 |
Interfaces |
|
Interfaces Fundamentals
Introduction
An interface is a structural layout that resembles a class but has the following characteristics:
- An interface presents a layout or design that classes and/or structures can follow to define their particular behaviors
- Like a class or a structure, an interface has methods and/or properties as members
- Unlike a class or a structure, an interface doesn't implement the methods and/or properties that are its members
- A new class or a structure can be derived from an interface. Since an interface presents a layout or design that classes and/or structures can follow, and since an interface doesn't implement any of its methods or properties, any class or structure that derives from an interface must implement all the members of the interface. As a result, a class or structure that is based on an interface is said to "implement" the interface as opposed to derive from the interface
Creating an Interface
The basic formula to create an interface is:
[ access-modifier(s) ] [ Shadows ] Interface name
members
End Interface
The access modifiers can be any of those we have seen in previous lessons (Public, Protected, Friend, Private, or Protected Friend). If you omit the access modifier, it is assumed to be Public. By tradition or good habits, the name of an interface starts with I. The section between the Interface name line the the End Interface line is the body of the interface. Here is an example of a starting
interface:
Public Interface IPolygon
End Interface
You can create an interface in a Visual Basic file that has the .vb extension. If you are creating the interface in the file of a webpage, you should include it in a <script> section. This can be done as follows:
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
End Interface
</script>
After creating an interface, you can implement it, which, as mentioned in our introduction, consists of creating a class or a structure from it. When implementing an interface, instead of the Inherits keyword, use Implements followed by the name of the interface. Here is an example of a new class named Triangle and that is based on the above IPolygon interface:
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon
End Class
</script>
As with other classes, once you have implemented the
class, you can create objects from it and instantiate it using the New
operator. Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<script runat="server">
Public Interface IPolygon
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon
End Class
</script>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<title>Geometry - Polygons</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
Dim tri As New Triangle()
%>
</body>
</html>
The Members of an Interface
Introduction
As mentioned earlier, the purpose of an
interface is to create a skeleton for classes. When creating an interface, in its body, create the necessary members. In the class or a structure that is based on the interface, you must implement the members. To do this, at the end of the first line that presents the member in the class, type the Implements keyword, followed by the name of the interface, followed by a period, and ending with the name of the member.
A member can start with the Shadows keyword if necessary.
Unlike classes and structures, the following keywords are not allowed on the members of an interface: Public, Private, Friend, Protected, Shared, Overrides, MustOverride, and Overridable.
Adding a Procedure to an Interface
An interface can contain one or more methods. A method that is a sub-procedure follows this formula:
Sub method-name()
When implementing the method in a class, use the following formula;
access-modifier Sub method-name() Implements interface-name.method-name
Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<script runat="server">
Public Interface IPolygon
Sub Describe()
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon
Public Sub Describe() Implements IPolygon.Describe
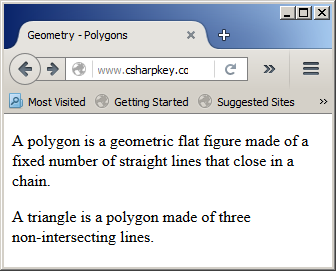
My.Response.Write("<p>A polygon is a geometric flat figure made of a fixed number of straight lines that close in a chain.</p>" &
"<p>A triangle is a polygon made of three non-intersecting lines.</p>")
End Sub
End Class
</script>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<title>Geometry - Polygons</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
Dim tri As New Triangle()
tri.Describe()
%>
</body>
</html>
This would produce:
A Function as a Member of an Interface
To add a function to an interface, use this formula:
Function name() As data-type
When implementing the function in the body of the class, make sure you return the propriate type of value. Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<script runat="server">
