|
The Service and the Server |
|
|
|
After installing Microsoft SQL Server, you can start
using it.
Because Microsoft SQL Server works as a service to the
operating system, in order to use it, you must make sure its service has
started. Sometimes you will have to start the service and sometimes you will
have to stop it. To check it, you can open
the Control Panel and the Administrative Tools. In the Administrative Tools
window, open the Services.
|
In the Services window, check the status
of the SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER), the SQL Server Agent (MSSQLSERVER), and the
SQL Server Browser:
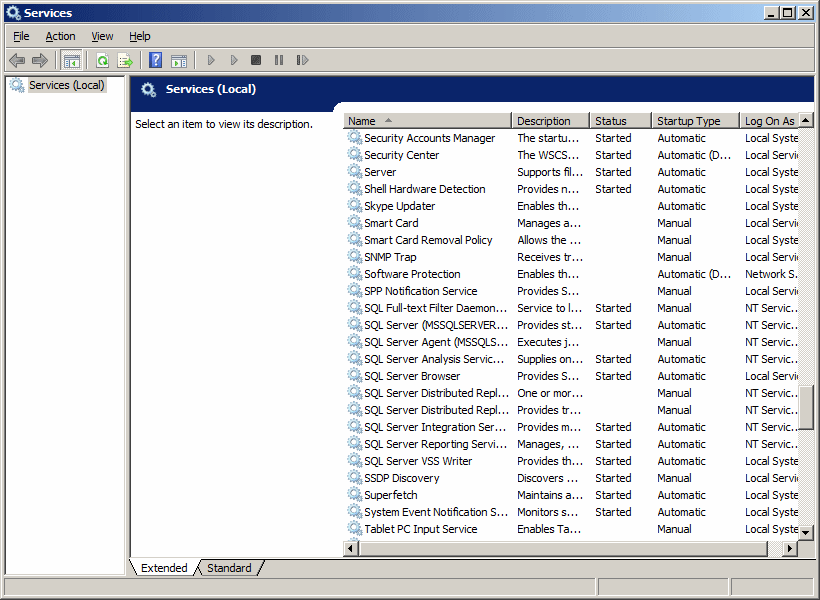
If the MSSQLSERVER service is stopped, you
should start
it. To do this, you can right-click it and click Start. If it fails to
start, check the account with which you logged in:
- If you are using Microsoft Windows XP-7 and you logged in
as Administrator but did not provide a password, you should open Control
Panel, access User Accounts, open the Administrator account, and create
a password for it
- If you are using a server (Microsoft Windows Server 2003 or Microsoft
Windows Server 2008), make sure you logged in with an account that can
start a service
Once the service has started, it should be labeled
Started:
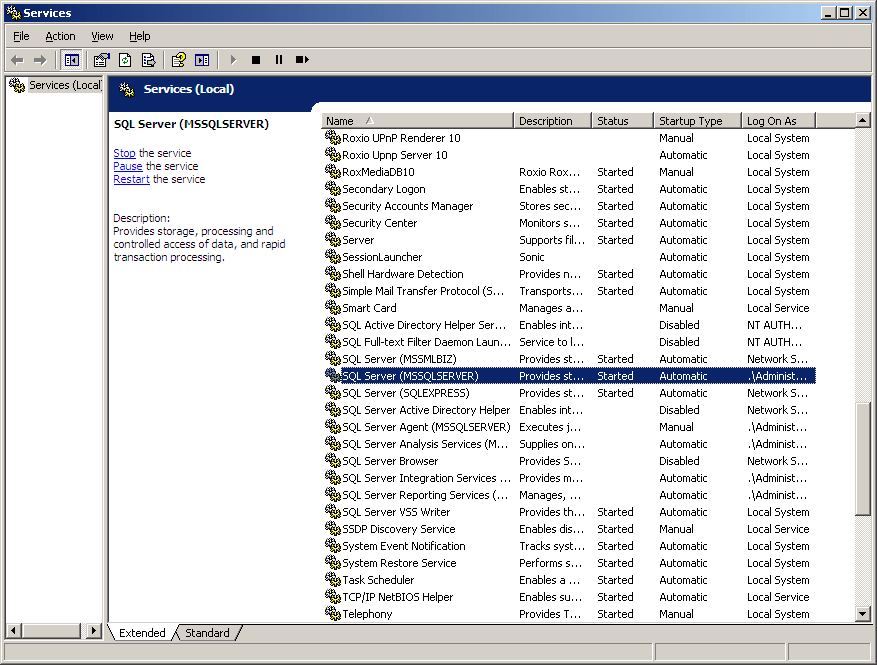
|
Opening Microsoft SQL Server |
|
To launch Microsoft SQL Server, you can click Start
-> (All) Programs -> Microsoft SQL Server 2008 -> SQL Server
Management Studio
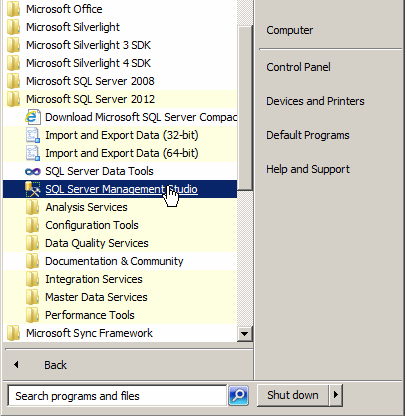
When it starts, it would present a dialog box that
expects you to log in.
