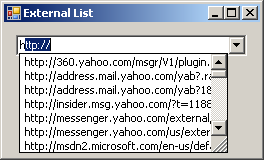
The user can continue typing. If the desired item appears in the list, the user can select it. Otherwise, as the user is typing, the closest match displays in the text box part of the control
 |
 |
Using a Custom List
Instead of using an external list, you can create your own. To do this, use the AutoCompleteCustomSource property. At design time, to create a list of strings, access the Properties window for the text box. In the Properties window, click the ellipsis button of the AutoCompleteCustomSource field to open the String Collection Editor. Enter the strings separated by a hard Return, and click OK. You can also programmatically create the list. To assist you, the .NET Framework provides a class named AutoCompleteStringCollection. The AutoCompleteStringCollection class implements the IList, the ICollection, and the IEnumerable interfaces.
After creating the custom list, to let the combo box use it, set the AutoCompleteMode property to CustomSource.
![]() Practical Learning: Auto Completing a Combo Box
Practical Learning: Auto Completing a Combo Box
private void btnCalculate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
double priceContainer = 0.00,
priceIngredient = 0.00,
priceScoops = 0.00,
orderTotal = 0.00;
int numberOfScoops = 1;
// Find out what container the customer requested
// The price of a container depends on which one the customer selected
if (cbxContainers.Text == "Cone")
priceContainer = 0.55;
else if (cbxContainers.Text == "Cup")
priceContainer = 0.75;
else
priceContainer = 1.15;
// If the customer selected an ingredient, which is not "None", add $.95
if (cbxIngredients.Text != "None")
priceIngredient = 0.95;
try
{
// Get the number of scoops
numberOfScoops = int.Parse(this.txtScoops.Text);
if (numberOfScoops == 2)
priceScoops = 2.55;
else if (numberOfScoops == 3)
priceScoops = 3.25;
else
priceScoops = 1.85;
}
catch (FormatException)
{
MessageBox.Show("The value you entered for the scoops is not valid" +
"\nOnly natural numbers such as 1, 2, or 3 are allowed" +
"\nPlease try again", "Clarksville Ice Cream",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
// Make sure the user selected a flavor,
// otherwise, there is no reason to process an order
if (cbxFlavors.Text != "")
orderTotal = priceScoops + priceContainer + priceIngredient;
txtOrderTotal.Text = orderTotal.ToString("F");
}
Combo Boxes and Databases
Data Entry With Combo Boxes
Besides the text box, the .NET Framework provides many other controls that use text. For example, to limit the number of text selections the user can make, you can provide a combo box. In this case, you can retrieve the item the user selected and pass its Text value to the intended column of the table. Here is an example:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
public class Exercise : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
Label lblEmployeeName;
TextBox txtEmployeeName;
Label lblMaritalStatus;
DomainUpDown dudMaritalStatus;
Button btnCreateDatabase;
Button btnAddEmployee;
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
void InitializeComponent()
{
btnCreateDatabase = new Button();
btnCreateDatabase.Text = "Create Database";
btnCreateDatabase.Location = new Point(12, 12);
btnCreateDatabase.Width = 120;
btnCreateDatabase.Click += new EventHandler(btnCreateDatabaseClick);
lblEmployeeName = new Label();
lblEmployeeName.AutoSize = true;
lblEmployeeName.Text = "Employee Name:";
lblEmployeeName.Location = new Point(12, 44);
txtEmployeeName = new TextBox();
txtEmployeeName.Location = new Point(110, 44);
lblMaritalStatus = new Label();
lblMaritalStatus.AutoSize = true;
lblMaritalStatus.Text = "Marital Status:";
lblMaritalStatus.Location = new Point(12, 66);
dudMaritalStatus = new DomainUpDown();
dudMaritalStatus.Items.Add("Single");
dudMaritalStatus.Items.Add("Married");
dudMaritalStatus.Items.Add("Separated");
dudMaritalStatus.Items.Add("Divorced");
dudMaritalStatus.Items.Add("Widow");
dudMaritalStatus.Location = new Point(110, 66);
btnAddEmployee = new Button();
btnAddEmployee.Text = "Add Employee";
btnAddEmployee.Location = new Point(12, 110);
btnAddEmployee.Width = btnCreateDatabase.Width;
btnAddEmployee.Click += new EventHandler(btnAddEmployeeClick);
Text = "Database Exercise";
Controls.Add(lblEmployeeName);
Controls.Add(txtEmployeeName);
Controls.Add(lblMaritalStatus);
Controls.Add(dudMaritalStatus);
Controls.Add(btnAddEmployee);
Controls.Add(btnCreateDatabase);
StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
}
void btnCreateDatabaseClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source='EXPRESSION';" +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("IF EXISTS (SELECT name " +
"FROM sys.databases WHERE name = N'Exercise1' " +
") " +
"DROP DATABASE Exercise1; " +
"CREATE DATABASE Exercise1;", cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source='EXPRESSION'; " +
"Database='Exercise1'; " +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE SCHEMA Personnel;",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source='EXPRESSION';" +
"Database='Exercise1'; " +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Personnel.Employees" +
"(" +
" EmployeeName nvarchar(50)," +
" MaritalStatus nvarchar(24)" +
");",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
private void btnAddEmployeeClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source='EXPRESSION';" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=SSPI;"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("INSERT INTO Personnel.Employees " +
"VALUES(N'" + txtEmployeeName.Text + "', N'" +
dudMaritalStatus.Text + "');",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
public class Program
{
[STAThread]
static int Main()
{
System.Windows.Forms.Application.Run(new Exercise());
return 0;
}
}
The problem with the text box is that a user may be tempted to type just about any value, including a value that is not appropriate. Fortunately, the .NET Framework provides alternate controls. One of the controls you can use it is the numeric up-down. That control imposes on the user to only select a value, which means the user cannot just type anything.
