Windows Controls: Scroll Bars
|
Windows Controls: Scroll Bars |
|
|
Introduction to Scroll Bars |
|
Overview |
|
|
Automatic Scroll Bars |
|
Some controls need a scroll bar to efficiently implement their functionality. The primary example is the edit control, which is used to display text. On that control, when the text is too long, the user needs to be able to scroll down and up to access the document fully. In the same way, if the text is too wide, the user needs to be able to scroll left and right to view the whole document. When creating a text-based document or window, you can easily ask that one or both scroll bars be added. Of course, an edit control must be able to handle multiple lines of text. This is taken care of by adding the ES_MULTILINE flag to its styles. Then:
Of course, you can use only one, two, three or all four styles. |
|
|
|

|
Control-Based Scroll Bars |
|
Introduction |
|
Microsoft Windows provides another type of scroll bar. Treated as its own control, a scroll bar is created like any other window and can be positioned anywhere on its host. To create a scroll bar as a Windows control, call the CreateWindow() or the CreateWindowEx() functions and specify the class name as SCROLLBAR. |
|
|
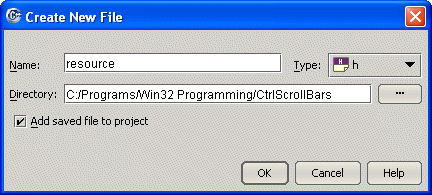
#define IDD_CONTROLS_DLG 101 #define IDC_CLOSE_BTN 1000
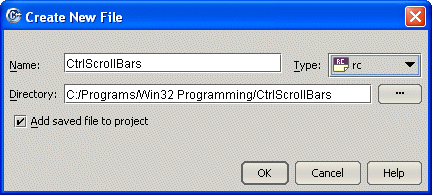
#include "resource.h"
IDD_CONTROLS_DLG DIALOG DISCARDABLE 200, 150, 235, 151
STYLE DS_MODALFRAME | WS_POPUP | WS_CAPTION | WS_SYSMENU
CAPTION "Windows Controls"
FONT 8, "MS Sans Serif"
BEGIN
PUSHBUTTON "&Close",IDC_CLOSE_BTN,178,7,50,14
END#include <windows.h>
#ifdef __BORLANDC__
#pragma argsused
#endif
#include "resource.h"
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
HWND hWnd;
HINSTANCE hInst;
LRESULT CALLBACK DlgProc(HWND hWnd, UINT Msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
int APIENTRY WinMain( HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow )
{
hInst = hInstance;
DialogBox(hInst, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_CONTROLS_DLG),
hWnd, reinterpret_cast<DLGPROC>(DlgProc));
return 0;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT CALLBACK DlgProc(HWND hWndDlg, UINT Msg,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch(Msg)
{
case WM_INITDIALOG:
return TRUE;
case WM_COMMAND:
switch(wParam)
{
case IDC_CLOSE_BTN:
EndDialog(hWndDlg, 0);
return TRUE;
}
break;
case WM_CLOSE:
PostQuitMessage(WM_QUIT);
break;
}
return FALSE;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------|
Scroll Bar Creation |
|
The easiest way to add a scroll bar to a project is through the resource script of the project. The syntax to follow is: SCROLLBAR id, x, y, width, height [[, style [[, ExtendedStyle]]]] This declaration starts with the SCROLLBAR keyword as the name of the class that creates a scroll bar. The id is the identification of the control The x parameter is the Left parameter of the control The y parameter is the Top parameter of the control The width parameter is the distance from the left to the right border of the control The height parameter is the distance from the top to the bottom border of the control These 5 parameters are required. Here is an example: SCROLLBAR IDC_SCROLLBAR1,10,45,215,11 Alternatively, to create a scroll bar, you can use either the CreateWindow() or the CreateWindowEx() functions, specifying the class name as SCROLLBAR. Here is an example: |
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT CALLBACK DlgProc(HWND hWndDlg, UINT Msg,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch(Msg)
{
case WM_INITDIALOG:
CreateWindowEx(0L,
"SCROLLBAR",
NULL, // There is no text to display
WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE,
50,
20,
220,
21,
hWndDlg,
NULL,
hInst,
NULL);
return TRUE;
case WM_CLOSE:
PostQuitMessage(WM_QUIT);
break;
}
return FALSE;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
A third alternative is to create your own class. Here is an example: |
#include <windows.h>
#include "Resource.h"
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
class WScrollBar
{
public:
WScrollBar();
HWND Create(HWND parent, HINSTANCE hinst,
DWORD dStyle = WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE,
int x = 0, int y = 0, int width = 200, int height = 20);
virtual ~WScrollBar();
HWND hWndScrollBar;
private:
};
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
WScrollBar::WScrollBar()
{
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
WScrollBar::~WScrollBar()
{
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
HWND WScrollBar::Create(HWND parent, HINSTANCE hinst,
DWORD dStyle, int x, int y, int width, int height)
{
hWndScrollBar = CreateWindow("SCROLLBAR", NULL, dStyle,
x, y, width, height, parent,
