
Variants of Button Controls
 |
Variants of Button Controls |
Introduction Radio Buttons
Overview
A radio button is a control that appears in a group with other radio buttons so that the user can click one of the buttons to activate it. This action de-activates the other radio buttons of the same group. This is referred to as mutual exclusivity.
Database: Sweet Star ClothiersThe following database is a fictional company that creates or sows clothes (various types). The company employs three categories of people, especially with regards to their pay:
|
![]() Practical Learning: Introducing Radio Buttons
Practical Learning: Introducing Radio Buttons
Creating Radio Buttons
There are various ways to get a radio button or a group of
radio buttons to a form or report. The easiest way is to start by adding an
Option Group and use its wizard. The wizard allows you to create a list of items
that will later be converted into radio buttons. Another technique is to click
the Option Button
![]() from the Controls section of the Ribbon and click inside
a container such as a group box on a form or report.
from the Controls section of the Ribbon and click inside
a container such as a group box on a form or report.
Characteristics of Radio Buttons
The Option Value of a Radio Button
In Microsoft Access, the radio buttons are considered a collection of controls that belong to a group box. In the collection of radio buttons, each of them uses an index. This index is represented by a property named Option Value. The first radio button (or rather one of the radio buttons in the group) has an index or Option Value of 1, the third (or another) has an index or Option Value of 2, and so on.
If you use the Option Group Wizard to create the radio buttons, the
wizard automatically creates those
numbers and allows you to change them in the second page of the wizard, which you shouldn't change unless you have a group reason. If you manually add the radio buttons (using the Option Button
![]() ), you must then specify the Option Values yourself.
), you must then specify the Option Values yourself.
![]() Practical
Learning: Introducing Option Values
Practical
Learning: Introducing Option Values



CREATE TABLE Employees
(
EmployeeID COUNTER,
EmployeeNumber TEXT,
FirstName STRING,
LastName CHAR,
Title VARCHAR,
PayCategory BYTE,
HourlySalary DOUBLE,
YearlySalary FLOAT
);CREATE TABLE Payrolls
(
PayrollID AUTOINCREMENT(10001),
PayDate DATE,
EmployeeNumber TEXT,
WorkUnits STRING,
NetPay DOUBLE
);| Field Name | Field Size | Format | Caption |
| EmployeeID | Employee ID | ||
| EmployeeNumber | 12 | Employee # | |
| FirstName | 25 | First Name | |
| LastName | 25 | Last Name | |
| Title | 50 | ||
| PayCategory | Pay Category | ||
| HourlySalary | Fixed | Hourly Salary | |
| YearlySalary | Fixed | Yearly Salary |
| Field Name | Field Size | Format | Caption |
| PayrollID | Payroll ID | ||
| PayDate | Long Date | Pay Date | |
| EmployeeNumber | 12 | Employee # | |
| WorkUnits | 40 | Work Units | |
| NetPay | Fixed | Net Pay |
Radio Buttons and the Record Source
The radio buttons don't have a Record Source property. That job is left to the group box. After specifying that property, you can manage the values of the radio buttons.
As mentioned already, the radio buttons are stored in an integer-based collection where each radio button is recognized by its numeric index. Therefore, the field that manages the values of a group of control should be a a natural number. Its data type can be a Byte, an Integer, or a Long type. In the records, each value will correspond to a radio button.
![]() Practical Learning: Setting the Record Source of Radio Buttons
Practical Learning: Setting the Record Source of Radio Buttons


| Control | Caption | Name | Other Properties | |
| Label |
|
Sweet Star Clothiers | Font Name: Bodoni MT Black Font Size: 22 Font Color: Blue, Accent1, Lighter 60% |
|
| Line |
|
Border Color: Accent 4 | ||
| Label |
|
Payroll Preparation | Font Name: Bodoni MT Black Font Size: 26 Font Color: white |
|
| Text Box |
|
Employee #: | txtEmployeeNumber | |
| Text Box |
|
txtEmployeeName | ||
| Option Group |
|
Pay Category | fraPayCategory | |
| Text Box |
|
Work Units: | txtWorkUnits | |
| Button |
|
Calculate Salary | cmdCalculateSalary | |
| Text Box |
|
Time Worked: | txtTimeWorked | |
| Text Box |
|
Net Pay: | txtNetPay | |
| Button |
|
Submit Payroll | cmdSubmitPayroll | |
| Button |
|
Close | cmdClose | |
Events of Radio Buttons
Remember that, in Microsoft Access (unlike Win32), radio buttons rely on their parent the group box for their management. This means that, when a radio button is clicked, you must refer to the group box to find out what button was clicked. As a matter of fact, when a radio button is clicked, it is in fact the group box that fires the On Click event. When a radio button is clicked, the group box holds the index of that radio button. Consequently, if you want to know what radio button was clicked, find out the current value of the group box. To do that, you can use any appropriate conditional statement (If...ElseIf or Select Case) or function (IIf, Choose, or Switch).
