Introduction to Conditional Switches
Introduction to Conditional Switches
Introduction to Case Switches
Breaking a Case
Imagine you have a list of values that can each respond to a condition as being true but you want to consider only one of those values. To let you check each one of those values, the C# language provides the switch conditional statement. It takes a value as done when calling a method. It also has a body delimited by curly brackets. In its body, each value is preceded by the case keyword. The formula to create a switch statement is:
switch(expression) { case choice1: statement1; break; case choice2: statement2; break; case choice-n: statement-n; break; }
The object or expression that holds the value to examine is passed to the parentheses of switch. The body of the switch contains one or more sections that each starts with the case keyword. Each case section considers one possible value that is followed by a colon. After the case statement, write code that must be applied to only that outcome. The case clause must end with break;.
The switch statement accepts different types of expressions or values.
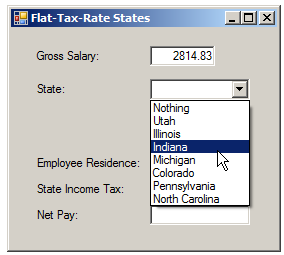
![]() Practical Learning: Switching a String
Practical Learning: Switching a String
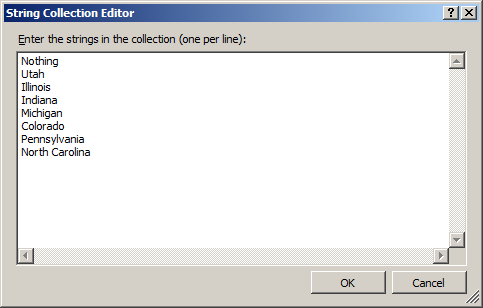
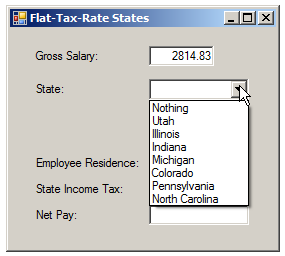
Nothing Utah Illinois Indiana Michigan Colorado Pennsylvania North Carolina
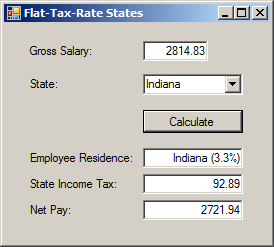
| Control | (Name) | Text | TextAlign |
| Label | Gross Salary: | ||
| TextBox | txtGrossSalary | 0 | Right |
| Label | State: | ||
| TextBox | cbxStates | ||
| Button | btnCalculate | Calculate | |
| Label | txtEmployeeResidence | ||
| TextBox | txtEmployeeResidence | Right | |
| Label | txtIncomeTax | ||
| TextBox | Right | ||
| Label | Net Pay: | ||
| TextBox | txtNetPay | Right |
Switching a String
Probably the easiest type of value to deal with is text because it can hold any value. This means that the expression you want to consider could have disparate combinations of characters. Still in the body of the switch, each case section should deal with a valid value of the possible outcomes.
![]() Practical Learning: Switching a String
Practical Learning: Switching a String
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace PayrollPreparation07
{
public partial class PayrollEvaluation : Form
{
public PayrollEvaluation()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnCalculate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
double taxes = 0.00;
string residence = "None";
string state = cbxStates.Text;
double salary = Convert.ToDouble(txtGrossSalary.Text);
switch (state)
{
case "Colorado":
taxes = salary * 4.63 / 100.00;
residence = "Colorado (4.63%)";
break;
case "Illinois":
taxes = salary * 3.75 / 100.00;
residence = "Illinois (3.75%)";