The values of some list-based controls are stored in an indexed list. When a user has made a (single) selection from such a control, you can get the index of the selection and pass it as the value of the column. Here is an example:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
public class Exercise : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
Label lblMaritalStatus;
ComboBox cbxMaritalStatus;
Button btnAddEmployee;
Button btnCreateDatabase;
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
void InitializeComponent()
{
btnCreateDatabase = new Button();
btnCreateDatabase.Text = "Create Database";
btnCreateDatabase.Location = new Point(12, 12);
btnCreateDatabase.Width = 120;
btnCreateDatabase.Click += new EventHandler(btnCreateDatabaseClick);
btnAddEmployee = new Button();
btnAddEmployee.Text = "Add Employee";
btnAddEmployee.Location = new Point(12, 76);
btnAddEmployee.Width = btnCreateDatabase.Width;
btnAddEmployee.Click += new EventHandler(btnAddEmployeeClick);
lblMaritalStatus = new Label();
lblMaritalStatus.AutoSize = true;
lblMaritalStatus.Text = "Marital Status:";
lblMaritalStatus.Location = new Point(12, 44);
cbxMaritalStatus = new ComboBox();
cbxMaritalStatus.Items.Add("Single");
cbxMaritalStatus.Items.Add("Married");
cbxMaritalStatus.Items.Add("Separated");
cbxMaritalStatus.Items.Add("Divorced");
cbxMaritalStatus.Items.Add("Widow");
cbxMaritalStatus.DropDownStyle = ComboBoxStyle.DropDownList;
cbxMaritalStatus.Location = new Point(120, 44);
Text = "Database Exercise";
Controls.Add(lblMaritalStatus);
Controls.Add(cbxMaritalStatus);
Controls.Add(btnAddEmployee);
Controls.Add(btnCreateDatabase);
StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
}
void btnCreateDatabaseClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source='EXPRESSION';" +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("IF EXISTS (SELECT name " +
"FROM sys.databases WHERE name = N'Exercise1' " +
") " +
"DROP DATABASE Exercise1; " +
"CREATE DATABASE Exercise1;", cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source='EXPRESSION'; " +
"Database='Exercise1'; " +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE SCHEMA Personnel;",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source='EXPRESSION';" +
"Database='Exercise1'; " +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Personnel.Employees" +
"(" +
" MaritalStatus int" +
");",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
private void btnAddEmployeeClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source='EXPRESSION';" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=SSPI;"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("INSERT INTO Personnel.Employees " +
"VALUES(" + cbxMaritalStatus.SelectedIndex + ");",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
public class Program
{
[STAThread]
static int Main()
{
System.Windows.Forms.Application.Run(new Exercise());
return 0;
}
}
Combo Boxes and Data Selection
A combo box is made to show a list of values. When it comes to a database,, a combo box can show one, some, or all of the values of a column of a table. As a descendant of the Control class, the combo box has a Text property. This means that it primarily follows the ways a label or text box displays the value of a column of a table; but showing just one value would deceive the purpose of using a combo box.
