Conditional Conjunctions and Disjunctions
Conditional Conjunctions and Disjunctions
Conditional Conjunctions
Nesting a Conditional Statement
A conditional statement has a body, which is from where the condition is defined to where its behavior ends. In the body of the conditional statement, you can create another conditional statement. This is referred to as nesting the condition. In a method of a class, the condition nesting can be formulated as follows:
if( condition1 ) // The nesting, main, parent, first, or external condition
if( condition2 ) // The nested, child, second, or internal condition
statement(s)
If the code of a condition involves many lines of code, you can delimite its body with curly brackets:
if( condition1 )
{
if( condition2 )
{
statement(s)
}
}
In the same way, you can nest one conditional statement in one, then nest that new one in another conditional statement, and so on. In a method, this can be formulated as follows:
if( condition1 )
if( condition2 )
if( condition3 )
statement(s)
If a section of code is long, you can include its child code in curly brackets:
if( condition1 )
{
if( condition2 )
{
if( condition3 )
{
statement(s)
}
}
}
![]() Practical Learning: Introducing Boolean Conjunctions
Practical Learning: Introducing Boolean Conjunctions
| Control | (Name) | Text | TextAlign |
| Label | Number of Shares: | ||
| TextBox | txtNumberOfShares | 0 | Right |
| Label | Price Per Share: | ||
| TextBox | txtPricePerShare | 0.00 | Right |
| Button | btnCalculate | Calculate | |
| Label | Principal | ||
| TextBox | txtPrincipal | Right | |
| Label | Commission | ||
| TextBox | txtCommission | Right | |
| Label | Total Investment: | ||
| TextBox | txtTotalInvestment | Right |
Remember that you can nest one condition in another condition as in:
if( condition1 )
if( condition2 )
statement(s)
Or:
if( condition1 )
{
if( condition2 )
{
statement(s)
}
}
When you nest a condition, you are in fact indicating that "if condition1 verifies, then if condition2 verifies, do this...". The external condition must be verified first as being true or false (depending on how you wrote the conditional statement). If that first (the external) condition is true, the second (the internal) condition is checked. If the first (or external) condition is not valid, the second (the internal) condition is not evaluated. To support a simplified technique to apply this description, the C# language provides the Boolean "AND" operator, represented as &&. Its primary formula is:
condition1 && condition2
You must formulate each condition to produce a true or a false result. The result is as follows:
The conjunction operation can be resumed as follows:
| Condition 1 | Contition 2 | Condition 1 AND Condition 2 |
| False | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| True | False | False |
| True | True | True |
![]() Practical Learning: Introducing Boolean Conjunctions
Practical Learning: Introducing Boolean Conjunctions
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace StockBrokerCompany1
{
public partial class StocksProcessing : Form
{
public StocksProcessing()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnCalculate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
double commission = 0.00;
int numberOfShares = int.Parse(txtNumberOfShares.Text);
double pricePerShare = double.Parse(txtPricePerShare.Text);
double principal = numberOfShares * pricePerShare;
if (principal >= 0 && principal <= 2500)
commission = 26.25 + (principal * 0.0014);
if (principal > 2500 && principal <= 6000)
commission = 45 + (principal * 0.0054);
if (principal > 6000 && principal <= 20000)
commission = 60.00 + (principal * 0.0028);
if (principal > 20000 && principal <= 50000)
commission = 75.00 + (principal * 0.001875);