NULL, hinst, NULL);
return hWndScrollBar;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
HWND hWnd;
HINSTANCE hInst;
LRESULT CALLBACK DlgProc(HWND hWnd, UINT Msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
INT WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
hInst = hInstance;
DialogBox(hInst, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_CONTROLS_DLG),
hWnd, reinterpret_cast<DLGPROC>(DlgProc));
return FALSE;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT CALLBACK DlgProc(HWND hWndDlg, UINT Msg,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
WScrollBar ScrBar;
switch(Msg)
{
case WM_INITDIALOG:
ScrBar.Create(hWndDlg, hInst);
return TRUE;
case WM_COMMAND:
switch(wParam)
{
case IDCANCEL:
EndDialog(hWndDlg, 0);
break;
}
break;
case WM_CLOSE:
PostQuitMessage(WM_QUIT);
break;
}
return FALSE;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
#define IDD_CONTROLS_DLG 101 #define IDC_CLOSE_BTN 1000 #define IDC_SCROLLER 1001 |
#include "resource.h"
IDD_CONTROLS_DLG DIALOG DISCARDABLE 200, 150, 235, 151
STYLE DS_MODALFRAME | WS_POPUP | WS_CAPTION | WS_SYSMENU
CAPTION "Windows Controls"
FONT 8, "MS Sans Serif"
BEGIN
PUSHBUTTON "&Close",IDC_CLOSE_BTN,178,7,50,14
SCROLLBAR IDC_SCROLLER,10,45,215,11
END
|

|
Scroll Bar Characteristics |
|
As mentioned already, there are two categories of scroll bars. The desired category is set using one of the scroll bar styles. As you can see from the above picture, the default orientation of a scroll bar is horizontal whose value is SBS_HORZ. If you want to produce a vertical scroll bar, you can OR the SBS_VERT style in addition to Windows styles but do not OR both SBS_HORZ and SBS_VERT styles on the same control. Here is an example that creates a vertical scroll bar control. Here is an example that creates a vertical scroll bar: |
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT CALLBACK DlgProc(HWND hWndDlg, UINT Msg,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
WScrollBar ScrBar;
switch(Msg)
{
case WM_INITDIALOG:
ScrBar.Create(hWndDlg, hInst, WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | SBS_VERT,
20, 10, 20, 200);
return TRUE;
case WM_CLOSE:
PostQuitMessage(WM_QUIT);
break;
}
return FALSE;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
This would produce:
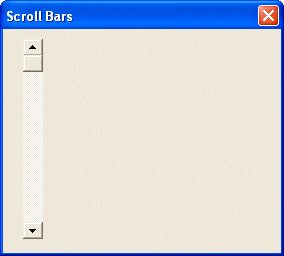
|
|
|
|
Scroll Bar Functions |
The SCROLLBAR class provides various functions that can be used to set its limits or change its position, etc. To use the scroll bar as a control, you should know its limits. These define the minimum and the maximum values that the thumb can navigate to. To set this range of values, you can call the SetScrollRange() function. Its syntax is:
BOOL SetScrollRange(HWND hWnd, int nBar, int nMinPos, int nMaxPos, BOOL bRedraw);
Here is an example:
#include <windows.h>
#include "Resource.h"
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
class WScrollBar
{
public:
WScrollBar();
HWND Create(HWND parent, HINSTANCE hinst,
DWORD dStyle = WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE,
int x = 0, int y = 0, int width = 200, int height = 20);
virtual ~WScrollBar();
HWND hWndScrollBar;
BOOL SetScrollRange(int min = 0, int max = 100, BOOL redraw = TRUE);
private:
};
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
WScrollBar::WScrollBar()
{
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
WScrollBar::~WScrollBar()
{
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
HWND WScrollBar::Create(HWND parent, HINSTANCE hinst,
DWORD dStyle, int x, int y, int width, int height)
{
hWndScrollBar = CreateWindow("SCROLLBAR", NULL, dStyle,
x, y, width, height, parent, NULL, hinst, NULL);
return hWndScrollBar;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
BOOL WScrollBar::SetScrollRange(int min, int max, BOOL redraw)
{
BOOL SSR = ::SetScrollRange(hWndScrollBar, SB_CTL, min, max, TRUE);
return SSR;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
HWND hWnd;
HINSTANCE hInst;
LRESULT CALLBACK DlgProc(HWND hWnd, UINT Msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
INT WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
hInst = hInstance;
DialogBox(hInst, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_CONTROLS_DLG),
hWnd, reinterpret_cast<DLGPROC>(DlgProc));
return FALSE;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT CALLBACK DlgProc(HWND hWndDlg, UINT Msg,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
WScrollBar ScrBar;
switch(Msg)
{
case WM_INITDIALOG:
ScrBar.Create(hWndDlg, hInst, WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | SBS_VERT,
20, 10, 20, 200);
ScrBar.SetScrollRange(0, 224);
return TRUE;
case WM_CLOSE:
PostQuitMessage(WM_QUIT);
break;
}
return FALSE;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