break;
case "Indiana":
taxes = salary * 3.3 / 100.00;
residence = "Indiana (3.3%)";
break;
case "Michigan":
taxes = salary * 4.25 / 100.00;
residence = "Michigan (4.25%)";
break;
case "North Carolina":
taxes = salary * 5.75 / 100.00;
residence = "North Carolina (5.75%)";
break;
case "Pennsylvania":
taxes = salary * 3.07 / 100.00;
residence = "Pennsylvania (3.07%)";
break;
case "Utah":
taxes = salary * 5 / 100.00;
residence = "Utah (5%)";
break;
}
txtEmployeeResidence.Text = residence;
txtStateIncomeTax.Text = taxes.ToString("F");
txtNetPay.Text = (salary - taxes).ToString("F");
}
}
}
namespace PayrollEvaluation06
{
static public class Calculations
{
public static double Add(double a, double b)
{
return a + b;
}
static public double Subtract(double a, double b)
{
return a - b;
}
public static double Multiply(double a, double b)
{
return a * b;
}
public static double Add5(double a, double b, double c, double d, double e)
{
return a + b + c + d + e;
}
public static double Multiply3(double a, double b, double c)
{
return a * b * c;
}
}
}namespace PayrollEvaluation06
{
public class TimeSheet
{
public double Monday { get; set; }
public double Tuesday { get; set; }
public double Wednesday { get; set; }
public double Thursday { get; set; }
public double Friday { get; set; }
public TimeSheet()
{
Monday = 0.00;
Tuesday = 0.00;
Wednesday = 0.00;
Thursday = 0.00;
Friday = 0.00;
}
public TimeSheet(double mon, double tue,
double wed, double thu, double fri)
{
Monday = mon;
Tuesday = tue;
Wednesday = wed;
Thursday = thu;
Friday = fri;
}
}
}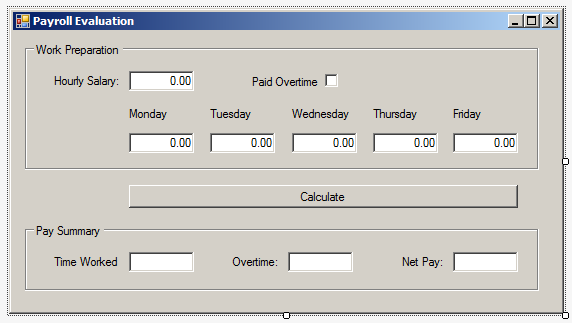
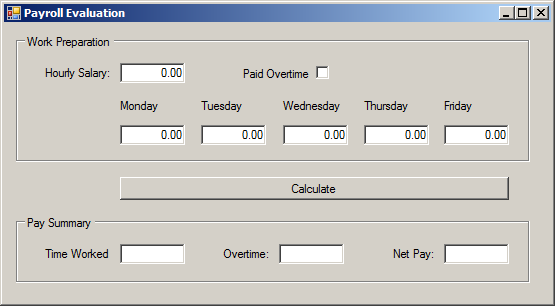
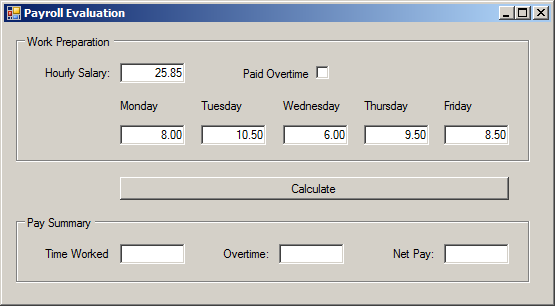
| Control | (Name) | Text | Other Properties |
| GroupBox | Work Preparation | ||
| Label | Hourly Salary: | ||
| TextBox | txtHourlySalary | 0.00 | TextAlign: Right |
| CheckBox | chkPaidOvertime | Paid Overtime | CheckAlign: MiddleRight |
| Label | Monday | ||
| Label | Tuesday | ||
| Label | Wednesday | ||
| Label | Thursday | ||
| Label | Friday | ||
| TextBox | txtMonday | 0.00 | Right |
| TextBox | txtTuesday | 0.00 | Right |
| TextBox | txtWednesday | 0.00 | Right |
| TextBox | txtThursday | 0.00 | Right |
| TextBox | txtFriday | 0.00 | Right |
| Button | btnCalculate | Calculate | |
| GroupBox | Pay Summary | ||
| Label | Time Worked: | ||
| TextBox | txtTimeWorked | Right | |
| Label | Overtime: | ||
| TextBox | txtOvertime | Right | Right |
| Label | Net Pay: | ||
| TextBox | txtNetPay | Right |
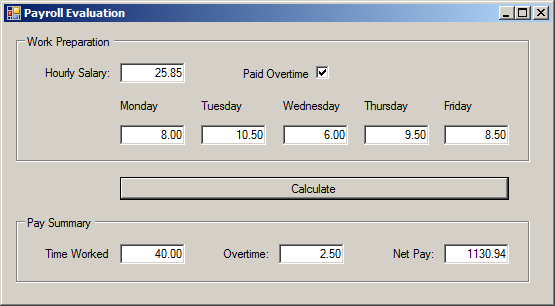
Switching to a Boolean Value
If you want to consider one of two outcomes of a Boolean expression, pass a Boolean variable or an expression that produces a Boolean value to a switch statement. One case would consider a true value and another case would consider a false value.