 Practical Learning: Clicking Some Radio Buttons
Practical Learning: Clicking Some Radio Buttons
Private Sub PayCategory_Click()
' When a radio button is clicked, find out from the
' option group what radio button was clicked.
' The first radio button has a value of 1,
' the second has a value of 2, and so on
If PayCategory = 1 Then
YearlySalary.Visible = True
HourlySalary.Visible = False
ElseIf PayCategory = 2 Then
YearlySalary.Visible = False
HourlySalary.Visible = True
Else ' If PayCategory = 3 Then
YearlySalary.Visible = False
HourlySalary.Visible = False
End If
End SubPrivate Sub Form_Current()
If PayCategory = 1 Then
YearlySalary.Visible = True
HourlySalary.Visible = False
ElseIf PayCategory = 2 Then
YearlySalary.Visible = False
HourlySalary.Visible = True
Else ' If PayCategory = 3 Then
YearlySalary.Visible = False
HourlySalary.Visible = False
End If
End SubPrivate Sub cmdClose_Click()
DoCmd.Close
End SubPrivate Sub cmdCalculateSalary_Click()
Dim units As Integer
Dim others As Double
Dim first60 As Double
Dim grossSalary As Double
Dim between60And88 As Double
If IsNull(fraPayCategory) Then
MsgBox "There is no payroll to evaluate.", _
vbOKOnly Or vbInformation, "Sweet Star Clothiers"
Exit Sub
End If
Select Case fraPayCategory
Case 1
txtNetPay = FormatNumber(CDbl(Nz(txtWorkUnits)) / 24)
Case 2
If IsNull(txtTimeWorked) Or Nz(txtTimeWorked) = 0 Then
MsgBox "Please type the number of hours worked", _
vbOKOnly Or vbInformation, "Sweet Star Clothiers"
Exit Sub
End If
txtNetPay = FormatNumber(CDbl(Nz(txtWorkUnits)) * CDbl(Nz(txtTimeWorked)))
Case 3
If IsNull(txtWorkUnits) Or Nz(txtWorkUnits) = 0 Then
MsgBox "Please type the number of clothes (shirts and/or pants) produced (sown).", _
vbOKOnly Or vbInformation, "Sweet Star Clothiers"
Exit Sub
End If
units = CInt(Nz(txtWorkUnits))
If units <= 60 Then
grossSalary = units * 20.22
ElseIf units <= 88 Then
first60 = 60 * 20.86
others = (units - 60) * 22.18
grossSalary = first60 + others
Else
first60 = 60 * 22.59
between60And88 = (88 - 60) * 24.07
others = (units - 88) * 27.16
grossSalary = first60 + between60And88 + others
End If
txtNetPay = FormatNumber(CDbl(Nz(grossSalary)))
End Select
End SubOverview
A check box is a Windows control that indicates that a value is true or false. You can manually create the control or let Microsoft Access take care of that. In this latter case, you can create a Boolean column and add/or a check box on a form or report.
To support check boxes, Microsoft Access VBA provides a class named CheckBox.