if (principal > 50000 && principal <= 500000)
commission = 131.25 + (principal * 0.0009);
if (principal > 500000)
commission = 206.25 + (principal * 0.000075);
txtPrincipal.Text = principal.ToString("F");
txtCommission.Text = commission.ToString("F");
txtTotalInvestment.Text = (principal + commission).ToString("F");
}
}
}
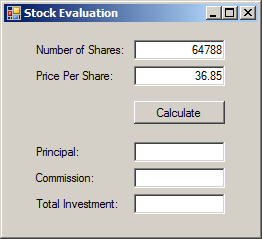
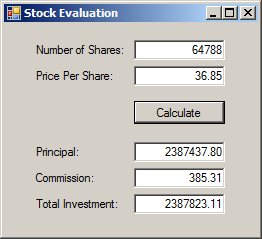
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace StockBrokerCompany1
{
public partial class StocksProcessing : Form
{
public StocksProcessing()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnCalculate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
double commission = 0.00;
int numberOfShares = int.Parse(txtNumberOfShares.Text);
double pricePerShare = double.Parse(txtPricePerShare.Text);
double principal = numberOfShares * pricePerShare;
if( (principal >= 0) && (principal <= 2500) )
commission = 26.25 + (principal * 0.0014);
if( (principal > 2500) && (principal <= 6000) )
commission = 45 + (principal * 0.0054);
if( (principal > 6000) && (principal <= 20000) )
commission = 60.00 + (principal * 0.0028);
if( (principal > 20000) && (principal <= 50000) )
commission = 75.00 + (principal * 0.001875);
if( (principal > 50000) && (principal <= 500000) )
commission = 131.25 + (principal * 0.0009);
if( principal > 500000 )
commission = 206.25 + (principal * 0.000075);
txtPrincipal.Text = principal.ToString("F");
txtCommission.Text = commission.ToString("F");
txtTotalInvestment.Text = (principal + commission).ToString("F");
}
}
}namespace Chemistry06
{
public enum Phase
{
Gas,
Liquid,
Solid,
Unknown
}
public class Element
{
public string Symbol { get; set; }
public string ElementName { get; set; }
public int AtomicNumber { get; set; }
public double AtomicWeight { get; set; }
public Phase Phase { get; set; }
public Element()
{
}
public Element(int number)
{
AtomicNumber = number;
}
public Element(string symbol)
{
Symbol = symbol;
}
public Element(int number, string symbol, string name, double mass, Phase phase)
{
ElementName = name;
AtomicWeight = mass;
Phase = phase;
Symbol = symbol;
AtomicNumber = number;
}
}
}
| Control | (Name) | Text |
| Label | Element Symbol: | |
| TextBox | txtElementSymbol | |
| Button | btnFind | Find |
| GroupBox | Element Detais | |
| Label | Symbol: | |
| TextBox | txtSymbol | |
| Label | Atomic Number: | |
| TextBox | txtAtomicNumber | |
| Label | Element Name: | |
| TextBox | txtElementName | |
| Label | Atomic Weight: | |
| TextBox | txtAtomicWeight | |
| Label | Phase: | |
| TextBox | txtPhase |
Combining Various Conjunctions
Depending on your goal, if two conditions are not enough, you can create as many conjunctions as you want. The formula to follow is:
condition1 && condition2 && condition3 && . . . && condition_n
When the expression is checked, if any of the operations is false, the whole operation is false. The only time the whole operation is true is if all of the operations are true.
Of course, you can nest a Boolean condition inside another conditional statement.
Boolean Disjunctions
A Boolean disjunction is a conditional statement where you combine more than one condition but only one of the conditions needs to be true for the whole operation to be true. This operation is performed using the Boolean "OR" operator represented as ||. The primary formula to follow is:
condition1 || condition2
The operation works as follows:
The operation can be resumed as follows:
| Condition 1 | Contition 2 | Condition 1 AND Condition 2 | Condition 1 OR Condition 2 |
| False | False | False | False |
| False | True | False | True |
| True | False | False | True |
| True | True | True | True |
![]() Practical Learning: Introducing Logical Disjunctions