If the values of a column are each unique, you can use a data reader to get each value and add it to the combo box. Here is an example:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
public class Exercise : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
Label lblEmployeeName;
TextBox txtEmployeeName;
Label lblEmploymentStatus;
ComboBox cbxEmploymentsStatus;
Button btnBinder;
Button btnCreateDatabase;
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
void InitializeComponent()
{
btnCreateDatabase = new Button();
btnCreateDatabase.Text = "Create Database";
btnCreateDatabase.Location = new Point(12, 12);
btnCreateDatabase.Width = 120;
btnCreateDatabase.Click += new EventHandler(btnCreateDatabaseClick);
btnBinder = new Button();
btnBinder.Text = "Bind";
btnBinder.Location = new Point(140, 12);
btnBinder.Click += new EventHandler(btnBinderClick);
lblEmployeeName = new Label();
lblEmployeeName.AutoSize = true;
lblEmployeeName.Text = "Employee Name:";
lblEmployeeName.Location = new Point(12, 44);
txtEmployeeName = new TextBox();
txtEmployeeName.Location = new Point(140, 44);
lblEmploymentStatus = new Label();
lblEmploymentStatus.Text = "Status";
lblEmploymentStatus.Location = new Point(12, 70);
cbxEmploymentsStatus = new ComboBox();
cbxEmploymentsStatus.Location = new Point(140, 70);
cbxEmploymentsStatus.DropDownStyle = ComboBoxStyle.DropDownList;
Text = "Database Exercise";
Controls.Add(lblEmployeeName);
Controls.Add(txtEmployeeName);
Controls.Add(btnBinder);
Controls.Add(btnCreateDatabase);
Controls.Add(lblEmploymentStatus);
Controls.Add(cbxEmploymentsStatus);
StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
}
void btnCreateDatabaseClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); " +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("IF EXISTS (SELECT name " +
"FROM sys.databases WHERE name = N'Exercise1' " +
") " +
"DROP DATABASE Exercise1; " +
"CREATE DATABASE Exercise1;", cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); Database='Exercise1'; " +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE SCHEMA Personnel;", cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); Database='Exercise1'; " +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Personnel.EmploymentsStatus(EmplStatus nvarchar(20), " +
"Notes nvarchar(max));", cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); Database='Exercise1'; " +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("INSERT INTO Personnel.EmploymentsStatus(EmplStatus) " +
"VALUES(N'Full Time')," +
" (N'Part Time')," +
" (N'Unspecified');",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); Database='Exercise1'; " +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Personnel.Employees(EmployeeNumber nvarchar(8), " +
"FirstName nvarchar(24), LastName nvarchar(24), " +
"EmployeeName AS LastName + N', ' + FirstName," +
"Title nvarchar(50), EmplStatus nvarchar(20));", cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local); Database='Exercise1'; " +
"Integrated Security='SSPI';"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("INSERT INTO Personnel.Employees(EmployeeNumber, " +
"FirstName, LastName, Title, EmplStatus) " +
"VALUES(N'927049', N'Aaron', N'Swanson', N'General Owner', N'Full Time')," +
" (N'297113', N'Jane', N'Simms', 'Account Associate', N'Full Time')," +
" (N'804070', N'Justine', N'Aronson', 'Accountant', N'Part Time')," +
" (N'284825', N'Paul', N'DaCosta', 'Webmaster', N'Unspecified')," +
" (N'508085', N'Peter', N'Mukoko', 'Acquisition Support', N'Part Time')," +
" (N'380408', N'Desmond', N'Perez', 'Account Associate', N'Full Time');",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
private void btnBinderClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
cbxEmploymentsStatus.Items.Clear();
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=SSPI;"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise = new SqlCommand("SELECT ALL * FROM Personnel.EmploymentsStatus;",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
SqlDataReader rdrEmployees = cmdExercise.ExecuteReader();
while(rdrEmployees.Read())
{
cbxEmploymentsStatus.Items.Add(rdrEmployees[0].ToString());
}
}
}
}
public class Program
{
[STAThread]
static int Main()
{
System.Windows.Forms.Application.Run(new Exercise());
return 0;
}
}
If the column has repeating values and you use the same technique, the combo box also would have repeating values. In most cases, this would not be professional. To make sure the combo box displays unique values, you can various alternatives. You can use a loop to check whether the combo box has a certain value already and decide whether to add or ignore the value. Here is an example:
private void btnBinderClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
cbxEmploymentsStatus.Items.Clear();
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=SSPI;"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise = new SqlCommand("SELECT ALL * FROM Personnel.Employees;",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
SqlDataReader rdrEmployees = cmdExercise.ExecuteReader();
while(rdrEmployees.Read())
{
// Add the value only if it't not yet in the combo box
if (!cbxEmploymentsStatus.Items.Contains(rdrEmployees[5].ToString()))
cbxEmploymentsStatus.Items.Add(rdrEmployees[5].ToString());
}
}
}
An alternative is to apply the DISTINCT keyword to the SELECT statement. Here is an example:
private void btnBinderClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
cbxEmploymentsStatus.Items.Clear();
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=SSPI;"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise = new SqlCommand("SELECT DISTINCT(EmplStatus) FROM Personnel.Employees;",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
SqlDataReader rdrEmployees = cmdExercise.ExecuteReader();
while(rdrEmployees.Read())
{
cbxEmploymentsStatus.Items.Add(rdrEmployees[0].ToString());
}
}
}
|
|
||
| Home | Copyright © 2010-2020, FunctionX | |
|
|
||