![]() Practical Learning: Switching to a Boolean Value
Practical Learning: Switching to a Boolean Value
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace PayrollEvaluation06
{
public partial class PayrollPreparation : Form
{
public PayrollPreparation()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
void EvaluateOvertimeSalary(TimeSheet ts, double hourlySalary)
{
double overtimePay;
double overtime = 0.00;
// mon + tue + wed + thu + fri
double timeWorked = Calculations.Add5(ts.Monday, ts.Tuesday, ts.Wednesday, ts.Thursday, ts.Friday);
double netPay = hourlySalary * timeWorked;
if (timeWorked > 40.00)
{
// timeWorked - 40.00
overtime = Calculations.Subtract(timeWorked, 40.00);
// hourlySalary * 1.50 * overtime
overtimePay = Calculations.Multiply3(hourlySalary, 1.50, overtime);
// (hourlySalary * 40.00) + overtimePay
netPay = Calculations.Add(Calculations.Multiply(hourlySalary, 40.00), overtimePay);
}
txtTimeWorked.Text = timeWorked.ToString("F");
txtOvertime.Text = overtime.ToString("F");
txtNetPay.Text = netPay.ToString("F");
}
private void btnCalculate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
double mon = Convert.ToDouble(txtMonday.Text);
double tue = Convert.ToDouble(txtTuesday.Text);
double wed = Convert.ToDouble(txtWednesday.Text);
double thu = Convert.ToDouble(txtThursday.Text);
double fri = Convert.ToDouble(txtFriday.Text);
double hSalary = Convert.ToDouble(txtHourlySalary.Text);
TimeSheet record = new TimeSheet(mon, tue, wed, thu, fri);
switch (chkPaidOvertime.Checked)
{
case true:
EvaluateOvertimeSalary(record, hSalary);
break;
case false:
double timeWorked = Calculations.Add5(ts.Monday, ts.Tuesday, ts.Wednesday, ts.Thursday, ts.Friday);
txtTimeWorked.Text = timeWorked.ToString("F");
txtOvertime.Text = "0.00";
txtNetPay.Text = (timeWorked * hSalary).ToString("F");
break;
}
}
}
}

namespace Chemistry07
{
public enum Phase
{
Gas,
Liquid,
Solid,
Unknown
}
public class Element
{
public string Symbol { get; set; }
public string ElementName { get; set; }
public int AtomicNumber { get; set; }
public double AtomicWeight { get; set; }
public Phase Phase { get; set; }
public Element() {}
public Element(int number) => AtomicNumber = number;
public Element(string symbol) => Symbol = symbol;
public Element(int number, string symbol, string name, double mass, Phase phase)
{
ElementName = name;
AtomicWeight = mass;
Phase = phase;
Symbol = symbol;
AtomicNumber = number;
}
}
}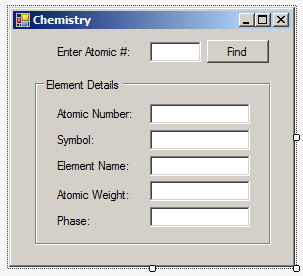
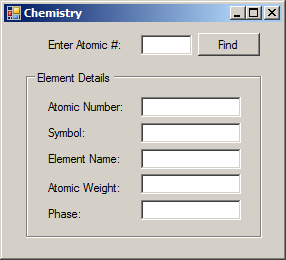
| Control | (Name) | Text |
| Label | Enter Atomic #:: | |
| TextBox | txtValueEntered | |
| Button | btnFind | Find |
| GroupBox | Element Detais | |
| Label | Atomic Number: | |
| TextBox | txtAtomicNumber | |
| Label | Symbol: | |
| TextBox | txtSymbol | |
| Label | Element Name: | |
| TextBox | txtElementName | |
| Label | Atomic Weight: | |
| TextBox | txtAtomicWeight | |
| Label | Phase: | |
| TextBox | txtPhase |
Switching Integral Values
Switching an Integer
Probably the most regularly used type of value in a switch expression is a natural number. The object or expression passed to the switch can come from any source as long as it represents a constant integer.
