 |
Data Entry With Date and Time Values
|
| |
|
|
A date is a type of number that measures the number of
units, called days, that have occurred since another starting date. To
express this number (the date), there are rules you should (must) follow.
The rules depend on each language. To know the rules for US English, from
the Control Panel, you can open the Regional and Language Options window,
click the Customize button, and access the Date tab:
|
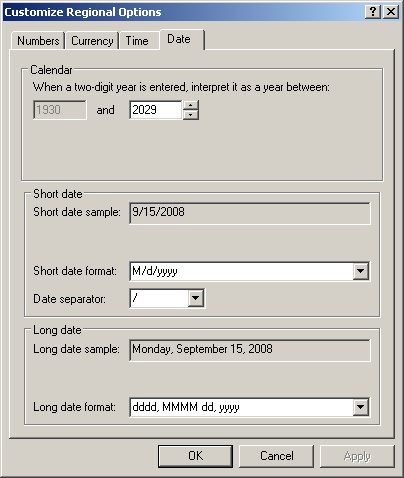
We will come back to some aspects of these rules.
To enter a date in a cell, you use a format. In US English,
you use a combination of a month, a day, and a year. These entities must be
separated. The separation depends on both you and the way the operating system
handles dates.
To express a month, you have a choice between a number and a
name. If you decide to use a number, it should (must) be between 1 included and
the 12 included. If the month is between 1 and 9, you can precede it with 0 or
not. If you want to express a month with a name, you have two choices. You can
use a long name or a short name. The long names of month are January, February,
March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, and
December. Their equivalent short names use three letters each and they are
Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, and Dec respectively.
A day is expressed using a number that starts with 1 and
ends with either 30 or 31 depending on the month except for February. The month
of February can have either 28 or 29 days depending on something called the leap
year. If the day value is between 1 and 9 included, you can enter it with a
leading 0 or not.
The year is entered with 2 or 4 digits. If you enter the
year with 2 digits, Microsoft Office Excel 2007 may ask you to specify whether
you want to use the current century (2000 to 2100) or the previous century (1900
to 1999). To be safe, you should always enter the year with 4 digits.
As mentioned already, when entering a date, you must
separate the values of the month, the day, and the year. In US English, the
symbol used to separate these entities is the forward slash "/" as you
can see from the Date Separator combo box in the Customize Regional Options. An
example of entering a date would be 02/18/1998.
In reality, Microsoft Excel is very flexible and
understanding with date formats. For example, instead of the forward slash, when
entering a date, you can use the dash "-". An example would be
02-18-1998. After entering the date and pressing either Tab or Enter or clicking
another cell, if Microsoft Excel can successfully analyze the value and conclude
that it is a date, it would convert it to the right format. In this case, the
date would be converted to 02/18/1998.
As mentioned already, Microsoft Excel also allows you to use
the name of a month. You must follow some rules if you choose this format. If
you want to specify the name of a month, use one of the following formats:
- dd-mmm
- dd mmm
- dd-mmmm
- dd mmmm
To use this format, enter the day value using one or two
digits. If the day is less than 10, you can enter it with a leading 0. After the
day, either leave an empty space or enter -, followed by the short or the long
name of the month. Examples are 04-Jan or 16 Apr or 8-December or 26 December.
Alternatives to these formats are:
- mmm dd
- mmm-dd
- mmmm dd
- mmmm-dd
In this case, start the date with the month as a short or a
long name, followed by either an empty space or -, followed by the day value.
These would have the same effect.
After entering the date with only the day and the month,
Microsoft Excel would analyze the value. If the application concludes that the
value is a date, it would use the current year for that date and convert it to a
valid date.
|
 Practical
Learning: Entering Simple Dates Practical
Learning: Entering Simple Dates
|
|
- The CPAR1.xlsx workbook should still be opened and the Repair Invoice
worksheet active.
Click Cell B6 and type, type 01-Oct and, on the Formula Bar, click
the Enter button  . .
Notice that Microsoft Excel has recognized the value as date and, in the
Formula Bar, notice that Microsoft Excel added the current year to complete
the date
- Save the workbook
|
|