 |
Microsoft Visual C#: The Types of Relationships |
|
|
Creating and Using Relationships |
|
|
A One-to-Many Relationship: A Re-Introduction to
Relationships |
|
|
|
In a typical database, you can create, among other
things, two tables that each has a primary key and one of them has a foreign
key. As seen previously, the foreign key allows a child table to get records
from a parent table.
|
Normally, each record in the child table gets 0 or only
one value from the parent table and a record in the parent table can provide
one of its values to many records of the child table. An example would be a
list of employees where each employee belongs to a department. Obviously,
each employee can belong to only one department but many employees can
belong to the same department. This can be illustrated as follows:

This type of relationship is referred to as one-to-many.
This is the most regular type of relationship used in a relational database
and that's the type we have used so far.
|
 Practical
Learning: Creating a One-to-Many Relationship Practical
Learning: Creating a One-to-Many Relationship
|
|
- Start Microsoft Visual Studio
- To start a new applicaiton, on the main menu, click File -> New
Project...
- In the middle list, click Windows Forms Application and set the Name
to MonsonUniversity1
- Click OK
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click Form1.cs and click Rename
- Type MonsonUniversity.cs and press Enter
- Double-click the middle of the form and change the file as follows:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace MonsonUniversity1
{
public partial class MonsonUniversity : Form
{
public MonsonUniversity()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
internal void CreateDatabase()
{
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("IF EXISTS (" +
"SELECT name " +
"FROM sys.databases " +
"WHERE name = N'MonsonUniversity1')" +
"DROP DATABASE MonsonUniversity1; " +
"CREATE DATABASE MonsonUniversity1;", cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The SouthernEnergyCorp1 database has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE SCHEMA Academics;", cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("A new schema named Academics has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE SCHEMA Admissions;", cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("A new schema named Admissions has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE SCHEMA Administration;", cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("A new schema named Administration has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE SCHEMA Accounting;", cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("A new schema named Accounting has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Administration.Departments( " +
"DepartmentCode nchar(4) not null, " +
"Name nvarchar(50) not null, " +
"Constraint PK_Departments Primary Key(DepartmentCode));",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The Departments table has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Administration.Employees(" +
"EmployeeNumber nchar(8) not null," +
"FirstName nvarchar(20)," +
"MiddleName nvarchar(20)," +
"LastName nvarchar(20) not null," +
"DepartmentCode nchar(4)" +
" Constraint FK_Departments " +
" References Administration.Departments(DepartmentCode)," +
"Title nvarchar(50)," +
"HourlySalary money," +
"Constraint PK_Employees Primary Key(EmployeeNumber));",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The Employees table has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Academics.Majors(" +
"MajorID int identity(1001, 1) not null," +
"Major nvarchar(40)," +
"EmployeeNumber nchar(8) not null" +
" Constraint FK_Deans " +
" References Administration.Employees(EmployeeNumber)," +
"Constraint PK_Majors Primary Key(MajorID));",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The Majors table has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Academics.Minors(" +
"MinorID int identity(1001, 1) not null," +
"Minor nvarchar(40)," +
"Constraint PK_Minors Primary Key(MinorID));",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The Minors table has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Admissions.Semesters(" +
"SemesterID int identity(10001, 1) not null, " +
"Semester nvarchar(40), " +
"Constraint PK_Semesters Primary Key(SemesterID));",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The Semesters table has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Academics.Courses(" +
"CourseCode nchar(8) not null, " +
"CourseName nvarchar(100), " +
"Credits smallint not null, " +
"CourseDescription nvarchar(max), " +
"Constraint PK_Courses Primary Key(CourseCode));",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The Courses table has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Admissions.Students(" +
"StudentNumber nchar(8) not null, " +
"FirstName nvarchar(20), " +
"MiddleName nvarchar(20), " +
"LastName nvarchar(20), " +
"AcademicCategory nvarchar(40), " + // Graduate or Undergraduate
"MajorID int " +
" Constraint FK_StudentsMajors " +
" References Academics.Majors(MajorID), " +
"MinorID int " +
" Constraint FK_StudentsMinors " +
" References Academics.Minors(MinorID), " +
"Constraint PK_Students Primary Key(StudentNumber));",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The Students table has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
private void MonsonUniversity_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
CreateDatabase();
}
}
}
- Press Ctrl + F5 to execute
- Click OK on each message box
- Close the form and return to your programming environment
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
| Button |
 |
Majors |
btnMajors |
| Button |
 |
Minors |
btnMinors |
| Button |
 |
Semesters |
btnSemesters |
| Button |
 |
Courses |
btnCourses |
| Button |
 |
Employees |
btnEmployees |
| Button |
 |
Departments |
btnDepartments |
| Button |
 |
Students |
btnStudents |
| Button |
 |
Close |
btnClose |
|
- On the main menu, click Data -> Show Data Sources
- In the Data Sources window, click Add New Data Source...
- On the first page of the wizard, make sure Database is selected and
click Next
- In the second page of the wizard, make sure Dataset is selected and
click Next
- In the third page of the wizard, click New Connection...
- In the Server Name combo box, select the server or type
(local)
- In the Select or Enter a Database Name combo box, select
MonsonUniversity1
- Click Test Connection
- Click OK twice
- On the Data Source Configuration Wizard, make sure the
MonsonUniversity1 connection is selected
Click the + button of
Connection String
- Click Next
- Change the connection string to csMonsonUniversity
- Click Next
- Click the check box of Tables (to select all tables)
- Change the name of the data set to dsMonsonUniversity

- Click Finish
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows Form...
- Change the name to Majors
- Click Add
- From the Data Sources window, drag Majors and drop it on the form
- Adjust the design as you see fit. Here is an example:

- On the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows Form...
- Change the name to Minors
- Click Add
- From the Data Sources window, drag Minors and drop it on the form
- Adjust the design as you see fit. Here is an example:

- On the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows Form...
- Change the name to Semesters
- Click Add
- From the Data Sources window, drag Minors and drop it on the form
- Adjust the design as you see fit. Here is an example:

- On the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows Form...
- Change the name to Courses
- Click Add
- From the Data Sources window, drag Minors and drop it on the form
- Adjust the design as you see fit. Here is an example:

- On the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows Form...
- Change the name to Departments
- Click Add
- From the Data Sources window, drag Minors and drop it on the form
- Adjust the design as you see fit. Here is an example:
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows Form...
- Change the name to Employees
- Click Add
- From the Data Sources window, drag Minors and drop it on the form
- Under the form, click the binding source item and, using the
Properties window, change its (Name) to bsEmployees
- Design the form as follows:

|
| Control |
Name |
Text |
Other Properties |
| DataGridView |
|
|
|
Anchor: Top, Bottom, Left, Right |
| Group Box |
 |
|
Filtering Records |
Anchor: Bottom, Left, Right |
| RadioButton |
 |
rdoShowAll |
Show all employees |
|
| RadioButton |
 |
rdoDepartment |
Show only employees of the |
|
| ComboBox |
 |
cbxDepartments |
|
DropDownStyle: DropDownList |
| Label |
 |
|
department |
|
| RadioButton |
 |
rdoDeans |
Show deans only |
|
| RadioButton |
 |
rdoDeansAndPresidents |
Show deans and presidents |
|
| Label |
 |
|
Records |
Anchor: Top, Left, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
txtCount |
0 |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Button |
 |
btnClose |
Close |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
|
- Right-click the form and click View Code
- Change the Load event as follows:
private void Employees_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.taEmployees.Fill(this.dsMonsonUniversity.Employees);
// Fill the combo box with the departments codes
foreach (DataRow row in dsMonsonUniversity.Employees.Rows)
if (!cbxDepartments.Items.Contains(row["DepartmentCode"]))
cbxDepartments.Items.Add(row["DepartmentCode"]);
// Show the current number of records
txtCount.Text = dsMonsonUniversity.Employees.Count.ToString();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the first radio button
- Implement its event as follows:
private void rdoShowAll_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bsEmployees.Filter = "";
txtCount.Text = bsEmployees.Count.ToString();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the second radio button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void rdoDepartment_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// If nothing is selected in the combo box, there is no filter
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(cbxDepartments.Text))
bsEmployees.Filter = "";
else // If a department is selected, apply it to the filter
bsEmployees.Filter = "DepartmentCode = '" + cbxDepartments.Text + "'";
// Show the current number of records
txtCount.Text = bsEmployees.Count.ToString();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the combo box
- Implement its event:
private void cbxDepartments_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// If the corresponding radio button is selected, select it
rdoDepartment.Checked = true;
// Behave as if the radio button was clicked
rdoDepartment_CheckedChanged(sender, e);
}
- Return to the form and double-click the third radio button
- Implement the top event as follows:
private void rdoDeans_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bsEmployees.Filter = "Title LIKE '%dean%'";
txtCount.Text = bsEmployees.Count.ToString();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the fourth radio button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void rdoDeansAndPresidents_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bsEmployees.Filter = "(Title LIKE '%dean%') OR (Title LIKE '%president%')";
txtCount.Text = bsEmployees.Count.ToString();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the Close button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
- On the main menu, click Project -> Add Windows Form...
- Change the name to Students
- Click Add
- From the Data Sources window, drag Minors and drop it on the form
- Under the form, click the binding source item and, using the
Properties window, change its (Name) to bsEmployees
- Design the form as follows:

|
| Control |
Name |
Text |
Other Properties |
| DataGridView |
|
|
|
Anchor: Top, Bottom, Left, Right |
| Group Box |
 |
|
Filtering Records |
Anchor: Bottom, Left, Right |
| RadioButton |
 |
rdoShowAll |
Show all students |
|
| RadioButton |
 |
rdoStudentNumber |
Show the record whose student number is |
|
| TextBox |
 |
txtStudentNumber |
|
|
| Button |
 |
btnStudentNumber |
Show |
|
| RadioButton |
 |
rdoLastName |
Show only students whose last name is or contains |
|
| TextBox |
 |
txtLastName |
|
|
| Button |
 |
btnLastName |
Show |
|
| RadioButton |
 |
rdoMajor |
Show only students whose major is |
|
| TextBox |
 |
txtMajor |
|
|
| Button |
 |
btnMajor |
Show |
|
| Label |
 |
|
Records |
Anchor: Top, Left, Right |
| TextBox |
 |
txtCount |
0 |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
| Button |
 |
btnClose |
Close |
Anchor: Bottom, Right |
|
- Double-click the first radio button
- Implement its event as follows:
private void rdoShowAll_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bsStudents.Filter = "";
txtCount.Text = bsStudents.Count.ToString();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the first Show button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnStudentNumber_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtStudentNumber.Text))
return;
rdoStudentNumber.Checked = true;
bsStudents.Filter = "StudentNumber = '" + txtStudentNumber.Text + "'";
txtCount.Text = bsStudents.Count.ToString();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the second Show button
- Implement its event:
private void btnLastName_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtLastName.Text))
return;
rdoLastName.Checked = true;
bsStudents.Filter = "LastName LIKE '%" + txtLastName.Text + "%'";
txtCount.Text = bsStudents.Count.ToString();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the third Show button
- Implement the top event as follows:
private void btnMajor_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtMajor.Text))
return;
rdoMajor.Checked = true;
bsStudents.Filter = "MajorID = " + int.Parse(txtMajor.Text);
txtCount.Text = bsStudents.Count.ToString();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the Close button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
- Display the first form
- Double-click the Majors button and implement its event as follows:
private void MonsonUniversity_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// CreateDatabase();
}
private void btnMajors_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Majors studies = new Majors();
studies.ShowDialog();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the Minors button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnMinors_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Minors studies = new Minors();
studies.ShowDialog();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the Semesters button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnSemesters_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Semesters sems = new Semesters();
sems.ShowDialog();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the Courses button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnCourses_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Courses studies = new Courses();
studies.ShowDialog();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the Employees button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnEmployees_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Employees staff = new Employees();
staff.ShowDialog();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the Departments button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnDepartments_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Departments dept = new Departments();
dept.ShowDialog();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the Students button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnStudents_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Students pupils = new Students();
pupils.ShowDialog();
}
- Execute the application
- Click the Departments button
- On the Departments form, click the Add New button
- Create the following departments:
| DepartmentCode |
Name |
| HRMN |
Human Resources - Personnel |
| ADMS |
Admissions - Students Affairs |
| FINA |
Finances - Accounting |
| ITEC |
Information Technology |
- Click the Save button
- Close the Departments form
- Create the following employees:
| Empl # |
First Name |
Middle Name |
Last Name |
Department Code |
Title |
Hourly Salary |
| 27922702 |
Donald |
Henry |
Leighton |
HRMN |
President |
|
| 50249441 |
Anthony |
Robert |
Parrish |
HRMN |
Provost |
|
| 19302484 |
Jeannette |
Veronica |
Holms |
HRMN |
Vice President for Government Relations |
|
| 20485052 |
Simon |
|
Lew |
FINA |
Vice-President and Chief Financial Officer |
|
| 27559475 |
Kellie |
Joan |
Tierney |
ADMS |
Vice-President and Dean of Undergraduate Studies |
|
| 38188248 |
Charles |
|
McAhan |
ITEC |
Vice-President and Chief Technology Officer |
|
| 90804792 |
Ann |
Laura |
Tenney |
FINA |
Cashier |
16.62 |
| 79700429 |
Judith |
Suzie |
London |
ADMS |
Dean of Business Studies |
|
| 16113841 |
Laura |
Fannie |
Joansen |
ADMS |
Dean of Litterary Studies |
|
| 11395822 |
Richard |
Matthew |
Little |
ITEC |
IT Support |
22.04 |
| 30840724 |
Fatima |
Georgia |
Williams |
FINA |
Accountant |
24.86 |
| 16173974 |
Veronica |
Bethanie |
Pitts |
ADMS |
Dean of Commercial and Financial Studies |
|
| 97417315 |
Eleanor |
Virginia |
Pearlman |
ITEC |
Webmaster |
18.72 |
| 20000582 |
Catherine |
|
Lehmann |
ADMS |
Intern |
12.47 |
| 24759135 |
|
|
Hawthorne |