If the limits of the controls have already been set, you can find them out by calling the GetScrollRange() function. Its syntax is:
BOOL GetScrollRange(HWND hWnd, int nBar, LPINT lpMinPos, LPINT lpMaxPos);
Here is an example:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
class WScrollBar
{
public:
WScrollBar();
HWND Create(HWND parent, HINSTANCE hinst,
DWORD dStyle = WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE,
int x = 0, int y = 0, int width = 200, int height = 20);
virtual ~WScrollBar();
HWND hWndScrollBar;
BOOL SetScrollRange(int min = 0, int max = 100, BOOL redraw = TRUE);
BOOL GetScrollRange(int *min, int *max) const;
private:
};
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
WScrollBar::WScrollBar()
{
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
WScrollBar::~WScrollBar()
{
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
HWND WScrollBar::Create(HWND parent, HINSTANCE hinst,
DWORD dStyle, int x, int y, int width, int height)
{
hWndScrollBar = CreateWindow("SCROLLBAR", NULL, dStyle,
x, y, width, height, parent,
NULL, hinst, NULL);
return hWndScrollBar;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
BOOL WScrollBar::SetScrollRange(int min, int max, BOOL redraw)
{
BOOL SSR = ::SetScrollRange(hWndScrollBar, SB_CTL, min, max, TRUE);
return SSR;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
BOOL WScrollBar::GetScrollRange(int *min, int *max) const
{
BOOL GSR = ::GetScrollRange(hWndScrollBar, SB_CTL, min, max);
return GSR;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
When a window that has a scroll bar control comes up, the thumb is positioned in its minimum value. You may want the control to be positioned somewhere else than that. This attribute is taken care of by the SetScrollPos() function. Its syntax:
int SetScrollPos(HWND hWnd, int nBar, int nPos, BOOL bRedraw);
You can implement and use this function as follows:
#include <windows.h>
#include "Resource.h"
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
class WScrollBar
{
public:
WScrollBar();
HWND Create(HWND parent, HINSTANCE hinst,
DWORD dStyle = WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE,
int x = 0, int y = 0, int width = 200, int height = 20);
virtual ~WScrollBar();
HWND hWndScrollBar;
BOOL SetScrollRange(int min = 0, int max = 100, BOOL redraw = TRUE);
BOOL GetScrollRange(int *min, int *max) const;
int SetScrollPos(const int pos);
private:
};
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
WScrollBar::WScrollBar()
{
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
WScrollBar::~WScrollBar()
{
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
HWND WScrollBar::Create(HWND parent, HINSTANCE hinst,
DWORD dStyle, int x, int y, int width, int height)
{
hWndScrollBar = CreateWindow("SCROLLBAR", NULL, dStyle,
x, y, width, height, parent, NULL, hinst, NULL);
return hWndScrollBar;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
BOOL WScrollBar::SetScrollRange(int min, int max, BOOL redraw)
{
BOOL SSR = ::SetScrollRange(hWndScrollBar, SB_CTL, min, max, TRUE);
return SSR;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
BOOL WScrollBar::GetScrollRange(int *min, int *max) const
{
BOOL GSR = ::GetScrollRange(hWndScrollBar, SB_CTL, min, max);
return GSR;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
int WScrollBar::SetScrollPos(const int position)
{
int SSP = ::SetScrollPos(hWndScrollBar, SB_CTL, position, TRUE);
return SSP;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
HWND hWnd;
HINSTANCE hInst;
LRESULT CALLBACK DlgProc(HWND hWnd, UINT Msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
INT WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
hInst = hInstance;
DialogBox(hInst, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_CONTROLS_DLG),
hWnd, reinterpret_cast<DLGPROC>(DlgProc));
return FALSE;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT CALLBACK DlgProc(HWND hWndDlg, UINT Msg,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
WScrollBar ScrBar;
switch(Msg)
{
case WM_INITDIALOG:
ScrBar.Create(hWndDlg, hInst, WS_CHILD | WS_VISIBLE | SBS_VERT,
20, 10, 20, 200);
ScrBar.SetScrollRange(0, 224);
ScrBar.SetScrollPos(88);
return TRUE;
case WM_CLOSE:
PostQuitMessage(WM_QUIT);
break;
}
return FALSE;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
|
|
Scroll Bar Messages |
|
To use a scroll bar, a person either clicks one of its buttons, clicks and hold the mouse on one of its buttons, drags the thumb, or clicks an area on either side of the thumb. Any of these actions sends a message that specifies the item the user clicked or dragged. To support this, each category of scroll bar sends the appropriate message. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Home | ||
|
|
||