
C File Processing
 |
C File Processing |
|
C How To Process Files |
|
File processing is traditionally performed using the FILE class. In the strict C sense, FILE is a structure and it is defined in the stdio.h header file. This object is equipped with variables used to indicate what operation would be performed. To use this structure, you can first declare an instance of the FILE structure. Here is an example: FILE *Starter; After instantiating the structure, you can define what to do with it, using one of the provided functions. Because FILE was created as a C structure, it does not have member functions. The functions used to perform its related operations on files are also declared in the stdio.h header file. |
|
|
Opening and/or Saving Files |
|
To create a new file, open an existing file, or save a file, you use the fopen() function. Its syntax is: FILE *fopen(const char *FileName, const char *Mode); The first argument, FileName, must be a valid name of a file. If the user is creating or saving a new file, you can let him specify the name of the file, following the rules of the operating system. If the user is opening an existing file, you can make sure the file really exists, retrieve its name and pass it to the
fopen() function. |
|
|
If the operation performed using the fopen() function is successful, the function returns a pointer to the FILE instance that was declared. The FILE structure is usually used in C and C++ console programs that must conform to console applications. However, when used in VCL applications, because applications are created in a visual development, you should let the users use the Save and Open common dialog boxes that they are used to. In this case, if the user is opening a file, you can pass the FileName member variable of the common dialog box to the fopen() function. Because the fopen() function takes a pointer to char while the Save and Open dialog boxes use AnsiString members, you should convert The TOpenDialog::FileName or the TSaveDialog::FileName to a C string. After using a file, you should/must close its stream. This is done using the fclose() function. Its syntax is: int fclose(FILE *stream); To use this function, you must let it know what instance of the FILE object you are closing. |
|
|
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------- #include <vcl.h> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; #pragma hdrstop #include "Main.h" //--------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall TfrmMain::btnOpenClick(TObject *Sender)
{
FILE *FOpen;
if( OpenDialog1->Execute() )
{
FOpen = fopen(OpenDialog1->FileName.c_str(), "r+");
if( FOpen == NULL )
{
ShowMessage("The file could not be opened");
return;
}
}
fclose(FOpen);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall TfrmMain::btnSaveClick(TObject *Sender)
{
FILE *FSave;
if( SaveDialog1->Execute() )
{
FSave = fopen(SaveDialog1->FileName.c_str(), "w");
if( FSave == NULL )
{
ShowMessage("The file could not be saved");
return;
}
}
fclose(FSave);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
Reading From and Writing to Files |
|
To save a file, you must write data to its contents. This operation is performed using the fprintf() or the fwprintf() functions. Their syntaxes are: int fprintf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...); int fwprintf(FILE *stream, const wchar_t *format, ...); Each one of these functions takes a few arguments depending on how it is used. The first argument, stream, must be an instance of a FILE structure. The second argument is a string that specifies how data will be formatted and possibly positioned in the stream instance.The string typically starts with the % symbol followed by one or more characters that represents a format. Different formats are used depending on the type of data of the variable that is being written. You can use one the following characters:
After specifying the format, you can type the name of the variable that is being saved. You can repeatedly use the fprintf() function for each variable you want to save. If you have opened a file and want to retrieve data stored from it, you can use the fscanf() or the fwscanf() function. Their syntaxes are: int fscanf(FILE *stream, const char *format[, address, ...]); int fwscanf(FILE *stream, const wchar_t *format[, address, ...]); The first argument, stream, must be a valid instance of a FILE structure. The second argument, format, follows the same rules as for the fprintf() and the fwprintf() functions. After typing the format, type the name of the variable that is being retrieved. |
|
|
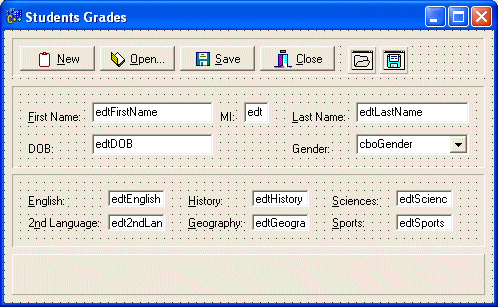
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall TfrmMain::btnOpenClick(TObject *Sender)
{
FILE *FOpen;
char FirstName[30], LastName[30], DOB[40];
int Gender;
char English[6], Language2[6], History[6],
Geography[6], Sciences[6], Sports[6];
if( OpenDialog1->Execute() )
{
FOpen = fopen(OpenDialog1->FileName.c_str(), "r+");
if( FOpen == NULL )
{
ShowMessage("The file could not be opened");
return;
}
fscanf(FOpen, "%s", FirstName);
fscanf(FOpen, "%s", LastName);
fscanf(FOpen, "%s", DOB);
fscanf(FOpen, "%d", &Gender);
fscanf(FOpen, "%s", English);
fscanf(FOpen, "%s", Language2);
fscanf(FOpen, "%s", History);
fscanf(FOpen, "%s", Geography);
fscanf(FOpen, "%s", Sciences);
fscanf(FOpen, "%s", Sports);
edtFirstName->Text = FirstName;
edtLastName->Text = LastName;
edtDOB->Text = DOB;
cboGender->ItemIndex = Gender;
edtEnglish->Text = English;
edt2ndLanguage->Text = Language2;
edtHistory->Text = History;
edtGeography->Text = Geography;
edtSciences->Text = Sciences;
edtSports->Text = Sports;
}
fclose(FOpen);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
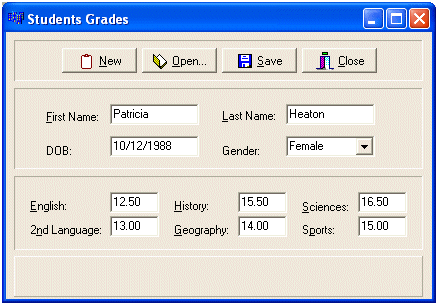
void __fastcall TfrmMain::btnSaveClick(TObject *Sender)
{
FILE *FSave;
char FirstName[30], LastName[30], DOB[40];
int Gender;
double English, Language2, History, Geography, Sciences, Sports;
strcpy(FirstName, edtFirstName->Text.c_str());
strcpy(LastName, edtLastName->Text.c_str());
strcpy(DOB, edtDOB->Text.c_str());
Gender = cboGender->ItemIndex;
English = StrToFloat(edtEnglish->Text);
Language2 = StrToFloat(edt2ndLanguage->Text);
History = StrToFloat(edtHistory->Text);
Geography = StrToFloat(edtGeography->Text);
Sciences = StrToFloat(edtSciences->Text);
Sports = StrToFloat(edtSports->Text);
if( SaveDialog1->Execute() )
{
FSave = fopen(SaveDialog1->FileName.c_str(), "w");
if( FSave == NULL )
{
ShowMessage("The file could not be opened");
return;
}
fprintf(FSave, "%s\n", FirstName);
fprintf(FSave, "%s\n", LastName);
fprintf(FSave, "%s\n", DOB);
fprintf(FSave, "%d\n", Gender);
fprintf(FSave, "%.2f\n", English);
fprintf(FSave, "%.2f\n", Language2);
fprintf(FSave, "%.2f\n", History);
fprintf(FSave, "%.2f\n", Geography);
fprintf(FSave, "%.2f\n", Sciences);
fprintf(FSave, "%.2f\n", Sports);
}
fclose(FSave);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
| Home | Copyright © 2005-2012, FunctionX, Inc. | |