Public Interface IPolygon
Sub Describe()
Function Calculate(ByVal side As Double) As Double
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon
Public Sub Describe() Implements IPolygon.Describe
My.Response.Write("<p>A polygon is a geometric flat figure made of a fixed number of straight lines that close in a chain.</p>" &
"<p>A triangle is a polygon made of three non-intersecting lines.</p>")
End Sub
Public Function Calculate(ByVal side As Double) As Double Implements IPolygon.Calculate
Return side * 3.0
End Function
End Class
</script>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<title>Geometry - Polygons</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
Dim side = 48.17
Dim tri As New Triangle()
tri.Describe()
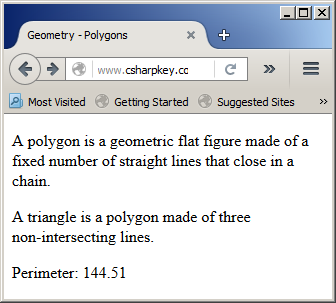
Response.Write("<p>Perimeter: " & tri.Calculate(side) & "</p>")
%>
</body>
</html>
This would produce:
A Property in an Interface
An interface can contain one or more properties. If a property is intended to be read-write, the formula to create it is:
Property property-name As data-type
When implementing the property in a class, end its first line with Implements, a period, and the name of the property. Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<script runat="server">
Public Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
End Class
</script>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<title>Geometry - Polygons: The Equilateral Triangle</title>
</head>
<body>
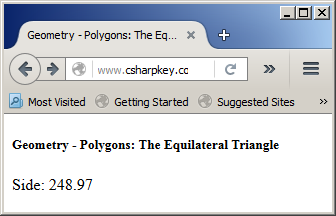
<h5>Geometry - Polygons: The Equilateral Triangle</h5>
<%
Dim length As Double = 248.97
Dim equilateral As Triangle
equilateral = New Triangle(length)
Response.Write("<p>Side: " & equilateral.Side & "</p>")
%>
</body>
</html>
This would produce:
If the property is intended to be read-only, the formula to create it is:
ReadOnly Property name Get
Notice that you must start with the ReadOnly keyword and end with Get. When implementing the property, at the end of the first line, omit Get to use it in the body of the property. Here
is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<script runat="server">
Public Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Area As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(3.0) / 4.0
End Get
End Property
End Class
Sub btnCalculateClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim side = 0.0
Dim equilateral As Triangle
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtSide.Text) Then
side = CDbl(txtSide.Text)
End If
equilateral = New Triangle(side)
txtArea.Text = equilateral.Area
End Sub
</script>
<style>
#main-title
{
font-size: 1.08em;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
font-family: Georgia, Garamond, 'Times New Roman', Times, serif;
}
#whole
{
margin: auto;
width: 205px;
}
</style>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<title>Geometry - Polygons: The Equilateral Triangle</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="main-title">Geometry - Polygons: The Equilateral Triangle</p>
<form id="frmGeometry" runat="server">
<div id="whole">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Side:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtSide" Width="75px" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><asp:Button id="btnCalculate" runat="server"
Text="Calculate" Width="85px"
OnClick="BtnCalculateClick" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Area:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtArea" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Here is an example of running the program:
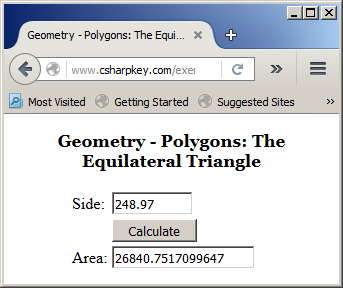
If the property is intended to be write-only, the formula to create it is:
WriteOnly Property name Set
Other than that, you can create as many classes as you want and that implement an interface of your choice. Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<script runat="server">
Public Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Public Class Hexagon
Implements IPolygon
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(3.0) * 3.0 / 2.0
End Get
End Property
End Class
Sub btnCalculateClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim side = 0.00
Dim figure As Hexagon
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtSide.Text) Then
side = CDbl(txtSide.Text)
End If
figure = New Hexagon(side)
txtArea.Text = figure.Area
End Sub
</script>
<style>
#main-title
{
font-size: 1.08em;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
font-family: Georgia, Garamond, 'Times New Roman', Times, serif;
}
#whole
{
margin: auto;
width: 205px;
}
</style>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<title>Geometry - Polygons: The Hexagon</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="main-title">Geometry - Polygons: The Hexagon</p>