ADMS |
Dean of History and Geography |
|
| 64020757 |
Kimberly |
Carlette |
Edelman |
ADMS |
Dean of Socioly and Psychology |
|
| 94273941 |
Martin |
Andrew |
Schweinstenman |
FINA |
Cashier |
15.55 |
| 79384795 |
Seraphine |
Angie |
Roeper |
ADMS |
Dean of Business Studies |
|
| 92748695 |
Robert |
John |
Preston |
ADMS |
|
Dean of Computer Studies |
- Close the Employees form
- Create the following majors:
| Major |
EmployeeNumber |
| Accounting |
79384795 |
| Business Administration |
79384795 |
| English |
16113841 |
| History |
24759135 |
| Finance |
16173974 |
| Computer Information Technology |
92748695 |
| Computer Science |
92748695 |
| Marketing |
16173974 |
| Criminal Justice |
16113841 |
| Information Systems Management |
92748695 |
| Psychology |
64020757 |
- Create the following minors:
| Minor |
| Accounting |
| African American Studies |
| Art History |
| English |
| Business Administration |
| Computing |
| Criminal Justice |
| Forensics |
| Economics |
| Finance |
| Mathematical Sciences |
| Marketing |
| Philosophy |
| Political Science |
| Psychology |
| Sociology |
| Speech Communication |
| Women''s Studies |
- Create the following semester:
| Semester |
| FALL 2010 |
| SUMMER 2010 |
| SPRING 2010 |
| FALL 2011 |
| SUMMER 2011 |
| SPRING 2011 |
| FALL 2012 |
| SUMMER 2012 |
| SPRING 2012 |
| FALL 2013 |
| SUMMER 2013 |
| SPRING 2013 |
- Create the following courses:
| CourseCode |
CourseName |
Credits |
| ACCT 220 |
Principles of Accounting I |
3 |
| ACCT 221 |
Principles of Accounting II |
3 |
| ACCT 310 |
Intermediate Accounting I |
3 |
| ACCT 311 |
Intermediate Accounting II |
3 |
| ACCT 320 |
Fraud Detection and Deterrence |
3 |
| BEHS 220 |
Diversity Awareness |
3 |
| BEHS 365 |
Individuals, Society and Environmental Sustainability |
3 |
| BMGT 110 |
Introduction to Business and Management |
3 |
| BMGT 304 |
Managing E-Commerce in Organizations |
3 |
| BMGT 312 |
Women in Business |
3 |
| CMIS 101 |
Introduction to Problem Solving and Algorithm Design |
3 |
| CMIS 170 |
Introduction to XML |
3 |
| CMIS 320 |
Relational Databases |
3 |
| CMIS 420 |
Advanced Relational Databases |
3 |
| CMST 306 |
Introduction to Visual Basic Programming |
3 |
| CMST 385 |
Internet and Web Design |
3 |
| ENGL 240 |
Introduction to Fiction, Poetry, and Drama |
3 |
| ENGL 454 |
Modern World Drama |
3 |
| HIST 104 |
Introduction to Archaeology |
3 |
| HIST 115 |
World History I |
3 |
| HIST 116 |
World History II |
3 |
| PSYC 100 |
Introduction to Psychology |
3 |
| PSYC 306 |
Psychology of Happiness |
1 |
| PSYC 307 |
Parapsychology |
1 |
| PSYC 308 |
Introduction to Black Psychology |
1 |
| WRTG 101 |
Introduction to Writing |
3 |
| WRTG 288 |
Standard English Grammar |
3 |
| WRTG 388 |
Advanced Grammar and Style |
3 |
| WRTG 394 |
Advanced Business Writing |
3 |
- Create the following students:
| StudentNumber |
FirstName |
MiddleName |
LastName |
AcademicCategory |
MajorID |
MinorID |
| 88130480 |
Marie |
Annette |
Robinson |
Undergraduate |
1003 |
1003 |
| 24795711 |
Roger |
Dermot |
Baker |
Undergraduate |
1005 |
1002 |
| 18073572 |
Patrick |
|
Wisne |
Undergraduate |
1001 |
1004 |
| 97394285 |
Jessica |
Danielle |
Shepard |
Undergraduate |
1007 |
1001 |
| 94708257 |
Christopher |
Sheldon |
Jones |
Undergraduate |
1002 |
1005 |
| 48009520 |
Diane |
|
Rossi |
Undergraduate |
1006 |
1009 |
| 20947085 |
Linette |
Jeanne |
Robin |
Graduate |
|
|
| 82475364 |
Heidy |
Judith |
Cooke |
Graduate |
|
|
| 29480759 |
Maxwell |
Peter |
Carlson |
Undergraduate |
1007 |
1007 |
| 72938479 |
Marc |
Kenny |
Dickson |
Undergraduate |
1009 |
1005 |
| 31741957 |
Joel |
Alexander |
Elliott |
Graduate |
|
|
| 61824668 |
Stephen |
David |
Kramer |
Undergraduate |
1006 |
1002 |
| 27582647 |
Kimberly |
Julie |
Wise |
Undergraduate |
1008 |
1013 |
| 92847957 |
Emmanuel |
|
Orenstein |
Undergraduate |
1007 |
1001 |
| 20946681 |
Becky |
|
Wilkopf |
Graduate |
|
|
| 24928472 |
Albert |
Kevin |
Thorne |
Undergraduate |
1002 |
1006 |
| 27114857 |
Michael |
Alexander |
Horns |
Undergraduate |
1001 |
1005 |
| 37495884 |
Daniel |
Joseph |
Wiser |
Graduate |
|
|
| 71513159 |
Berthe |
Henriette |
Essimbi |
Undergraduate |
1003 |
1001 |
| 28374957 |
Billie |
Judith |
Cannon |
Undergraduate |
1006 |
1008 |
| 82580947 |
Steve |
Bruce |
Maxwell |
Undergraduate |
1002 |
1004 |
| 20409220 |
Jasmine |
|
Campino |
Undergraduate |
1010 |
1005 |
| 92584668 |
Jeoseph |
David |
Callahan |
Undergraduate |
1007 |
1009 |
| 79272413 |
Steve |
Alan |
Philbrick |
Undergraduate |
1011 |
1015 |
| 20488400 |
Joseph |
|
Beal |
Undergraduate |
1004 |
1006 |
| 92084157 |
Daniella |
Helen |
Politanoff |
Graduate |
|
|
| 97013268 |
Lucy |
Andrea |
Harding |
Graduate |
|
|
| 20204862 |
James |
|
Kennan |
Undergraduate |
1006 |
1010 |
- Close the forms and return to your programming environment
|
A Variance to a One-To-Many Relationship
|
|
Mutual reference is a scenario in which each of two
tables references the other. As a variant to a one-to-many relationship,
some records of a table A may get their foreign value from a table B, then
some records of table B may get their foreign value from a table C, and
finally some records of table C would get their foreign value from table A.
Another variant is where some records of a table A would
get their foreign value from a table B but also some records of the table B
would get their foreign value from table A. To illustrate, once again
imagine you have a table of employees and each employee is recorded as
belonging to a certain department. Obviously, an employee can (should)
belong to only one department. This can be illustrated as follows:

For each department, you may want to specify who the
manager is. Obviously, the manager must be an employee, from the table of
employees. This can be illustrated as follows:

Here is an example of creating the tables and their
constraints:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace TopicsOnDataRelationships
{
public partial class Exercise : Form
{
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnCreateDatabase_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=SSPI;"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE SCHEMA Management;",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=SSPI;"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE SCHEMA Personnel;", cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Management.Departments( " +
"DepartmentCode nchar(4) not null, " +
"Name nvarchar(50) not null, " +
"EmployeeNumber nchar(6), " +
"Constraint PK_Departments Primary Key(DepartmentCode));",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Personnel.Employees(" +
"EmployeeNumber nchar(6) not null, " +
"FirstName nvarchar(20), " +
"LastName nvarchar(20) not null, " +
"Title nvarchar(50), " +
"HourlySalary money, " +
"DepartmentCode nchar(4) " +
" Constraint FK_Departments References " +
"Management.Departments(DepartmentCode), " +
"Constraint PK_Employees Primary Key(EmployeeNumber));",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The databas has been created.",
"Exercise",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
}
}
If you decide to create a diagram (especially if you
didn't create the primary and foreign keys), you should have a link going
from each table to the other, using the appropriate fields. Here is an
example:

When creating the records, you can proceed as done so
far. Here are examples:
private void btnCreateRecords_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("INSERT Management.Departments(DepartmentCode, Name)" +
"VALUES(N'HRMN', N'Human Resources')," +
" (N'ITEC', N'Information Technology')," +
" (N'PRSN', N'Personnel');",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("INSERT Personnel.Employees " + // (EmployeeNumber, FirstName, LastName, Title, HourlySalary, DepartmentCode)
"VALUES (N'792702', N'Frank', N'Cassini', N'General Manager', 30.25, N'HRMN')," +
" (N'249441', N'Patrick', N'Levine', N'Regional Manager', 28.46, N'HRMN')," +
" (N'302484', N'Catherine', N'Borrow', N'Shift Supervisor', 25.72, N'PRSN')," +
" (N'485052', N'Jerry', N'Fesman', N'Head Cashier', 18.64, N'PRSN')," +
" (N'279475', N'Alex', N'Simkins', N'Intern', 12.48, N'PRSN')," +
" (N'908047', N'Grace', N'McDermott', N'Cashier', 14.72, N'PRSN')," +
" (N'395822', N'Craig', N'Newman', N'IT Support', 20.26, N'ITEC')," +
" (N'381848', N'John', N'Hough', N'Cashier', 13.52, N'PRSN')," +
" (N'300724', N'Matt', N'Kern', N'Accountant', 24.58, N'HRMN')," +
" (N'974115', N'Elsa', N'Steinberg', N'Webmaster', 16.94, N'ITEC')," +
" (N'974005', N'David', N'Miller', N'Intern', 10.48, N'ITEC')," +
" (N'273941', N'Jessica', N'Redding', N'Cashier', 12.63, N'PRSN');",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("UPDATE Management.Departments " +
"SET EmployeeNumber = N'792702' WHERE DepartmentCode = N'HRMN';",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("UPDATE Management.Departments " +
"SET EmployeeNumber = N'249441' WHERE DepartmentCode = N'ITEC';",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("UPDATE Management.Departments " +
"SET EmployeeNumber = N'302484' WHERE DepartmentCode = N'PRSN';",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The records have been created.",
"Exercise",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
private void btnShowRecords_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntEmployees =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdEmployees =
new SqlCommand("SELECT * FROM Personnel.Employees; ",
cntEmployees);
SqlDataAdapter sdaEmployees = new SqlDataAdapter(cmdEmployees);
DataSet dsEmployees = new DataSet("EmployeesSet");
cntEmployees.Open();
sdaEmployees.Fill(dsEmployees);
dgvEmployees.DataSource = dsEmployees.Tables[0];
}
using (SqlConnection cntDepartments =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdDepartments =
new SqlCommand("SELECT * FROM Management.Departments; ",
cntDepartments);
SqlDataAdapter sdaDepartments = new SqlDataAdapter(cmdDepartments);
DataSet dsDepartments = new DataSet("EmployeesSet");
cntDepartments.Open();
sdaDepartments.Fill(dsDepartments);
dgvDepartments.DataSource = dsDepartments.Tables[0];
}
}
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
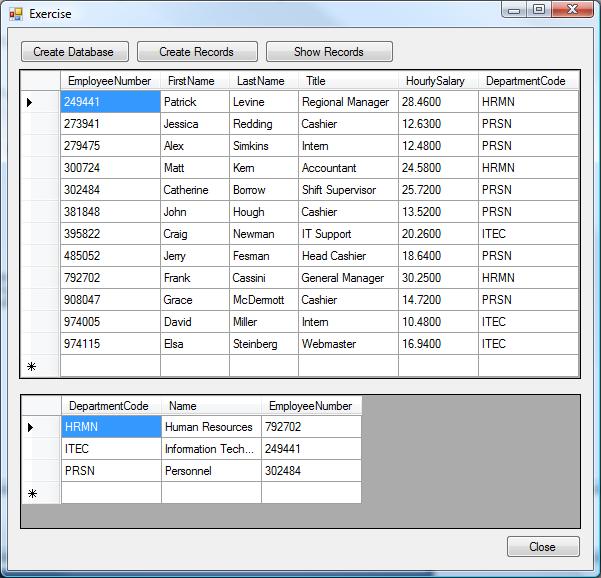
Using joins, you can create a statement that would show
the actual values of the fields. Here is an example:
private void btnShowRecords_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntEmployees =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdEmployees =
new SqlCommand("SELECT Personnel.Employees.EmployeeNumber, " +
"Personnel.Employees.FirstName, " +
"Personnel.Employees.LastName, " +
"Personnel.Employees.Title, " +
"Personnel.Employees.HourlySalary, " +
"Management.Departments.Name " +
"FROM Personnel.Employees " +
"INNER JOIN Management.Departments " +
"ON Personnel.Employees.DepartmentCode = Management.Departments.DepartmentCode; ",
cntEmployees);
SqlDataAdapter sdaEmployees = new SqlDataAdapter(cmdEmployees);
DataSet dsEmployees = new DataSet("EmployeesSet");
cntEmployees.Open();
sdaEmployees.Fill(dsEmployees);
dgvEmployees.DataSource = dsEmployees.Tables[0];
}
}

|
A One-to-One Relationship: A Self-Referencing
Table
|
|
Imagine you have two lists where a value from one list
can provide 0 or 1 value to a record of the other list, and only one record
of a child list can get its foreign value from the other list. This can be
illustrated as follows:

This type of relationship is referred to as one-to-one.
To give you an example, imagine you have a list of employees and you want to
specify the supervisor or manager of each employee. This can be illustrated
as follows:
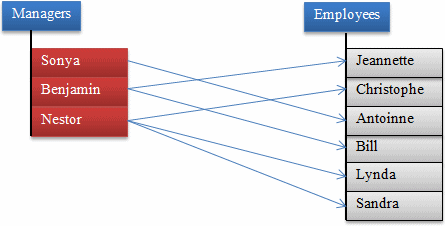
By definition, a manager is primarily an employee like
any other. This means that the primary information of a manager is the same
as that of any other employee. This also implies that if you had to use
separate tables, one for managers and another for employees, you would have
two similar tables, and there is a chance that information would be
duplicated in both tables. As a result, a one-to-one relationship is usually
created using only one table, in which case the table would reference
itself. In other words, some records would reference (be linked to) other
records of the same table. This can be illustrated as follows:

Here is an example that implements this snenario:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace TopicsOnDataRelationships
{
public partial class Exercise : Form
{
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnCreateDatabase_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=SSPI;"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE SCHEMA Personnel;", cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Personnel.Employees(" +
"EmployeeNumber nvarchar(10) not null," +
"FirstName nvarchar(20)," +
"LastName nvarchar(20) not null," +
"Title nvarchar(50)," +
"Supervisor nvarchar(10) null," +
"HourlySalary money);",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("INSERT Personnel.Employees(EmployeeNumber, FirstName, " +
"LastName, Title, HourlySalary) VALUES" +
"(N'792702', N'Frank', N'Cassini', N'General Manager', 30.25)," +
"(N'249441', N'Patrick', N'Levine', N'Regional Manager', 28.46)," +
"(N'302484', N'Catherine', N'Borrow', N'Shift Supervisor', 25.72);",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
using (SqlConnection cntExercise =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdExercise =
new SqlCommand("INSERT Personnel.Employees VALUES" +
"(N'485052', N'Jerry', N'Fesman', N'Head Cashier', N'792702', 18.64)," +
"(N'279475', N'Alex', N'Simkins', N'Intern', N'302484', 12.48)," +
"(N'908047', N'Grace', N'McDermott', N'Cashier', N'302484', 14.72)," +
"(N'395822', N'Craig', N'Newman', N'IT Support', N'249441', 20.26)," +
"(N'381848', N'John', N'Hough', N'Cashier', N'302484', 13.52)," +
"(N'300724', N'Matt', N'Kern', N'Accountant', N'792702', 24.58)," +
"(N'974115', N'Elsa', N'Steinberg', N'Webmaster', N'302484', 16.94)," +
"(N'974005', N'David', N'Miller', N'Intern', N'249441', 10.48)," +
"(N'273941', N'Jessica', N'Redding', N'Cashier', N'302484', 12.63);",
cntExercise);
cntExercise.Open();
cmdExercise.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The Employees table and its records have been created.",
"Exercise",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
private void btnShowRecords_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntEmployees =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdEmployees =
new SqlCommand("SELECT ALL * FROM Personnel.Employees; ",
cntEmployees);
SqlDataAdapter sdaEmployees = new SqlDataAdapter(cmdEmployees);
DataSet dsEmployees = new DataSet("EmployeesSet");
cntEmployees.Open();
sdaEmployees.Fill(dsEmployees);
dgvEmployees.DataSource = dsEmployees.Tables[0];
}
}
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
}
}
The regular SELECT * statement of this table only shows
the list of employees and the supervisor of each employee appears only as a
number, which can make it difficult to actually identify the supervisor:

By using a join, you can create a SELECT
statement where the JOIN is ON itself.
When formulating the statement, you must use the table twice, in which case
you should (must) create an alias for each. Here is an example:
private void btnShowRecords_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntEmployees =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='Exercise1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdEmployees =
new SqlCommand("SELECT staff.FirstName, staff.LastName, staff.Title, " +
"staff.HourlySalary, staff.EmployeeNumber, " +
"managers.LastName + N', ' + managers.FirstName AS Manager " +
"FROM Personnel.Employees staff JOIN Personnel.Employees managers " +
" ON staff.Supervisor = managers.EmployeeNumber;",
cntEmployees);
SqlDataAdapter sdaEmployees = new SqlDataAdapter(cmdEmployees);
DataSet dsEmployees = new DataSet("EmployeesSet");
cntEmployees.Open();
sdaEmployees.Fill(dsEmployees);
dgvEmployees.DataSource = dsEmployees.Tables[0];
}
}
This would produce:

Just as done for many tables in a database, you can
create a table that relates to itself. To start, the table must have a
primary key. Since you are creating an actual relationship, the table must
have a foreign key and that key must reference the primary key of the same
table. Of course, the name of the column that represents the foreign key
must have a different name than that of the primary key column. Here is an
example:
CREATE DATABASE Exercise;
GO
USE Exercise;
GO
CREATE TABLE Employees
(
EmployeeID int identity(1, 1) not null,
EmployeeNumber nchar(10) not null,
FirstName nvarchar(20),
LastName nvarchar(20) not null,
Title nvarchar(50),
ManagerID int
CONSTRAINT FK_Employees References Employees(EmployeeID),
HourlySalary money,
CONSTRAINT PK_Employees Primary Key(EmployeeID)
);
GO
INSERT Employees(EmployeeNumber, FirstName, LastName, Title, HourlySalary)
VALUES(N'792702', N'Frank', N'Cassini', N'General Manager', 30.25);
INSERT Employees(EmployeeNumber, FirstName, LastName, Title, HourlySalary)
VALUES(N'249441', N'Patrick', N'Levine', N'Regional Manager', 28.46);
INSERT Employees(EmployeeNumber, FirstName, LastName, Title, HourlySalary)
VALUES(N'302484', N'Catherine', N'Borrow', N'Shift Supervisor', 25.72);
INSERT Employees(EmployeeNumber, FirstName, LastName, Title, ManagerID, HourlySalary)
VALUES(N'485052', N'Jerry', N'Fesman', N'Head Cashier', 1, 18.64),
(N'279475', N'Alex', N'Simkins', N'Intern', 3, 12.48),
(N'908047', N'Grace', N'McDermott', N'Cashier', 3, 14.72),
(N'395822', N'Craig', N'Newman', N'IT Support', 2, 20.26),
(N'381848', N'John', N'Hough', N'Cashier', 3, 13.52),
(N'300724', N'Matt', N'Kern', N'Accountant', 1, 24.58),
(N'974115', N'Elsa', N'Steinberg', N'Webmaster', 3, 16.94),
(N'974005', N'David', N'Miller', N'Intern', 2, 10.48),
(N'273941', N'Jessica', N'Redding', N'Cashier', 3, 12.63);
GO
If you create a diagram for the table, it would have a
curb that goes from and lands on itself. Here is an example:

As seen previously, you can then create a join that gets
the records from the table. Here is an example:
SELECT staff.EmployeeID AS [Empl ID], staff.EmployeeNumber As [Empl #],
staff.FirstName AS [First Name],
staff.LastName AS [Last Name], staff.Title,
staff.HourlySalary AS Salary,
managers.LastName + N', ' + managers.FirstName AS Manager
FROM Employees staff JOIN Employees managers
ON staff.ManagerID = managers.EmployeeID;
GO
|
A Many-To-Many Relationship: Junction Tables
|
|
Consider a database for a university with its tables of
students and courses:
CREATE DATABASE MonsonUniversity1;
GO
USE MonsonUniversity1;
GO
CREATE SCHEMA Studies;
GO
CREATE SCHEMA Admissions;
GO
CREATE TABLE Studies.Courses
(
CourseCode nchar(10) not null,
CourseName nvarchar(100),
Credits smallint not null,
CourseDescription nvarchar(max),
CONSTRAINT PK_Courses PRIMARY KEY(CourseCode)
);
GO
INSERT INTO Studies.Courses(CourseCode, CourseName, Credits)
VALUES(N'CMIS 101', N'Introduction to Problem Solving and Algorithm Design', 3),
(N'CMIS 170', N'Introduction to XML', 3),
(N'CMIS 320', N'Relational Databases', 3),
(N'CMIS 420', N'Advanced Relational Databases', 3),
(N'CMST 306', N'Introduction to Visual Basic Programming', 3),
(N'CMST 385', N'Internet and Web Design', 3);
GO
CREATE TABLE Admissions.Students
(
StudentNumber nchar(20) not null,
FirstName nvarchar(20),
MiddleName nvarchar(20),
LastName nvarchar(20),
CONSTRAINT PK_Students PRIMARY KEY(StudentNumber)
);
GO
INSERT INTO Admissions.Students
VALUES(N'8130480', N'Frank', N'Daniel', N'Bigg'),
(N'2946681', N'Marianne', NULL, N'Roberts'),
(N'7113159', N'Angele', N'Cecilia', N'Douala'),
(N'2049220', N'James', NULL, N'Davidson'),
(N'7927413', N'Larry', N'Herbert', N'Bibang'),
(N'2048800', N'Ann', NULL, N'Roberts'),
(N'9701328', N'Celia', N'Gabriela', N'Edison'),
(N'9720048', N'Hermine', NULL, N'Nkolo');
GO
Imagine you have a list of students who are registering
for courses in a new semester:
- A student can register for one course (a type of one-to-one
relationship)
- A student can register for many courses

- Put it another way, many courses can have been registered by one
student
- Many students can register for the same course:

- If many students can register for the same course, this means that
one course can have been registered by many students:

- As a result, many students can register for many courses (or many
students can share many courses):

This type of relationship is referred to as
many-to-many.
Most of the time, to implement a many-to-many
relationship, besides the two tables that hold the normal records, you would
create one more table referred to as a junction table. The job of the
junction table is to get a value from one table, associate it to the desired
value of another table, repeat this step as many times as necessary, and
produce the necessary list. This can be illustrated as follows:

Obviously, the junction table should (must) have a
foreign key for each of the concerned tables. Here is an example of such a
table:
CREATE TABLE Admissions.Registrations
(
StudentNumber nchar(20),
CourseCode nchar(10),
);
In reality, you can add as many fields as you
judge necessary. Here is an example:
CREATE TABLE Admissions.Registrations
(
RegistrationID int identity(1, 1) not null,
StudentNumber nchar(20),
CourseCode nchar(10),
CONSTRAINT PK_Registrations PRIMARY KEY(RegistrationID)
);
GO
As mentioned already, when creating the records, you get
a value from one table and another value from the other table. Here are
examples:
INSERT INTO Admissions.Registrations(StudentNumber, CourseCode)
VALUES(N'8130480', N'CMIS 101'),
(N'2946681', N'CMIS 170'),
(N'7113159', N'CMST 385'),
(N'2049220', N'CMIS 320'),
(N'7927413', N'CMIS 320'),
(N'2946681', N'CMST 306'),
(N'2048800', N'CMIS 420'),
(N'2049220', N'CMST 306'),
(N'7113159', N'CMST 306'),
(N'9701328', N'CMIS 170'),
(N'9720048', N'CMIS 420'),
(N'9701328', N'CMST 306');
GO
|
A Variance to a Many-To-Many Relationship
|
|
As a variance of a many-to-many relationship, instead of
just two tables, you can create a junction table that unites three or more
tables. Once again, consider the example of students registering for
courses:
- When a semester starts, a student must select a semester for the
courses he wants to attend, and there are many courses available for
that semester. This means that the student would select a semester and
select one or more courses he wishes to attend. This can be illustrated
as follows:

- Many students can register for the same semester:

- To help them plan their academic career, many schools allow a
student to register courses for more than one semester. In this case, a
student can select (an) additional semester(s) and select courses she
wants to attend during each semester (in this example, we don't account
for a student who is repeating (re-taking) a course):

- As a result, over the course of academic years:
- A student would have attended many semesters:

- Many students would have attended many semesters (or a semester
can "have" many students):
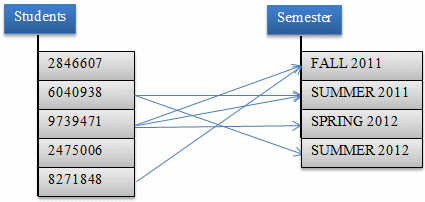
- A semester would show courses that were attended by many
students:

- Many semesters would show many courses that were available
- A course can be offered in many semesters
- Many courses can be offered in many semesters
- A course can have many students who attended it

- A course can have many students who attended it during different
semesters
- The records of many students would show many semesters they used
to attend many courses