![]() Practical Learning: Introducing Logical Disjunctions
Practical Learning: Introducing Logical Disjunctions
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Chemistry07
{
public partial class Chemistry : Form
{
public Chemistry()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnFind_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Element H = new Element(1, "H", "Hydrogen", 1.008, Phase.Gas);
Element He = new Element(2, "He", "Helium", 4.002602, Phase.Gas);
Element Li = new Element(3, "Li", "Lithium", 6.94, Phase.Solid);
Element Be = new Element(4, "Be", "Beryllium", 9.0121831, Phase.Solid);
Element B = new Element(5, "B", "Boron", 10.81, Phase.Solid);
Element C = new Element(name: "Carbon", mass: 12.011, symbol: "C", number: 6, phase: Phase.Solid);
Element N = new Element(7);
N.Symbol = "N";
N.AtomicWeight = 14.007;
N.ElementName = "Nitrogen";
N.Phase = Phase.Gas;
Element O = new Element("O")
{
AtomicNumber = 8,
ElementName = "Oxygen",
AtomicWeight = 15.999,
Phase = Phase.Gas
};
Element F = new Element("F") { AtomicNumber = 9, ElementName = "Fluorine",
AtomicWeight = 15.999, Phase = Phase.Gas };
Element Ne = new Element("Ne")
{
AtomicNumber = 10, ElementName = "Neon",
AtomicWeight = 20.1797, Phase = Phase.Gas
};
Element Na = new Element(11, "Na", "Sodium", 22.98976928, Phase.Solid);
Element Mg = new Element(12, "Mg", "Magnesium", 24.305, Phase.Solid);
Element Al = new Element(13, "Al", "Aluminium", 26.9815385, Phase.Solid);
Element Si = new Element() { ElementName = "Silicon", AtomicWeight = 28.085, Symbol = "Si", AtomicNumber = 14, Phase = Phase.Solid };
Element P = new Element() {
ElementName = "Phosphorus", AtomicWeight = 30.973761998,
Symbol = "P", AtomicNumber = 15, Phase = Phase.Solid };
Element S = new Element(16, "S", "Sulfur", 32.06, Phase.Solid);
Element Cl = new Element() { ElementName = "Chlorine", AtomicWeight = 35.446, Symbol = "Cl", AtomicNumber = 17, Phase = Phase.Gas };
Element Ar = new Element() { ElementName = "Argon", AtomicWeight = 39.792, Symbol = "Ar", AtomicNumber = 18, Phase = Phase.Gas };
Element K = new Element() { ElementName = "Potassium", Symbol = "K", Phase = Phase.Solid, AtomicWeight = 39.0983, AtomicNumber = 19 };
Element Ca = new Element() { Symbol = "Ca", Phase = Phase.Solid, AtomicNumber = 20, ElementName = "Calcium", AtomicWeight = 40.078 };
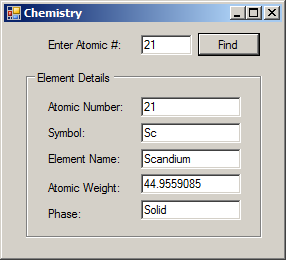
Element Sc = new Element() { AtomicNumber = 21, Symbol = "Sc", AtomicWeight = 44.9559085, Phase = Phase.Solid, ElementName = "Scandium" };
Element selected = new Element();
int number = int.Parse(txtValueEntered.Text);
switch (number)
{
case 20:
selected = Ca;
break;
case 12:
selected = Mg;
break;
case 5:
selected = B;
break;
case 17:
selected = Cl;
break;
case 15:
selected = P;
break;
case 6:
selected = C;
break;
case 21:
selected = Sc;
break;
case 7:
selected = N;
break;
case 9:
selected = F;
break;
case 2:
selected = He;
break;
case 10:
selected = Ne;
break;
case 11:
selected = Na;
break;
case 4:
selected = Be;
break;
case 13:
selected = Al;
break;
case 3:
selected = Li;
break;
case 19:
selected = K;
break;
case 14:
selected = Si;
break;
case 16:
selected = S;
break;
case 8:
selected = O;
break;
case 18:
selected = Ar;
break;
}
txtSymbol.Text = selected.Symbol;
txtAtomicNumber.Text = selected.AtomicNumber.ToString();