<form id="frmGeometry" runat="server">
<div id="whole">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Side:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtSide" Width="75px" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><asp:Button id="btnCalculate" runat="server"
Text="Calculate" Width="85px"
OnClick="BtnCalculateClick" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Area:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtArea" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Here is an example of running the program:
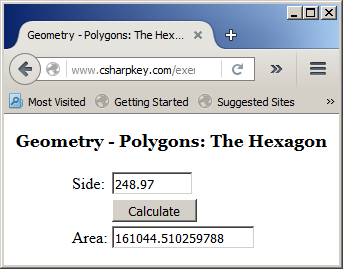
You can also add new members to the classes, members that are not related to the interface. Here are examples:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 3
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Height As Double
Get
Return Me.Edge * Math.Sqrt(3.0) / 2.0
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(3.0) / 4.0
End Get
End Property
End Class
Sub btnCalculateClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim side = 0.0
Dim equilateral As Triangle
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtSide.Text) Then
side = CDbl(txtSide.Text)
End If
equilateral = New Triangle(side)
txtHeight.Text = equilateral.Height
txtArea.Text = equilateral.Area
End Sub
</script>
<style>
#main-title
{
font-size: 1.08em;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
font-family: Georgia, Garamond, 'Times New Roman', Times, serif;
}
#whole
{
margin: auto;
width: 305px;
}
</style>
<title>Geometry - Polygons: The Equilateral Triangle</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="main-title">Geometry - Polygons: The Equilateral Triangle</p>
<form id="frmGeometry" runat="server">
<div id="whole">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Side:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtSide" Width="75px" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><asp:Button id="btnCalculate" runat="server"
Text="Calculate" Width="85px"
OnClick="BtnCalculateClick" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Height:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtHeight" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Area:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtArea" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Here is an example of using the webpage:
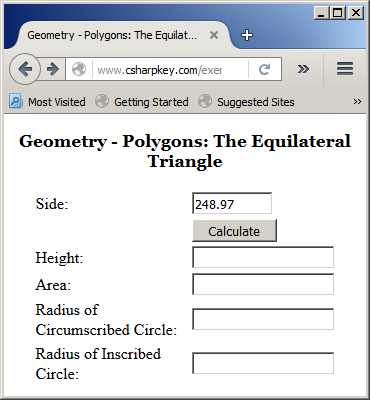
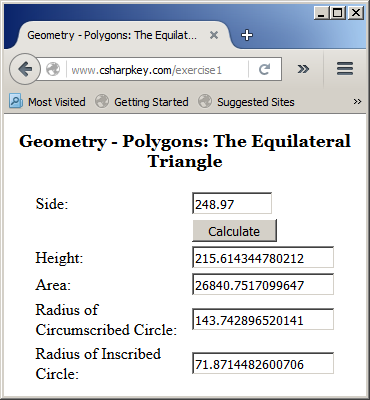
Primary Options on Using an Interface
Declaring a Variable of Interface Type
You cannot declare a variable of an interface and use it directly as you would a class. On the othe hand, you can declare a variable by using the name of the interface but not allocate memory for the variable. Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
</script>
<title>Geometry - Polygons</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
Dim figure As IPolygon
%>
</body>
</html>
When allocating memory for the object using the New operator, you must use a class that implements that interface. After that, you can use the object. Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Public Class Square
Implements IPolygon
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 4
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Diagonal As Double
Get
Return Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(2.00)
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side
End Get
End Property
End Class
Sub btnCalculateClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim side = 0.0
Dim plate As IPolygon
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtSide.Text) Then
side = CDbl(txtSide.Text)
End If
plate = New Square(side)
txtArea.Text = plate.Area
End Sub
</script>
<style>
#main-title
{
font-size: 1.08em;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
font-family: Georgia, Garamond, 'Times New Roman', Times, serif;
}
#whole
{
margin: auto;
width: 305px;
}
</style>
<title>Geometry - Polygons: The Square</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="main-title">Geometry - Polygons: The Square</p>
<form id="frmGeometry" runat="server">
<div id="whole">
<table style="width: 300px">
<tr>
<td>Side:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtSide" Width="75px" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><asp:Button id="btnCalculate" runat="server"
Text="Calculate" Width="85px"
OnClick="BtnCalculateClick" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Area:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtArea" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Here is an example of using the webpage:
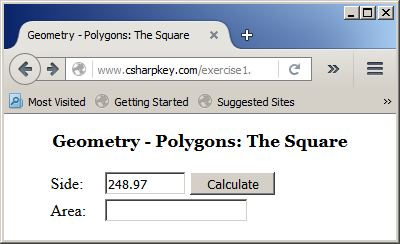
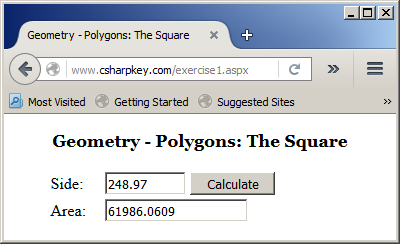
You can also declare the variable and allocate its memory on the same line. Here is an example:
<script runat="server">
. . .
