
ADO.NET and Paradox
 |
ADO.NET and Paradox |
ADO.NET allows you to create a GUI database application that can connect to almost any type of database used on Microsoft Windows. Besides SQL Server, Microsoft Access, and Oracle, you can also create an application that connects to a Paradox database. This can be done through ODBC as implemented in ADO.NET.
If you plan to create a database application that would use a Paradox database, you can start by opening Paradox. After launching Paradox, locate the directory alias you want to use or create one. For this application, we will use the C:\Programs\FunctionX directory and we had created its alias as Data
After creating or locating the alias and selecting it in Paradox, you can create the necessary table(s) by clicking File -> New -> Table... from Paradox' main menu:
After creating the table, you should save it:
After creating and saving the table, you can enter a few records to test it. To do this, you can first close then open it and click View -> Edit Data from the main menu: |

|
Creating a Data Source |
|
To create a connection to a Paradox database, you can use ODBC as it is featured in ADO.NET. Before doing this, you can create a data source. To do this, you can double-click the Data Source (ODBC) icon from Control Panel. In the ODBC Data Source Administrator, click New. In the the Create New Data Source dialog box, select Microsoft Paradox Driver (*.db):
Click Finish. In the ODBC Paradox Setup dialog box, enter a name in the Data Source Name text box:
Click OK twice. |
|
Application Creation |
|
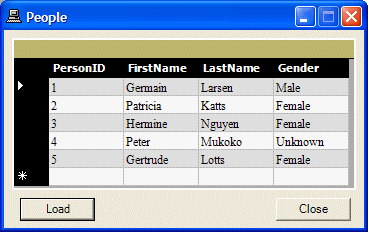
After creating a Paradox table and its ODBC data source, you can start a Windows Forms Application like any other. In its simplest format, you can equip a for with a DataGrid control and a button as follows:
To create a connection to a Paradox table, you can first declare a variable of type OdbcConnection. You can either use its second constructor that takes a string or you can access its ConnectionString property. Either of these allows you to specify how the connection would be carried. Here is an example: |
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Odbc;
namespace WindowsApplication37
{
/// <summary>
/// Summary description for Form1.
/// </summary>
public class PeopleView : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.Windows.Forms.DataGrid dataGrid1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button btnLoad;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button btnClose;
/// <summary>
/// Required designer variable.
/// </summary>
private System.ComponentModel.Container components = null;
public PeopleView()
{
//
// Required for Windows Form Designer support
//
InitializeComponent();
//
// TODO: Add any constructor code after InitializeComponent call
//
}
/// <summary>
/// Clean up any resources being used.
/// </summary>
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
#region Windows Form Designer generated code
/// <summary>
/// Required method for Designer support - do not modify
/// the contents of this method with the code editor.
/// </summary>
private void InitializeComponent()
{
System.Resources.ResourceManager resources = new System.Resources.ResourceManager(typeof(PeopleView));
this.dataGrid1 = new System.Windows.Forms.DataGrid();
this.btnLoad = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.btnClose = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this.dataGrid1)).BeginInit();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// dataGrid1
//
this.dataGrid1.AlternatingBackColor = System.Drawing.Color.WhiteSmoke;
this.dataGrid1.BackColor = System.Drawing.Color.Gainsboro;
this.dataGrid1.BackgroundColor = System.Drawing.Color.DarkGray;
this.dataGrid1.BorderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle.FixedSingle;
this.dataGrid1.CaptionBackColor = System.Drawing.Color.DarkKhaki;
this.dataGrid1.CaptionFont = new System.Drawing.Font("Tahoma", 8F, System.Drawing.FontStyle.Bold);
this.dataGrid1.CaptionForeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Black;
this.dataGrid1.DataMember = "";
this.dataGrid1.FlatMode = true;
this.dataGrid1.Font = new System.Drawing.Font("Times New Roman", 9F);
this.dataGrid1.ForeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Black;
this.dataGrid1.GridLineColor = System.Drawing.Color.Silver;
this.dataGrid1.HeaderBackColor = System.Drawing.Color.Black;
this.dataGrid1.HeaderFont = new System.Drawing.Font("Tahoma", 8F, System.Drawing.FontStyle.Bold);
this.dataGrid1.HeaderForeColor = System.Drawing.Color.White;
this.dataGrid1.LinkColor = System.Drawing.Color.DarkSlateBlue;
this.dataGrid1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(8, 8);
this.dataGrid1.Name = "dataGrid1";
this.dataGrid1.ParentRowsBackColor = System.Drawing.Color.LightGray;
this.dataGrid1.ParentRowsForeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Black;
this.dataGrid1.SelectionBackColor = System.Drawing.Color.Firebrick;
this.dataGrid1.SelectionForeColor = System.Drawing.Color.White;
this.dataGrid1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(344, 152);
this.dataGrid1.TabIndex = 0;
//
// btnLoad
//
this.btnLoad.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(16, 168);
this.btnLoad.Name = "btnLoad";
this.btnLoad.TabIndex = 1;
this.btnLoad.Text = "Load";
this.btnLoad.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.btnLoad_Click);
//
// btnClose
//
this.btnClose.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(272, 168);
this.btnClose.Name = "btnClose";
this.btnClose.TabIndex = 2;
this.btnClose.Text = "Close";
this.btnClose.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.btnClose_Click);
//
// PeopleView
//
this.AutoScaleBaseSize = new System.Drawing.Size(5, 13);
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(360, 198);
this.Controls.Add(this.btnClose);
this.Controls.Add(this.btnLoad);
this.Controls.Add(this.dataGrid1);
this.Icon = ((System.Drawing.Icon)(resources.GetObject("$this.Icon")));
this.MaximizeBox = false;
this.Name = "PeopleView";
this.StartPosition = System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
this.Text = "People";
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this.dataGrid1)).EndInit();
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// The main entry point for the application.
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new PeopleView());
}
private void btnLoad_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
OdbcConnection conPeople = new OdbcConnection("DSN=People;DefaultDir=C:\\Programs\\FunctionX;" +
"DBQ=C:\\Programs\\FunctionX;");
String strSelection = "SELECT Persons.* FROM Persons";
OdbcCommand cmdPeople = new OdbcCommand(strSelection, conPeople);
OdbcDataAdapter odaPeople = new OdbcDataAdapter(cmdPeople);
DataSet dsPersons = new DataSet("Persons");
odaPeople.Fill(dsPersons);
this.dataGrid1.DataSource = dsPersons;
this.dataGrid1.DataMember = dsPersons.Tables[0].TableName;
conPeople.Open();
conPeople.Close();
}
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
}
}
 |
|
|
||
| Home | Copyright © 2005-2016, FunctionX | |
|
|
||