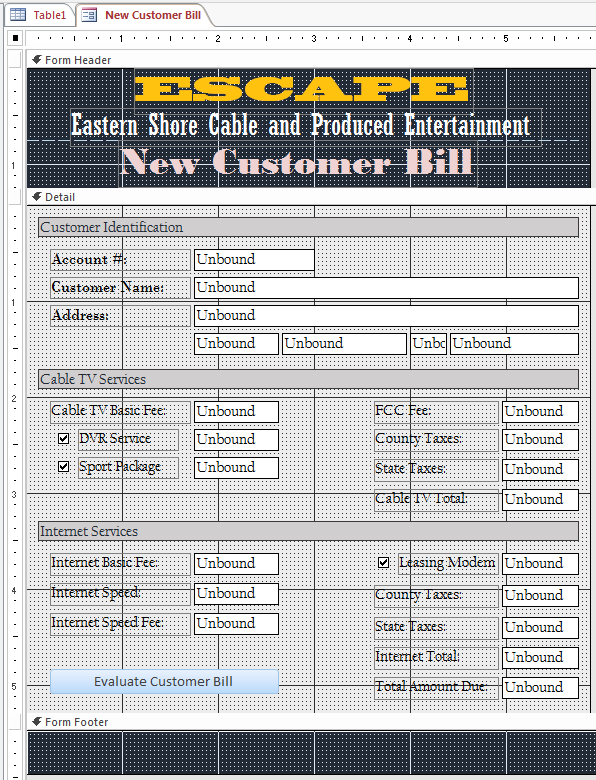
Database: ESCAPEESCAPE, which stands for Eastern Shore Cable and Produced Entertainment is fictitious cable TV and Internet service provider company that operates in eastern side of the United States. Its customers, or subscribers, purchase either or both cable TV and Internet connections. The company provides its subscribers with a cable TV box that receives the necessary signal. The company provides various options to the customers. These includes DVR as a feature used to video-record TV programs. Another option is the Sports Package that includes some exclusive channels. Other options include Foreign Package, Sport Team Package, etc. When it comes to the Internet services, customers have the option to purchase (and own) a router or lease one from the company. Another option is select a speed other than the default slow one. |
![]() Practical Learning: Introducing Check Boxes
Practical Learning: Introducing Check Boxes

| Control | Caption | Name | Other Properties | |
| Label |
|
ESCAPE | ||
| Label |
|
Eastern Shore Cable and Produced Entertainment | ||
| Line |
|
Border Style: Dashes | ||
| Label |
|
New Customer Account | ||
| Label |
|
Customer Identification | Back Color: Background 2, Darker 10% | |
| Text Box |
|
Account #: | txtAccountNumber | |
| Text Box |
|
First Name: | txtFirstName | |
| Text Box |
|
Last Name: | txtLastName | |
| Text Box |
|
Address: | txtAddress | |
| Text Box |
|
City: | txtCity | |
| Text Box |
|
County: | txtCounty | |
| Text Box |
|
State: | txtState | |
| Text Box |
|
ZIP Code: | txtZIPCode | |
| Label |
|
Cable TV Services | Back Color: Background 2, Darker 10% | |
| Text Box |
|
Cable TV Basic Fee: | txtCableTVBasicFee | Format: Fixed |
| Label |
|
Internet Services | Back Color: Background 2, Darker 10% | |
| Text Box |
|
Internet Basic Fee: | txtInternetBasicFee | Format: Fixed |

| Control | Caption | Name | Other Properties | |
| Label |
|
ESCAPE | ||
| Label |
|
Eastern Shore Cable and Produced Entertainment | ||
| Line |
|
Border Style: Dashes | ||
| Label |
|
New Customer Bill | ||
| Label |
|
Customer Identification | Back Color: Background 2, Darker 10% | |
| Text Box |
|
Account #: | txtAccountNumber | |
| Text Box |
|
Customer Name: | txtCustomerName | |
| Text Box |
|
Address: | txtAddress | |
| Text Box |
|
City: | txtCity | |
| Text Box |
|
txtCounty | ||
| Text Box |
|
txtState | ||
| Text Box |
|
txtZIPCode | ||
| Label |
|
Cable TV Services | Back Color: Background 2, Darker 10% | |
| Text Box |
|
Cable TV Basic Fee: | txtCableTVBasicFee | Format: Fixed |
| Text Box |
|
FCC Fee: | txtFCCFee | Format: Fixed |
| Text Box |
|
txtDVRServiceFee | Format: Fixed Visible: No |
|
| Text Box |
|
County Taxes: | txtCableTVCountyTaxes | Format: Fixed |
| Text Box |
|
txtSportsPackageFee | Format: Fixed Visible: No |
|
| Text Box |
|
State Taxes: | txtCableTVStateTaxes | Format: Fixed |
| Text Box |
|
Cable TV Total: | txtCableTVTotal | Format: Fixed |
| Label |
|
Internet Services | Back Color: Background 2, Darker 10% | |
| Text Box |
|
Internet Basic Fee: | txtInternetBasicFee | Format: Fixed |
| Text Box |
|
txtModemFee | Format: Fixed | |
| Text Box |
|
Internet Speed: | txtInternetSpeedApplied | Format: Fixed |
| Text Box |
|
County Taxes: | txtInternetCountyTaxes | Format: Fixed |
| Text Box |
|
Internet Speed Fee: | txtInternetSpeedFee | Format: Fixed |
| Text Box |
|
State Taxes: | txtInternetStateTaxes | Format: Fixed |
| Text Box |
|
Internet Total: | txtInternetTotal | Format: Fixed |
| Button |
|
Evaluate Customer Bill | cmdEvaluateCustomerBill | |
| Text Box |
|
Total Amount Due: | txtTotalAmountDue | Format: Fixed |
Private Sub cmdEvaluateCustomerBill_Click()
Dim InternetModemFee As Double
Dim DVRService As Double, SportsPackage As Double
Dim InternetBasicFee As Double, InternetSpeedFee As Double
Dim InternetCountyTaxes As Double, InternetStateTaxes As Double
Dim CableTVBasicFee As Double, CableTVTotal As Double, InternetTotal As Double
Dim FCCFee As Double, CableTVCountyTaxes As Double, CableTVStateTaxes As Double
CableTVBasicFee = CDbl(Nz(txtCableTVBasicFee))
DVRService = CDbl(Nz(txtDVRServiceFee))
SportsPackage = CDbl(Nz(txtSportsPackageFee))
FCCFee = (CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage) * 0.0205
CableTVCountyTaxes = 0#
CableTVStateTaxes = 0#
InternetStateTaxes = 0#
InternetCountyTaxes = 0#
' The following numbers/rates are random, for exercise purposes.