Sub btnCalculateClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim side = 0.0
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtSide.Text) Then
side = CDbl(txtSide.Text)
End If
Dim plate As IPolygon = New Square(side)
txtArea.Text = plate.Area
End Sub
</script>
If you use any of these two techniques, you can access only the members of the interface. The non-interface members of the class would not be available. As a result, the following will produce an error:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Public Class Square
Implements IPolygon
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 4
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Diagonal As Double
Get
Return Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(2.00)
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side
End Get
End Property
End Class
Sub btnCalculateClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim side = 0.0
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtSide.Text) Then
side = CDbl(txtSide.Text)
End If
Dim plate As IPolygon = New Square(side)
txtArea.Text = plate.Area
' Since the Diagonal is not a member of the interface, the variable
' (declared from the interface) cannot access it
txtDiagonal.Text = plate.Diagonal
End Sub
</script>
<style>
#main-title
{
font-size: 1.08em;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
font-family: Georgia, Garamond, 'Times New Roman', Times, serif;
}
#whole
{
margin: auto;
width: 305px;
}
</style>
<title>Geometry - Polygons: The Square</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="main-title">Geometry - Polygons: The Square</p>
<form id="frmGeometry" runat="server">
<div id="whole">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Side:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtSide" Width="75px" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><asp:Button id="btnCalculate" runat="server"
Text="Calculate" Width="85px"
OnClick="BtnCalculateClick" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Diagonal:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtDiagonal" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Area:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtArea" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Passing an Interface As Argument
If you are defining a procedure, a function, or a method that receives an argument and the argument is an object of a class that either inherits from another class or implements an interface, in some cases, you can pass either its parent class or the interface it implements. In the body of the procedure, you can access the members of the interface. Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Public Class Pentagon
Implements IPolygon
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 6
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(5.00 * (5.00 + (2.00 * Math.Sqrt(5.00))))/4.00
End Get
End Property
End Class
Sub Present(ByVal figure As IPolygon)
txtArea.Text = figure.Area
End Sub
Sub btnCalculateClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim side = 0.0
Dim pol As IPolygon
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtSide.Text) Then
side = CDbl(txtSide.Text)
End If
pol = New Pentagon(side)
Present(pol)
End Sub
</script>
<style>
#main-title
{
font-size: 1.08em;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
font-family: Georgia, Garamond, 'Times New Roman', Times, serif;
}
#whole
{
margin: auto;
width: 305px;
}
</style>
<title>Geometry - Polygons: The Pentagon</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="main-title">Geometry - Polygons: The Pentagon</p>
<form id="frmGeometry" runat="server">
<div id="whole">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Side:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtSide" Width="75px" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><asp:Button id="btnCalculate" runat="server"
Text="Calculate" Width="85px"
OnClick="BtnCalculateClick" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Area:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtArea" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Here is an example of using the webpage:
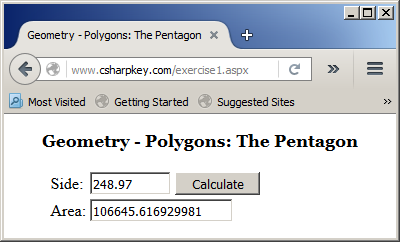
Keep in mind that you can access only the members of the interface.