txtElementName.Text = selected.ElementName;
txtAtomicWeight.Text = selected.AtomicWeight.ToString();
txtPhase.Text = selected.Phase.ToString();
}
}
}
namespace CompoundInterest3
{
public enum CompoundFrequency
{
Daily,
Weekly,
Monthly,
Quaterly,
Semiannually,
Annually
}
}
| Control | (Name) | Text | Other Properties |
| Label | Principal: | ||
| TextBox | txtPrincipal | 0.00 | TextAlign: Right |
| Label | Interest Rate: | ||
| TextBox | txtInterest Rate | 0.00 | TextAlign: Right |
| Label | % | ||
| Label | Periods: | ||
| TextBox | txtPeriods | 0 | TextAlign: Right |
| Label | Years: | ||
| GroupBox | Compound Frequency | ||
| RadioButton | rdoDaily | Daily | CheckAlign: MiddleRight |
| RadioButton | rdoQuaterly | Quaterly | CheckAlign: MiddleRight |
| RadioButton | rdoWeekly | Weekly | CheckAlign: MiddleRight |
| RadioButton | rdoSemiannually | Semiannually | CheckAlign: MiddleRight |
| RadioButton | rdoMonthly | Monthly | CheckAlign: MiddleRight |
| RadioButton | rdoAnnually | Annually | CheckAlign: MiddleRight |
| Button | btnCalculate | Calculate | |
| Label | Interest Earned: | ||
| TextBox | txtInterestEarned | TextAlign: Right | |
| Label | Future Value: | ||
| TextBox | txtFutureValue | TextAlign: Right |
Switching an Enumeration
The switch operation supports values based on an enumeration. When creating the statement, you can pass an expression that holds the value of an enumeration. In the body of the switch clause, each case can represent one of the members of the enumeration.
![]() Practical Learning: Introducing if...else if Conditions
Practical Learning: Introducing if...else if Conditions
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CompoundInterest3
{
public partial class CompoundInterest : Form
{
public CompoundInterest()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnCalculate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
double frequency = 0.00;
double principal = Convert.ToDouble(txtPrincipal.Text);
double interestRate = Convert.ToDouble(txtInterestRate.Text);
double periods = Convert.ToDouble(txtPeriods.Text);
double iRate = interestRate / 100.00;
CompoundFrequency compounding = CompoundFrequency.Daily;
if (rdoDaily.Checked)
compounding = CompoundFrequency.Daily;
if (rdoWeekly.Checked)
compounding = CompoundFrequency.Weekly;
if (rdoMonthly.Checked)
compounding = CompoundFrequency.Monthly;
if (rdoQuaterly.Checked)
compounding = CompoundFrequency.Quaterly;
if (rdoSemiannually.Checked)
compounding = CompoundFrequency.Semiannually;
if (rdoAnnually.Checked)
compounding = CompoundFrequency.Annually;
switch (compounding)
{
case CompoundFrequency.Daily:
frequency = 365.00;
break;
case CompoundFrequency.Weekly:
frequency = 52.00;
break;
case CompoundFrequency.Monthly:
frequency = 12.00;
break;
case CompoundFrequency.Quaterly:
frequency = 4.00;
break;
case CompoundFrequency.Semiannually:
frequency = 2.00;
break;
case CompoundFrequency.Annually:
frequency = 1.00;
break;
}
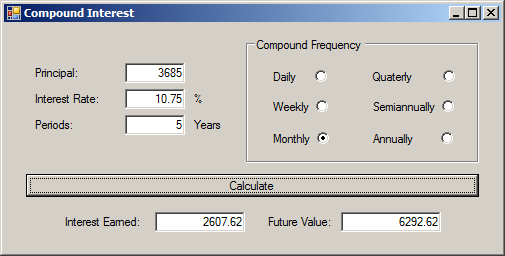
double futureValue = principal * Math.Pow((1.00 + (iRate / frequency)), frequency * periods);
double interestEarned = futureValue - principal;
txtInterestEarned.Text = interestEarned.ToString("F");
txtFutureValue.Text = futureValue.ToString("F");
}
}
}
|
|
||
| Previous | Copyright © 2001-2021, FunctionX | Next |
|
|
||