' I didn't check any website/documentation or state/county regulation for this.
Select Case txtState
Case "DC"
CableTVStateTaxes = (CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage) * 0.37
CableTVCountyTaxes = 0#
Case "MD"
CableTVStateTaxes = (CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage) * 0.245
Select Case txtCounty
Case "Anne Arundel"
CableTVCountyTaxes = (CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage) * 0.0505
Case "Howard"
CableTVCountyTaxes = (CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage) * 0.0338
Case "Montgomery"
CableTVCountyTaxes = (CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage) * 0.075
Case "Prince George"
CableTVCountyTaxes = (CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage) * 0.1015
Case Else
CableTVCountyTaxes = 0#
End Select
Case "VA"
CableTVStateTaxes = (CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage) * 0.055
Select Case txtCounty
Case "Culpeper"
CableTVCountyTaxes = (CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage) * 0.0425
Case "Prince William"
CableTVCountyTaxes = (CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage) * 0.0815
Case Else
CableTVCountyTaxes = 0#
End Select
Case Else
CableTVCountyTaxes = 0#
CableTVStateTaxes = 0#
End Select
CableTVTotal = CableTVBasicFee + DVRService + SportsPackage + FCCFee + CableTVCountyTaxes + CableTVStateTaxes
InternetBasicFee = CDbl(Nz(txtInternetBasicFee))
InternetModemFee = CDbl(Nz(txtModemFee))
InternetSpeedFee = CDbl(Nz(txtInternetSpeedFee))
InternetCountyTaxes = (InternetBasicFee + InternetModemFee + InternetSpeedFee) * 0.075
' The following numbers/rates are random, for exercise purposes.
' I didn't check any website/documentation or state/county regulation for this.
Select Case txtState
Case "DC"
InternetStateTaxes = (InternetBasicFee + InternetModemFee + InternetSpeedFee) * 0.6405
Case "MD"
InternetStateTaxes = (InternetBasicFee + InternetModemFee + InternetSpeedFee) * 0.575
Case "VA"
InternetStateTaxes = (InternetBasicFee + InternetModemFee + InternetSpeedFee) * 0.158
Case Else
InternetStateTaxes = 0#
End Select
InternetTotal = InternetBasicFee + InternetModemFee + InternetSpeedFee + InternetCountyTaxes + InternetStateTaxes
txtFCCFee = FormatNumber(FCCFee)
txtCableTVCountyTaxes = FormatNumber(CableTVCountyTaxes)
txtCableTVStateTaxes = FormatNumber(CableTVStateTaxes)
txtCableTVTotal = FormatNumber(CableTVTotal)
txtInternetCountyTaxes = FormatNumber(InternetCountyTaxes)
txtInternetStateTaxes = FormatNumber(InternetStateTaxes)
txtInternetTotal = FormatNumber(InternetTotal)
txtTotalAmountDue = FormatNumber(CableTVTotal + InternetTotal)
End SubA Boolean Field
A Boolean field is one that can have a value as True or False, Yes.or No, any number or 0. To add a Boolean field to a table:
To create a Boolean-based field in SQL, set its data type to YESNO, BIT, or LOGICAL. Here are examples:
Private Sub cmdTable_Click()
DoCmd.RunSQL "CREATE TABLE Contractors" & _
"(" & _
" FullName TEXT, " & _
" AvailableOnWeekend BIT, " & _
" OwnsACar LOGICAL, " & _
" CanShareOwnCar YESNO" & _
");"
End Sub
Creating a Check Box
To manually create a check box, display a form or report in the Design View. In the Controls section of the Ribbon, click the Check Box
![]() and click the desired area on the form or report.
and click the desired area on the form or report.