Returning an Interface
A function or a method can return an object based on an interface. When creating the function or method, specify its return type as the desired interface. Here is an example:
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Function Create() As IPolygon
End Function
</script>
Remember that you cannot simply instantiate an interface and directly use it as you would an object of a class. As a result, you cannot directly return an object based on an interface. Instead, you can declare a variable of a class that implements the interface and return that variable. In the code section where you need to use the object, you can get the value returned by the function and use it. Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Public Class Pentagon
Implements IPolygon
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 6
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Diagonal As Double
Get
Return Me.Side * ((1.00 * Math.Sqrt(5.00)) / 2.00)
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(5.00 * (5.00 + (2.00 * Math.Sqrt(5.00)))) / 4.00
End Get
End Property
End Class
Sub Present(ByVal figure As IPolygon)
txtArea.Text = figure.Area
End Sub
Function Create() As IPolygon
Dim side As Double = 0.0
Dim pol As IPolygon
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtSide.Text) Then
side = CDbl(txtSide.Text)
End If
pol = New Pentagon(side)
Return pol
End Function
Sub btnCalculateClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim shape As Pentagon
shape = Create()
Present(shape)
End Sub
</script>
<style>
#main-title
{
font-size: 1.08em;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
font-family: Georgia, Garamond, 'Times New Roman', Times, serif;
}
#whole
{
margin: auto;
width: 305px;
}
</style>
<title>Geometry - Polygons: The Pentagon</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="main-title">Geometry - Polygons: The Pentagon</p>
<form id="frmGeometry" runat="server">
<div id="whole">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Side:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtSide" Width="75px" runat="server" />
<asp:Button id="btnCalculate" runat="server"
Text="Calculate" Width="85px"
OnClick="BtnCalculateClick" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Area:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtArea" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
In reality, the function must return an object based on either the interface itself or of a class that implements the interface.
|
Options on Creating, Implementing, and Using Interfaces
Inheriting an Interface
An interface can be derived from another interface (but an interface cannot derive from a class). To create an interface based on another interface, use the Inherits keyword. Obviously the derived interface is supposed to add some behavior using methods and/or properties. Here is an example:
<script runat="server">
Public Interface IPolygon
Property Side() As Double
ReadOnly Property Area() As Double
End Interface
Public Interface IPolyhedron
Inherits IPolygon
ReadOnly Property Volume() As Double
End Interface
</script>
As you should know already that nothing is implemented in an interface, a member of the parent interface cannot be defined in a derived interface. Also, any class that needs the behavior(s) of the derived interface must implement all members of the derived interface and those of the parent interface(s). Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<script runat="server">
Public Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Public Interface IPolyhedron
Inherits IPolygon
ReadOnly Property Volume As Double
End Interface
Public Class Tetrahedron
Implements IPolyhedron
Protected Edge As Double
Public ReadOnly Faces As Integer
Public ReadOnly Edges As Integer
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Faces = 4
Me.Edges = 6
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
ReadOnly Property PyramidHeight As Double
Get
Return MyClass.Edge * Math.Sqrt(2.0 / 3.0)
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property FaceArea As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return MyClass.Edge * MyClass.Edge * Math.Sqrt(3.0) * 2.0
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property TotalArea As Double
Get
Return Me.FaceArea * 4
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Volume As Double Implements IPolyhedron.Volume
Get
Return MyClass.Edge * MyClass.Edge * MyClass.Edge * Math.Sqrt(2.0) / 12.0
End Get
End Property
End Class
Sub btnCalculateClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim side = 0.0
Dim tetra As Tetrahedron
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtSide.Text) Then
side = CDbl(txtSide.Text)
End If
tetra = New Tetrahedron(side)
txtFaces.Text = tetra.Faces
txtEdges.Text = tetra.Edges
txtPyramidHeight.Text = tetra.PyramidHeight
txtFaceArea.Text = tetra.FaceArea
txtTotalArea.Text = tetra.TotalArea
txtVolume.Text = tetra.Volume
End Sub
</script>
<style>
#main-title
{
font-size: 1.08em;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
font-family: Georgia, Garamond, 'Times New Roman', Times, serif;
}
#whole
{
margin: auto;
width: 305px;
}
</style>
<title>Geometric Volumes: The Tetrahedron</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="main-title">Geometric Volumes: The Tetrahedron</p>
<form id="frmGeometry" runat="server">
<div id="whole">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Side:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtSide" Width="75px" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><asp:Button id="btnCalculate" runat="server"
Text="Calculate" Width="85px"
OnClick="BtnCalculateClick" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Number of Faces:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtFaces" Width="75px" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Number of Edges:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtEdges" Width="75px" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Height of Pyramid:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtPyramidHeight" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Face Area:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtFaceArea" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Total Area:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtTotalArea" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Volume:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtVolume" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Here is an example of using the webpage:

In the same way, an interface can inherit from an interface that itself inherits from another interface, and from another, and so on.