Practical Learning: Introducing Logical Disjunctions
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Chemistry06
{
public partial class Chemistry : Form
{
public Chemistry()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnFind_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Element h = new Element(1, "H", "Hydrogen", 1.008, Phase.Gas);
Element b = new Element(5, "B", "Boron", 10.81, Phase.Solid);
Element c = new Element(name: "Carbon", mass: 12.011, symbol: "C", number: 6, phase: Phase.Solid);
Element n = new Element(7);
n.Symbol = "N";
n.AtomicWeight = 14.007;
n.ElementName = "Nitrogen";
n.Phase = Phase.Gas;
Element o = new Element("O")
{
AtomicNumber = 8,
ElementName = "Oxygen",
AtomicWeight = 15.999,
Phase = Phase.Gas
};
Element f = new Element("F")
{
AtomicNumber = 9,
ElementName = "Fluorine",
AtomicWeight = 15.999,
Phase = Phase.Gas
};
Element p = new Element()
{
ElementName = "Phosphorus",
AtomicWeight = 30.973761998,
Symbol = "P",
AtomicNumber = 15,
Phase = Phase.Solid
};
Element s = new Element(16, "S", "Sulfur", 32.06, Phase.Solid);
Element k = new Element() { ElementName = "Potassium", Symbol = "K", Phase = Phase.Solid, AtomicWeight = 39.0983, AtomicNumber = 19 };
Element selected;
string symbol = txtElementSymbol.Text;
if ( (symbol == "h") || (symbol == "H") ) { selected = h; }
else if( (symbol == "b") || (symbol == "B") ) { selected = b; }
else if( (symbol == "c") || (symbol == "C") ) { selected = c; }
else if( (symbol == "n") || (symbol == "N") ) { selected = n; }
else if( (symbol == "o") || (symbol == "O") ) { selected = o; }
else if( (symbol == "F") || (symbol == "f") ) { selected = f; }
else if( (symbol == "P") || (symbol == "p") ) { selected = p; }
else if( (symbol == "S") || (symbol == "s") ) { selected = s; }
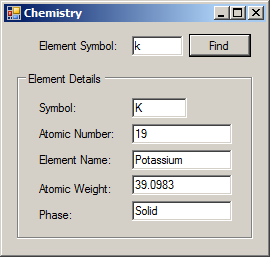
else if( (symbol == "k") || (symbol == "K") ) { selected = k; }
txtSymbol.Text = selected.Symbol;
txtAtomicNumber.Text = selected.AtomicNumber.ToString();
txtElementName.Text = selected.ElementName;
txtAtomicWeight.Text = selected.AtomicWeight.ToString();
txtPhase.Text = selected.Phase.ToString();
}
}
}
Combining Various Disjunctions
You can create a conditional statement that includes as many disjunctions as you want. The formula to follow is:
condition1 || condition2 || . . . || condition_n
The rule is the same: If any one of the individual operations is true, the whole operation is true. The whole operation is false only if all of the operations are false.
![]() Practical Learning: Introducing Logical Disjunctions
Practical Learning: Introducing Logical Disjunctions
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Chemistry06
{
public partial class Chemistry : Form
{
public Chemistry()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnFind_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Element h = new Element(1, "H", "Hydrogen", 1.008, Phase.Gas);
Element he = new Element(2, "He", "Helium", 4.002602, Phase.Gas);
Element li = new Element(3, "Li", "Lithium", 6.94, Phase.Solid);
Element be = new Element(4, "Be", "Beryllium", 9.0121831, Phase.Solid);
Element b = new Element(5, "B", "Boron", 10.81, Phase.Solid);
Element c = new Element(name: "Carbon", mass: 12.011, symbol: "C", number: 6, phase: Phase.Solid);
Element n = new Element(7);
n.Symbol = "N";
n.AtomicWeight = 14.007;
n.ElementName = "Nitrogen";
n.Phase = Phase.Gas;
Element o = new Element("O")
{
AtomicNumber = 8,
ElementName = "Oxygen",
AtomicWeight = 15.999,
Phase = Phase.Gas
};
Element f = new Element("F")
{
AtomicNumber = 9,
ElementName = "Fluorine",
AtomicWeight = 15.999,
Phase = Phase.Gas
};
Element ne = new Element("Ne")
{
AtomicNumber = 10,
ElementName = "Neon",
AtomicWeight = 20.1797,
Phase = Phase.Gas
};