|
 Practical
Learning: Launching Microsoft SQL Server Practical
Learning: Launching Microsoft SQL Server
|
|
- All Computers: Start the computer and log in
- All Computers: To launch Microsoft SQL Server, click Start -> (All) Programs ->
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 -> SQL Server Management Studio. A splash
screen will appear:

- All Computers: On the Connect to Server dialog box, click Cancel
|
The Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio |
|
There are many tools you will use in Microsoft SQL server.
One of them is called Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio. To access it, you
can click Start -> (All) Programs -> Microsoft SQL Server 2008 -> SQL
Server Management Studio. A dialog box would come up but you can click Cancel on
it:
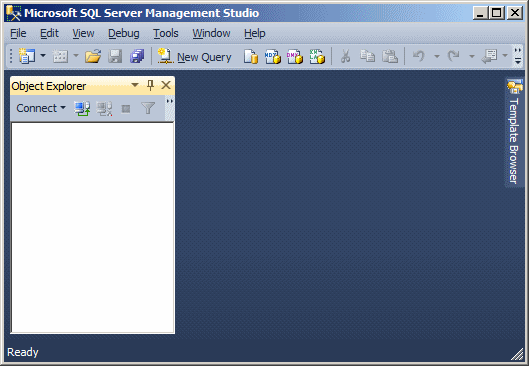
The top section of the SQL Server Management Studio displays
the classic title bar of a regular window, with an icon on the left, followed by
the title of the application, and the system buttons on the right side.
Under
the title bar, the menu bar displays categories of menus that you will use to
perform the various necessary operations.
The Standard toolbar displays under the main menu:

The Standard toolbar is just one of the available ones.
Eventually, when you perform an action that would benefit from another
toolbar, the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio would display that
toolbar. Still, if you want to show any toolbar, you can right-click any
menu item on the main menu or any button on a toolbar.
|
 Practical
Learning: Checking the Toolbars Practical
Learning: Checking the Toolbars
|
|
- All Computers: Right-click any menu item on the main menu or any button on a
toolbar:
- All Computers: Press Esc
The left side of the interface displays, by default, the Object Explorer
window, with its title bar labeled Object Explorer. If you don't see it, on the
main menu, you can click View -> Object Explorer.
The Object Explorer is a dockable window, meaning you can move it from
the left side to another side on the interface. To do this, you can click
and drag its title bar to a location of your choice. When you start
dragging, small boxes that represent the possible placeholders would come
up:
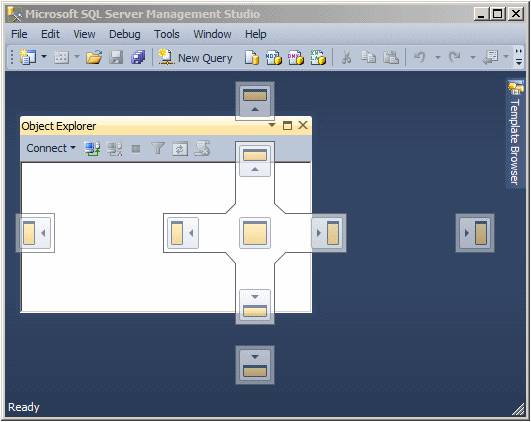
You can drag and drop to one of those placeholders.
The Object Explorer is also floatable, which means you
can place it somewhere in the middle of the interface:
To place the window back to its previous position, you can
double-click its title bar. The window can also be tabbed. This means that the
window can be positioned either vertically or horizontally.
At any time, if you do not want the Object Explorer, you can
close or hide it. To close the Object Explorer, click its close button.
On the right side of the
Object Explorer title, there are three buttons. If you click the first button
that points down, a menu would appear:
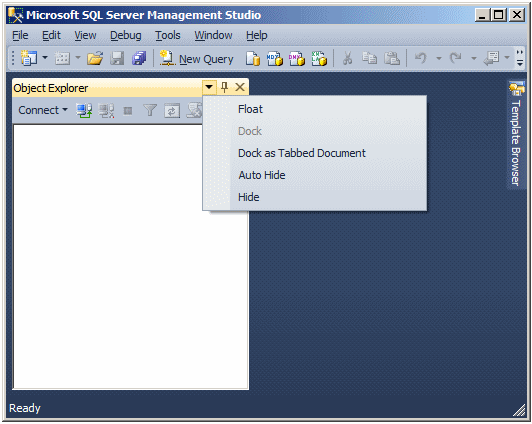
The menu allows you to specify whether you
want the window to be floated, docked, or tabbed.