Implementing Many Interfaces
You cannot create a class that inherits from many classes at the same time. Instead, you can create a class that implements more than one
interface. To create a class based on more than one interface, after the Implements keyword, enter the name of each interface and separate them with commas. Here is an example:
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Interface IPerimeter
ReadOnly Property Perimeter As Double
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon, IPerimeter
End Class
</script>
To make your code easy to read, you can write each interface on its own line. Here is an example:
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Interface IPerimeter
ReadOnly Property Perimeter As Double
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon,
IPerimeter
End Class
</script>
In the class, you must implement all members of the parent interfaces. If an inherited interface has (a) parent(s), you must also implement all members of the inherited ancestors (if any). Here is an example:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side As Double
ReadOnly Property Area As Double
End Interface
Interface IPerimeter
ReadOnly Property Perimeter As Double
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon,
IPerimeter
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 3
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Height As Double
Get
Return Me.Edge * Math.Sqrt(3.0) / 2.0
End Get
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Perimeter As Double Implements IPerimeter.Perimeter
Get
Return Me.Edge * Me.Sides
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(3.0) / 4.0
End Get
End Property
End Class
Sub btnCalculateClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim side = 0.0
Dim equilateral As Triangle
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(txtSide.Text) Then
side = CDbl(txtSide.Text)
End If
equilateral = New Triangle(side)
txtHeight.Text = equilateral.Height
txtPerimeter.Text = equilateral.Perimeter
txtArea.Text = equilateral.Area
End Sub
</script>
<style>
#main-title
{
font-size: 1.08em;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
font-family: Georgia, Garamond, 'Times New Roman', Times, serif;
}
#whole
{
margin: auto;
width: 305px;
}
</style>
<title>Geometry - Polygons: The Equilateral Triangle</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="main-title">Geometry - Polygons: The Equilateral Triangle</p>
<form id="frmGeometry" runat="server">
<div id="whole">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Side:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtSide" Width="75px" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><asp:Button id="btnCalculate" runat="server"
Text="Calculate" Width="85px"
OnClick="BtnCalculateClick" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Height:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtHeight" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Perimeter:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtPerimeter" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Area:</td>
<td><asp:TextBox id="txtArea" runat="server" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
In the above example, we created a class that implements only two interfaces. You can create a class that implements as many interfaces as you want. Also, the same interface can be implemented differently in different classes. Here are examples:
<%@ Page Language="VB" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head runat="server">
<script runat="server">
Interface IPolygon
Property Side() As Double
ReadOnly Property Area() As Double
End Interface
Interface IPerimeter
ReadOnly Property Perimeter() As Double
End Interface
Interface IPolyRadius
ReadOnly Property InscribedRadius() As Double
ReadOnly Property CircumscribedRadius() As Double
End Interface
Interface IPolyhedron
Inherits IPolygon
ReadOnly Property Volume() As Double
End Interface
Public Class Triangle
Implements IPolygon,
IPerimeter,
IPolyRadius
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 3
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side() As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Height() As Double
Get
Return Me.Edge * Math.Sqrt(3.0) / 2.0
End Get
End Property
' Also called Apothem
ReadOnly Property InscribedRadius() As Double Implements IPolyRadius.InscribedRadius
Get
Return Me.Edge * Math.Sqrt(3.0) / 6.0
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property CircumscribedRadius() As Double Implements IPolyRadius.CircumscribedRadius
Get
Return Me.Edge / Math.Sqrt(3.0)
End Get
