|
In the previous lesson, we saw that a table provides a good
technique of organizing a list of items and to store the list in a database
file. To create a table, you can type the expression CREATE TABLE
followed by the name of the table. The syntax starts with:
CREATE TABLE Name;
The CREATE and TABLE keywords must be used to let
the SQL interpreter know that you
want to create a table. The Name factor specifies the name of the new
table. The Name can use the rules and suggestions we reviewed for the
database objects.
In reality, a table needs at least one column. The formula
to create a column is:
CREATE TABLE Employees(ColumnName DataType)
A column is specified with a name and a data type. The
name can follow the rules and suggestions we
reviewed for the tables. In the next lesson, we will go through the details of
creating a table and its columns.
|
 Practical Learning: Creating a Table
Practical Learning: Creating a Table
|
|
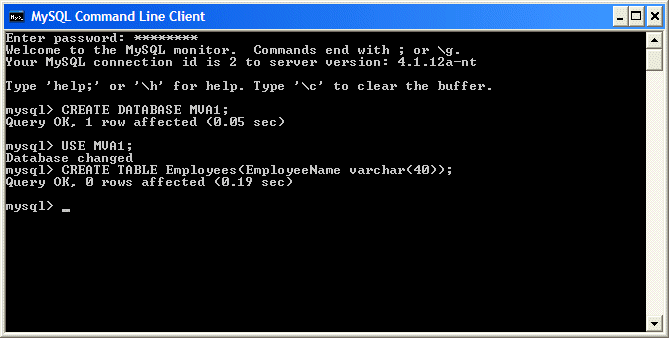
- Start your SQL environment
- To create a new database, execute the following statement:
- To make the new database the default, execute the following statement:
- To create a new table, execute the following statement:
CREATE TABLE Employees(EmployeeName varchar(40));
|
 |
|
A Database With Various Tables
|
|
We learned the basic
techniques of creating a table but we created only one table. Many
databases use more than one table. There is primarily no
relationship between two tables of the same database. You can create the
tables as you see fit and use them as you wish, in future lessons, we will
learn how to "connect" tables that belong to the same database
so that their information can be shared.
|