Element na = new Element(11, "Na", "Sodium", 22.98976928, Phase.Solid);
Element mg = new Element(12, "Mg", "Magnesium", 24.305, Phase.Solid);
Element al = new Element(13, "Al", "Aluminium", 26.9815385, Phase.Solid);
Element si = new Element() { ElementName = "Silicon", AtomicWeight = 28.085, Symbol = "Si", AtomicNumber = 14, Phase = Phase.Solid };
Element p = new Element()
{
ElementName = "Phosphorus",
AtomicWeight = 30.973761998,
Symbol = "P",
AtomicNumber = 15,
Phase = Phase.Solid
};
Element s = new Element(16, "S", "Sulfur", 32.06, Phase.Solid);
Element cl = new Element() { Phase = Phase.Gas, AtomicWeight = 35.446, ElementName = "Chlorine", AtomicNumber = 17, Symbol = "Cl" };
Element ar = new Element() { AtomicWeight = 39.792, Symbol = "Ar", Phase = Phase.Gas, ElementName = "Argon", AtomicNumber = 18 };
Element k = new Element() { ElementName = "Potassium", AtomicWeight = 39.0983, Symbol = "K", Phase = Phase.Solid, AtomicNumber = 19 };
Element selected = new Element();
string symbol = txtElementSymbol.Text;
if (symbol == "h" || symbol == "H") { selected = h; }
else if (symbol == "he" || symbol == "He" || symbol == "HE" || symbol == "hE") { selected = he; }
else if (symbol == "li" || symbol == "Li" || symbol == "LI" || symbol == "lI") { selected = li; }
else if (symbol == "be" || symbol == "Be" || symbol == "BE" || symbol == "bE") { selected = be; }
else if (symbol == "b" || symbol == "B") { selected = b; }
else if (symbol == "c" || symbol == "C") { selected = c; }
else if (symbol == "n" || symbol == "N") { selected = n; }
else if (symbol == "o" || symbol == "O") { selected = o; }
else if (symbol == "F" || symbol == "f") { selected = f; }
else if (symbol == "ne" || symbol == "Ne" || symbol == "NE" || symbol == "nE") { selected = ne; }
else if (symbol == "na" || symbol == "NA" || symbol == "Na" || symbol == "nA") { selected = na; }
else if (symbol == "mg" || symbol == "Mg" || symbol == "MG" || symbol == "mG") { selected = mg; }
else if (symbol == "al" || symbol == "Al" || symbol == "AL" || symbol == "aL") { selected = al; }
else if (symbol == "si" || symbol == "Si" || symbol == "SI" || symbol == "sI") { selected = si; }
else if (symbol == "P" || symbol == "p") { selected = p; }
else if (symbol == "S" || symbol == "s") { selected = s; }
else if (symbol == "CL" || symbol == "Cl" || symbol == "cL" || symbol == "cl") { selected = cl; }
else if (symbol == "aR" || symbol == "AR" || symbol == "ar" || symbol == "Ar") { selected = ar; }
else if (symbol == "k" || symbol == "K") { selected = k; }
txtSymbol.Text = selected.Symbol;
txtAtomicNumber.Text = selected.AtomicNumber.ToString();
txtElementName.Text = selected.ElementName;
txtAtomicWeight.Text = selected.AtomicWeight.ToString();
txtPhase.Text = selected.Phase.ToString();
}
}
}
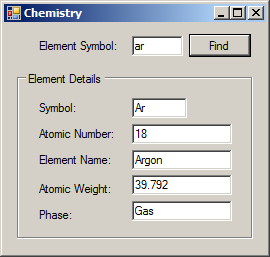
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Chemistry06
{
public partial class Chemistry : Form
{
public Chemistry()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnFind_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Element h = new Element(1, "H", "Hydrogen", 1.008, Phase.Gas);
Element he = new Element(2, "He", "Helium", 4.002602, Phase.Gas);
Element li = new Element(3, "Li", "Lithium", 6.94, Phase.Solid);
Element be = new Element(4, "Be", "Beryllium", 9.0121831, Phase.Solid);
Element b = new Element(5, "B", "Boron", 10.81, Phase.Solid);
Element c = new Element(name: "Carbon", mass: 12.011, symbol: "C", number: 6, phase: Phase.Solid);
Element n = new Element(7);
n.Symbol = "N";
n.AtomicWeight = 14.007;
n.ElementName = "Nitrogen";
n.Phase = Phase.Gas;
Element o = new Element("O")
{
AtomicNumber = 8,
ElementName = "Oxygen",
AtomicWeight = 15.999,
Phase = Phase.Gas
};
Element f = new Element("F")
{
AtomicNumber = 9,
ElementName = "Fluorine",