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Perimeter() As Double Implements IPerimeter.Perimeter
Get
Return Me.Edge * Me.Sides
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area() As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(3.0) / 4.0
End Get
End Property
End Class
Public Class Square
Implements IPolygon,
IPerimeter,
IPolyRadius
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 4
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side() As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Diagonal() As Double
Get
Return Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(2.0)
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property InscribedRadius() As Double Implements IPolyRadius.InscribedRadius
Get
Return Me.Edge / 2.0
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property CircumscribedRadius() As Double Implements IPolyRadius.CircumscribedRadius
Get
Return Me.Diagonal
End Get
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Perimeter() As Double Implements IPerimeter.Perimeter
Get
Return Me.Edge * Me.Sides
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area() As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side
End Get
End Property
End Class
Public Class Pentagon
Implements IPolygon,
IPerimeter
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 5
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side() As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Height() As Double
Get
Return Me.Edge * Math.Sqrt(5.0 + (2.0 * Math.Sqrt(5))) / 2.0
End Get
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Diagonal() As Double
Get
Return Me.Side * ((1 + Math.Sqrt(5.0)) / 2.0)
End Get
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Perimeter() As Double Implements IPerimeter.Perimeter
Get
Return Me.Edge * Me.Sides
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area() As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(5.0 * (5 + (2 * Math.Sqrt(5.0)))) / 4.0
End Get
End Property
End Class
Public Class Hexagon
Implements IPolygon,
IPerimeter
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 6
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side() As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Perimeter() As Double Implements IPerimeter.Perimeter
Get
Return Me.Edge * Me.Sides
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area() As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(3.0) * 3.0 / 2.0
End Get
End Property
End Class
Public Class Octagon
Implements IPolygon,
IPerimeter
Public ReadOnly Sides
Protected Edge As Double
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Sides = 8
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side() As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Perimeter() As Double Implements IPerimeter.Perimeter
Get
Return Me.Edge * Me.Sides
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Area() As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * 2.0 * (1 + Math.Sqrt(2.0))
End Get
End Property
End Class
Public Class Tetrahedron
Implements IPolyhedron,
IPolyRadius
Protected Edge As Double
Public ReadOnly Faces As Integer
Public ReadOnly Edges As Integer
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Faces = 4
Me.Edges = 6
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side() As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
ReadOnly Property PyramidHeight() As Double
Get
Return MyClass.Edge * Math.Sqrt(2.0 / 3.0)
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property InscribedRadius() As Double Implements IPolyRadius.InscribedRadius
Get
Return MyClass.Edge / Math.Sqrt(24.0)
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property CircumscribedRadius() As Double Implements IPolyRadius.CircumscribedRadius
Get
Return MyClass.Edge * Math.Sqrt(6.0) / 4.0
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property FaceArea() As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return MyClass.Edge * MyClass.Edge * Math.Sqrt(3.0) / 4.0
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property SurfaceArea() As Double
Get
Return MyClass.Edge * MyClass.Edge * Math.Sqrt(3.0)
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Volume() As Double Implements IPolyhedron.Volume
Get
Return MyClass.Edge * MyClass.Edge * MyClass.Edge * Math.Sqrt(2.0) / 12.0
End Get
End Property
End Class
Public Class Octahedron
Implements IPolyhedron,
IPolyRadius
Protected Edge As Double
Public ReadOnly Faces As Integer
Public ReadOnly Edges As Integer
Public Sub New(ByVal side As Double)
Me.Faces = 8
Me.Edges = 12
Me.Edge = side
End Sub
Public Property Side() As Double Implements IPolygon.Side