The right side of the window is made of an empty window. This area will be used to display either the contents of
what is selected in the Object Explorer, or to show a result of some operation.
As you will see later on, many other windows will occupy the right section but
they will share the same area. To make each known it will be represented with a
tab and the tab shows the name (or caption) of a window.
|
Close Microsoft SQL Server |
|
After using Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio, you
can close it. To do this:
- Click the icon on the left side of Microsoft SQL Server Management
Studio and click Close
- On the right side of the title bar, click the system Close button

- On the main menu, click File -> Exit
- Press Alt, F, X
|
Introduction to Connecting to Microsoft SQL Server |
|
In order to do anything significant in Microsoft SQL
Server, you will have to establish a connection to it. This depends on
whether Microsoft SQL Server is installed on the computer you are using or
you are connecting to an external server using a client/workstation.
If you start Microsoft SQL
Server Management Studio from the Start button, the Connect To Server dialog
box would come up:
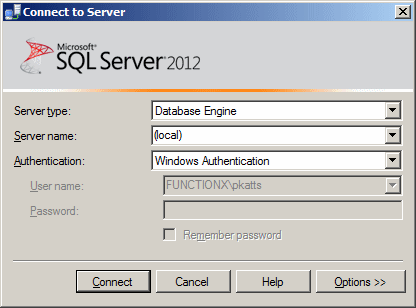
If you had started from the Start button but clicked
Cancel, to connect to a server:
- On the main menu, click File -> Connect Object Explorer...
- On the Standard toolbar, click the New Query button

- In the Object Explorer, click the arrow of the Connect button
and click one of the options, such as Database Engine...
Any of these actions would display the Connect to Server
dialog box.
|
Using a Stand-Alone Computer |
|
In the previous lesson, we saw two types of
installations: on a lone computer or with a client tools. We also
saw that the simplest way to use Microsoft SQL Server was with one computer.
In this case, after starting the computer and logging in, especially if you
log in with the same account you used to install Microsoft SQL Server, on
the Connect to Server dialog box, the Database Engine option would be selected in the
Server Type combo box. The name of the computer should be selected in the
Server Name combo box. In this case also, the easiest way to connect is to
select Windows Authentication in the Authentication combo box. The User Name
combo box should have the name of the computer, followed by a back slash,
and followed by the user name of the account that is currently logged in. You don't
have to enter a password (this is because you are using Windows
Authentication and because you are logged in already):
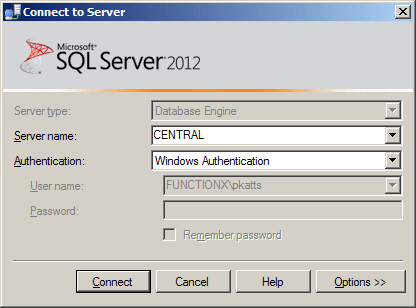
|
Connection in a Client/Server Environment |
|
 |
As mentioned in the previous lesson, if you are working
in a network environment, you may use a client that connects to a computer
on which Microsoft SQL Server is installed. If you had installed either
Microsoft SQL Server or the client tools on the current computer, you can
use that workstation to connect to Microsoft SQL Server. In this case, you use
a different type of authentication.
|
Before being able to connect, you must prepare the
server. Once the server can receive external connections, you can either
connect to it when you launch SQL Server Management Studio or change the connection
after starting Microsoft SQL Server.
|
Preparing the Server for Remote Connectivity |
|
In most cases, the default installation of Microsoft SQL Server doesn't
allow clients to connect to it. Sometimes, if you try establishing a connection
to the server (in this and the next lessons, we will see how that connection is
established), you may receive an error as "A network-related or
instance-specific error occurred while establishing a connection to SQL
Server.":
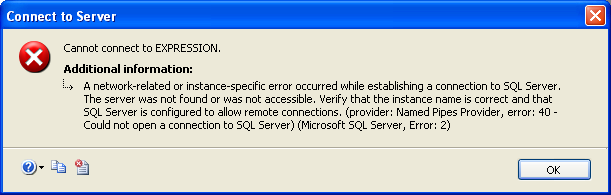
There are a few actions you must first perform,
from the operating system's firewall to Microsoft SQL Server's own
configuration.
One of the actions you should take care of for client
connectivity is to dig/create a hole in the firewall. To do this, click Start ->
Control Panel. Double-click Firewall. Using the Exceptions tab, create a
firewall.
Besides taking care of the firewall, you should configure
TCP/IP connectivity and create an alias.