You create the junction table the same way you do for
two tables: Add a foreign key for each of the tables. During data entry:
- Select a value from the first table. For our example, this would be
the student number of the student who is registering for the course
- Select a value from the second table. The value must appropriately
correspond to that of the first table. For our example, this would be
the semester during which the selected student wants to attend one or
more courses
- Select a value from the third table. The value must appropriately
correspond to that of the first table and that of the second table. For
our example, this would be the course that the student selected in the
first table wants to attend during the semester selected in the second
tabe
The beauty of this variant of a many-to-many
relationship would be revealed during data analysis when you want to find
out
- Whether a certain course is available for a certain semester (for
one reason or another, some courses are not offered during some
semesters)
- What (the names of) students registered for what semester. This
information helps with school statistics (enrollment, etc)
- What courses a student attended during a certain semester
- Did the student attend that course already?
- How many courses (credits) has the student accumulated already?
- Based on the student's major, is the course required for the
major? Is it required for the minor? Or is it an elective?
- How many students have already registered for a certain course that
would start soon. That would allow you to find out whether:
- There are still seats for the course and if so, how many
- There are enough students or the course should be canceled
|
 Practical
Learning: Creating a Many-To-Many Relationship Practical
Learning: Creating a Many-To-Many Relationship
|
|
- Display the first form and double-click an unoccupied area of its
body
- To create a many-to-many relationship, change the event as follows:
private void MonsonUniversity_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdMonsonUniversity =
new SqlCommand("CREATE TABLE Admissions.Registrations(" +
"RegistrationID int identity(10001, 1) not null," +
"StudentNumber nchar(8)," +
"SemesterID int not null," +
"CourseCode nchar(8)," +
"Constraint PK_Registrations Primary Key(RegistrationID));",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdMonsonUniversity.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The Registrations table has been created.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
- Execute the application to create the new form
- Click OK on the message box
- Close the form and return to your programming environment
- Delete the code in the Load event
private void MonsonUniversity_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
- To create a new form, on the main menu, click Project -> Add New
Windows Form...
- Set the name to CourseRegistration
- Click Add
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Other Properties |
| Label |
 |
Enter the student #: |
|
|
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtStudentNumber |
Modifiers: Public |
| Label |
 |
Select the semester: |
|
|
| ComboBox |
 |
|
cbxSemesters |
Modifiers: Public |
| Label |
 |
Type the course code: |
|
|
| TextBox |
 |
|
txtCourseCode |
Modifiers: Public |
| Button |
 |
OK |
btnOK |
DialogResult: OK |
| Button |
 |
Cancel |
btnCancel |
DialogResult: Cancel |
|
- To create a new form, on the main menu, click Project -> Add New
Windows Form...
- Set the name to Registrations
- Click Add
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
| DataGridView |
 |
|
|
| Button |
 |
New Registration... |
btnNewRegistration |
| Button |
 |
Close |
btnClose |
|
- Double-click the New Registration button
- Change the file as follows:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace MonsonUniversity1
{
public partial class Registrations : Form
{
public Registrations()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
void ShowRegistrations()
{
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdRegistrations =
new SqlCommand("SELECT ALL * FROM Admissions.Registrations;",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
SqlDataAdapter sdaRegistrations = new SqlDataAdapter(cmdRegistrations);
DataSet dsRegistrations = new DataSet("RegistrationsSet");
sdaRegistrations.Fill(dsRegistrations);
dgvRegistrations.DataSource = dsRegistrations.Tables[0];
}
}
private void btnNewRegistration_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
CourseRegistration cr = new CourseRegistration();
// Fill the combo box with the semesters
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdSemesters =
new SqlCommand("SELECT Semester " +
"FROM Admissions.Semesters " +
"ORDER BY Semester ASC;",
cntMonsonUniversity);
DataSet dsSemesters = new DataSet("SemestersSet");
SqlDataAdapter sdaSemesters = new SqlDataAdapter(cmdSemesters);
sdaSemesters.Fill(dsSemesters);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
foreach (DataRow row in dsSemesters.Tables[0].Rows)
cr.cbxSemesters.Items.Add(row["Semester"]);
}
if (cr.ShowDialog() == System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult.OK)
{
// The following code allos us to get the SemesterID value
// of the selected semester
int semesterID = 0;
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdSemesters =
new SqlCommand("SELECT Semester, SemesterID FROM Admissions.Semesters;",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
SqlDataReader sdrSemesters = cmdSemesters.ExecuteReader();
while (sdrSemesters.Read())
{
if (sdrSemesters[0].ToString() == cr.cbxSemesters.Text)
semesterID = int.Parse(sdrSemesters[1].ToString());
}
}
using (SqlConnection cntMonsonUniversity =
new SqlConnection("Data Source=(local);" +
"Database='MonsonUniversity1';" +
"Integrated Security=Yes"))
{
SqlCommand cmdSemesters =
new SqlCommand("INSERT INTO Admissions.Registrations(" +
"StudentNumber, SemesterID, CourseCode) " +
"VALUES('" + cr.txtStudentNumber.Text + "', " +
semesterID + ", '" + cr.txtCourseCode.Text + "');",
cntMonsonUniversity);
cntMonsonUniversity.Open();
cmdSemesters.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("The student has been registered for the course.",
"Monson University",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
ShowRegistrations();
}
}
}
- Return to the form and double-click an unoccupied area of its body
- Implement the event as follows:
private void Registrations_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ShowRegistrations();
}
- Return to the form and double-click the Close button
- Implement its event as follows:
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
- Display the form
- Add a button with the following properties:
(Name):
btnRegistrations
Font: Baskerville Old Face,
21.75pt, style=Bold (or any font of your choice)
Text:
Registrations

- Double-click the Registrations button and implement its event as
follows:
private void btnRegistrations_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Registrations reg = new Registrations();
reg.ShowDialog();
}
- Execute the application
- Click the Registrations button
- Create the following registrations:
| StudentNumber |
SemesterID |
CourseCode |
| 24795711 |
FALL 2010 |
CMIS 101 |
| 94708257 |
SPRING 2010 |
ACCT 220 |
| 20409220 |
FALL 2010 |
BMGT 312 |
| 71513159 |
FALL 2010 |
PSYC 306 |
| 94708257 |
SUMMER 2010 |
BEHS 220 |
| 20946681 |
SUMMER 2010 |
CMIS 170 |
| 29480759 |
FALL 2011 |
CMIS 170 |
| 82580947 |
SPRING 2010 |
ENGL 240 |
| 71513159 |
FALL 2010 |
HIST 104 |
| 20409220 |
FALL 2010 |
CMIS 320 |
| 94708257 |
SUMMER 2010 |
CMIS 320 |
| 92084157 |
FALL 2010 |
BEHS 220 |
| 94708257 |
FALL 2011 |
WRTG 288 |
| 71513159 |
SUMMER 2010 |
CMST 306 |
| 94708257 |
FALL 2010 |
CMIS 420 |
| 29480759 |
FALL 2011 |
WRTG 388 |
| 20409220 |
SUMMER 2010 |
CMST 306 |
| 71513159 |
SUMMER 2010 |
CMST 306 |
| 82580947 |
SPRING 2010 |
CMIS 420 |
| 24795711 |
SUMMER 2010 |
BEHS 220 |
| 92084157 |
SUMMER 2010 |
CMST 306 |
| 94708257 |
FALL 2011 |
ACCT 220 |
- Close the forms and return to your programming environment
|
|



