Get
Return Me.Edge
End Get
Set(ByVal value As Double)
Me.Edge = value
End Set
End Property
ReadOnly Property Midradius() As Double
Get
Return MyClass.Side / 2.0
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property InscribedRadius() As Double Implements IPolyRadius.InscribedRadius
Get
Return MyClass.Side / Math.Sqrt(6.0) / 6.0
End Get
End Property
' CircumsphereRadius
ReadOnly Property CircumscribedSphereRadius() As Double Implements IPolyRadius.CircumscribedRadius
Get
Return MyClass.Side * Math.Sqrt(2.0) / 2.0
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property SurfaceArea() As Double Implements IPolygon.Area
Get
Return MyClass.Side * MyClass.Side * Math.Sqrt(3.0) * 2.0
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property TotalArea() As Double
Get
Return MyClass.Side * MyClass.Side * MyClass.Side
End Get
End Property
ReadOnly Property Volume() As Double Implements IPolyhedron.Volume
Get
Return Me.Side * Me.Side * Me.Side * Math.Sqrt(2.0) / 3.0
End Get
End Property
End Class
</script>
<title>Geometry - Polygonal Figures</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Built-In Interfaces
Introduction
The .NET Framework provides a large collection of interfaces that you can implement in your classes. Many of the classes available in the .NET Framework implement
these interfaces. In some of your projects, you may have to implement an interface if its default behavior doesn't apply to your objects.
Cloning an Object
Copying an object consists of creating another sample of it and that contains the same values as the original. To make this operation
available to your class, you can implement an interface named ICloneable.
The ICloneable interface is defined in the System namespace of
the mscorlib.dll library.
The ICloneable interface is equipped with one method named
Clone. Its syntax is:
Function Clone As Object
To assist you with making a copy of a variable, the Object
class is equipped with a method named MemberwiseClone. This
means that all classes of the .NET Framework and any class you create in your project automatically inherits this method. The syntax of this
method is:
Protected Function MemberwiseClone As Object
Therefore, when implementing the ICloneable interface, in
your class, you can simply call
the MemberwiseClone() method.
Comparing Two Objects
Comparing two objects consists of finding out which one
comes first. The comparison is simple if you are dealing with values of
primitive types. For example, it is easy to know that 2 is lower than 5, but it
is not obvious to compare two objects created from a composite type, such as two
students, two cars, or two food items.
To assist you with comparing two objects, the .NET Framework
provides various comparable interfaces. One of these interfaces is named
IComparable. The IComparable interface is a member of the System namespace. Obviously you must define
what would be compared and how the comparison would be carried.
Most of the .NET Framework's classes that need to perform comparison
already implement the IComparable interface or one of its equivalents.
Formatting a Value
The collection of
techniques and formulas used by a language to display its values is referred to
as a format provider. When you use a variable that uses a particular formula to
display its value, to help you specify the right formula, the .NET Framework
provides the IFormatProvider interface. IFormatProvider
is defined in the System namespace.
There are two main
ways you can use the IFormatProvider. You can create a class
that implements it. The IFormatProvider is equipped with only one method:
GetFormat.
In most cases, you will use classes that already implement
the IFormatProvider interface. Those classes are equipped with an overridden
version of the ToString() method that takes IFormatProvider as argument.
Its syntax is:
Public Function ToString(provider As IFormatProvider) As String
This method requires that you build an IFormatProvider object
and pass it as argument. An alternative is to pass a string. This is possible
with another version of the ToString() method whose syntax is:
Public Function ToString(format As String) As String
This method takes a string as argument. The string can
take a character as one of the following:
| c |
C |
Currency values |
| d |
D |
Decimal numbers |
| e |
E |
Scientific numeric display such as
1.45e5 |
| f |
F |
Fixed decimal numbers |
| d |
D |
General and most common type of
numbers |
| n |
N |
Natural numbers |
| r |
R |
Roundtrip formatting |
| s |
S |
Hexadecimal formatting |
| p |
P |
Percentages |
| |