AtomicWeight = 15.999,
Phase = Phase.Gas
};
Element ne = new Element("Ne")
{
AtomicNumber = 10,
ElementName = "Neon",
AtomicWeight = 20.1797,
Phase = Phase.Gas
};
Element na = new Element(11, "Na", "Sodium", 22.98976928, Phase.Solid);
Element mg = new Element(12, "Mg", "Magnesium", 24.305, Phase.Solid);
Element al = new Element(13, "Al", "Aluminium", 26.9815385, Phase.Solid);
Element si = new Element() { ElementName = "Silicon", AtomicWeight = 28.085, Symbol = "Si", AtomicNumber = 14, Phase = Phase.Solid };
Element p = new Element()
{
ElementName = "Phosphorus",
AtomicWeight = 30.973761998,
Symbol = "P",
AtomicNumber = 15,
Phase = Phase.Solid
};
Element s = new Element(16, "S", "Sulfur", 32.06, Phase.Solid);
Element cl = new Element() { ElementName = "Chlorine", AtomicWeight = 35.446, Symbol = "Cl", AtomicNumber = 17, Phase = Phase.Gas };
Element ar = new Element() { AtomicWeight = 39.792, Symbol = "Ar", Phase = Phase.Gas, ElementName = "Argon", AtomicNumber = 18 };
Element k = new Element() { ElementName = "Potassium", Phase = Phase.Solid, AtomicNumber = 19, AtomicWeight = 39.0983, Symbol = "K" };
Element ca = new Element() { Symbol = "Ca", Phase = Phase.Solid, AtomicNumber = 20, ElementName = "Calcium", AtomicWeight = 40.078 };
Element selected = new Element();
string symbol = txtElementSymbol.Text;
if ( (symbol == "h") || (symbol == "H") ) { selected = h; }
else if( (symbol == "he") || (symbol == "He") || (symbol == "HE") || (symbol == "hE") ) { selected = he; }
else if( (symbol == "li") || (symbol == "Li") || (symbol == "LI") || (symbol == "lI") ) { selected = li; }
else if( (symbol == "be") || (symbol == "Be") || (symbol == "BE") || (symbol == "bE") ) { selected = be; }
else if( (symbol == "b") || (symbol == "B") ) { selected = b; }
else if( (symbol == "c") || (symbol == "C") ) { selected = c; }
else if( (symbol == "n") || (symbol == "N") ) { selected = n; }
else if( (symbol == "o") || (symbol == "O") ) { selected = o; }
else if( (symbol == "F") || (symbol == "f") ) { selected = f; }
else if( (symbol == "ne") || (symbol == "Ne") || (symbol == "NE") || (symbol == "nE") ) { selected = ne; }
else if( (symbol == "na") || (symbol == "NA") || (symbol == "Na") || (symbol == "nA") ) { selected = na; }
else if( (symbol == "mg") || (symbol == "Mg") || (symbol == "MG") || (symbol == "mG") ) { selected = mg; }
else if( (symbol == "al") || (symbol == "Al") || (symbol == "AL") || (symbol == "aL") ) { selected = al; }
else if( (symbol == "si") || (symbol == "Si") || (symbol == "SI") || (symbol == "sI") ) { selected = si; }
else if( (symbol == "P") || (symbol == "p") ) { selected = p; }
else if( (symbol == "S") || (symbol == "s") ) { selected = s; }
else if( (symbol == "CL") || (symbol == "Cl") || (symbol == "cL") || (symbol == "cl") ) { selected = cl; }
else if( (symbol == "aR") || (symbol == "AR") || (symbol == "ar") || (symbol == "Ar") ) { selected = ar; }
else if( (symbol == "k") || (symbol == "K") ) { selected = k; }
else if ((symbol == "Ca") || (symbol == "cA") || (symbol == "CA") || (symbol == "ca")) { selected = ca; }
txtSymbol.Text = selected.Symbol;
txtAtomicNumber.Text = selected.AtomicNumber.ToString();
txtElementName.Text = selected.ElementName;
txtAtomicWeight.Text = selected.AtomicWeight.ToString();
txtPhase.Text = selected.Phase.ToString();
}
}
}
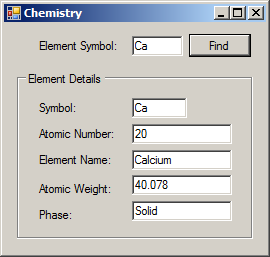
Combining Conjunctions and Disjunctions
Conjunctions and disjunctions can be used in the same expression. A conjunction (or disjunction) can be used to evaluate one sub-expression while a disjunction (or conjunction) can be used to evaluate another sub-expression.
![]() Practical Learning: Ending the Lesson
Practical Learning: Ending the Lesson
|
|
||
| Previous | Copyright © 2001-2021, FunctionX | Next |
|
|
||