 |
Microsoft Visual C# Example Application: The Standard
Deviation |
|
|
|
The standard deviation
is a value that indicates by how much the values of a set deviate from the
mean. To calculate the standard deviation, you can use the
following formula:
|
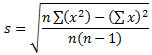
The factors in these equations are:
| Factor |
Description |
| x |
Each of the values used in the series |
| n |
The number of values in the series |
| Σ |
The sum of values |
| s |
The standard deviation |
|
 Application:
Calculating the Standard Deviation Application:
Calculating the Standard Deviation
|
|
- Start Microsoft Visual Studio
- To create a new application, on the main menu, click File -> New
Project...
- In the middle list, click Windows Forms Application
- Change the Name to StandardDeviation2
- Click OK
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click Form1.cs and click Rename
- Type Exercise.cs and press Enter
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Name |
Text |
| Label |
 |
|
Value: |
| TextBox |
 |
txtValue |
|
| Button |
 |
btnAdd |
Add |
| ListBox |
 |
lbxValues |
|
| Button |
 |
btnClear |
Clear |
| Label |
 |
|
Standard Deviation: |
| TextBox |
 |
txtStandard Deviation |
|
| Button |
 |
btnClose |
Close |
|
- Double-click an unoccupied area of the form
- Change the file as follows:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MeasuresOfCenter
{
public partial class Measures : Form
{
List<double> values;
public Measures()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Measures_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
values = new List<double>();
}
void ShowValues()
{
lbxValues.Items.Clear();
for (int i = 0; i < values.Count; i++)
lbxValues.Items.Add(values[i]);
}
}
}
- Return to the form
- Double-click the Add button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnAdd_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// This the value that will be added to the text box
double value = 0.00;
double sum = 0.00, sumSquares = 0.00, squareSums;
double stdDev = 0.00;
// Check that the user entered a value in the text box
if (txtValue.Text.Length == 0)
{
MessageBox.Show("You must enter a value.", "Standard Deviation");
return;
}
try
{
// Get the value the user entered
value = double.Parse(txtValue.Text);
// Add it to the collection
values.Add(value);
// Show the values in the list box
ShowValues();
txtValue.Text = "";
txtValue.Focus();
}
catch (FormatException)
{
MessageBox.Show("The value you entered is invalid.",
"Standard Deviation");
}
// Calculate the total for the sum
for (int i = 0; i < values.Count; i++)
sum += values[i];
squareSums = sum * sum;
for (int i = 0; i < values.Count; i++)
sumSquares += (values[i] * values[i]);
// Now we can calculate the standard deviation
double numerator = values.Count * sumSquares - squareSums;
double denominator = values.Count * (values.Count - 1);
stdDev = Math.Sqrt(numerator / denominator);
// Display the values(standard deviationand stuff)
txtCount.Text = values.Count.ToString();
txtSum.Text = sum.ToString("F");
txtSumSquares.Text = sumSquares.ToString("F");
txtSquareSums.Text = squareSums.ToString("F");
txtStandardDeviation.Text = stdDev.ToString("F");
}
- Return to the form
- To execute, press F5
- Enter a few values and click Add after each

- Close the form and return to your programming environment
- Double-click the Clear button
- Implement its event as follows:
private void btnClear_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
values.Clear();
lbxValues.Items.Clear();
txtValue.Text = "";
txtCount.Text = "";
txtSum.Text = "";
txtMean.Text = "";
txtStandardDeviation.Text = "";
txtValue.Focus();
}
- Return to the form
- To execute, press F5
- Enter a few values and click Add after each

- Click Clear
- Close the form and return to your programming environment
- Double-click the Close button
- Implement the event as follows:
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
- To execute, press F5
- Enter a few values and click Add after each

- Close the form and return to your programming environment
Application
|
|