To programmatically create a check box, call the CreateControl() method and pass the second argument as acCheckBox. Here is an example:
Private Sub cmdCreateControl_Click()
Dim ctlIsMarried As Control
Set ctlIsMarried = CreateControl("Exercise", AcControlType.acCheckBox)
Set ctlIsMarried = Nothing
End Sub
![]() Practical Learning:
Creating Check Boxes
Practical Learning:
Creating Check Boxes

| Control | Caption | Name | |
| Check Box |
|
Uses DVR Service | chkUsesDVRService |
| Check Box |
|
Uses Sports Package | chkUsesSportsPackage |
| Check Box |
|
Provides Own Modem | chkProvidesOwnModem |
| Control | Caption | Name | |
| Check Box |
|
DVR Service | chkIncludesDVRService |
| Check Box |
|
Sports Package | chkIncludesSportsPackage |
| Check Box |
|
Leasing Modem | chkIncludesModemLease |
Characteristics of a Check Box
The Control Source of a Boolean Field
If you want to link a check box to a column of a table, in its Property Sheet, set its Control Source to that column. If you are programmatically creating the control, pass the name of the table as the fourth argument and the name of the column as the fifth argument. Here is an example:
Private Sub cmdCreateControl_Click()
Dim ctlIsMarried As Control
Set ctlIsMarried = CreateControl("Fundamentals", _
AcControlType.acCheckBox, _
acSection.acDetail, _
"[Student Registration]", _
"[Full Time Student]", _
840, 300)
Set ctlIsMarried = Nothing
End Sub
Data Entry With a Boolean Field
To perform data entry on a check box, the user can check or uncheck it. To programmatically specify the value of a check box, access its Value property and assign True or False to it. Here is an example:
Private Sub cmdIsMarried_Click()
chkIsMarried.Value = True
End Sub
If you set the value to True, the control would display a check mark. If you set it to False, the check box would be emptied.
Boolean Data Entry With the SQL
To specify the value of a Boolean field during data entry, set its value to 0 or 1. Here are examples:
Private Sub cmdCreateRecord_Click()
DoCmd.RunSQL "INSERT INTO Contractors VALUES(" & _
"'Arlen Sinoko', 1, 0, 1);"
End Sub
If you set the value to 0, the field receives a value of false, which is the same as the check box being empty. If you set the value to 1, the field is considered true. In your code, you can also specify the value as True or False. Here are examples:
Private Sub cmdCreateRecord_Click()
DoCmd.RunSQL "INSERT INTO Contractors VALUES(" & _
"'William Woods', False, False, True);"
End Sub
The Value of a Check Box
To help you find out the state of a check box, its class is equipped with a Boolean property named Value. When it is False or 0, the check box is empty or unchecked. When the Value is True or -1, the control is checked. Because this is the default property, you can omit it when accessing the check box.
![]() Practical Learning:
Using the Value of a Check Box
Practical Learning:
Using the Value of a Check Box
Private Sub ResetForm()
txtAccountNumber = ""
txtCustomerName = " "
txtAddress = ""
txtCity = ""
txtCounty = ""
txtState = ""
txtZIPCode = ""
txtCableTVBasicFee = "0.00"
chkIncludesDVRService = False
txtDVRServiceFee = "0.00"
txtDVRServiceFee.Visible = False
chkIncludesSportsPackage = False
txtSportsPackageFee = "0.00"
txtSportsPackageFee.Visible = False
txtFCCFee = "0.00"
txtCableTVCountyTaxes = "0.00"
txtCableTVStateTaxes = "0.00"
txtCableTVTotal = "0.00"
txtInternetBasicFee = "24.50"
chkIncludesModemLease.Value = False
txtModemFee = "0.00"
txtModemFee.Visible = False
txtInternetSpeedApplied = ""
txtInternetSpeedFee = "0.00"
txtInternetCountyTaxes = "0.00"
txtInternetStateTaxes = "0.00"
txtInternetTotal = "0.00"
txtTotalAmountDue = "0.00"
End SubEvents of a Check Box
A check box is primarily a button. As such, its main event occurs when it is clicked.
![]() Practical Learning:
Clicking a Check Box
Practical Learning:
Clicking a Check Box
Private Sub chkIncludesDVRService_Click()
If chkIncludesDVRService.Value = True Then
txtDVRServiceFee.Visible = True
txtDVRServiceFee = "9.85"
Else
txtDVRServiceFee.Visible = False
txtDVRServiceFee = "0.00"
End If
End SubPrivate Sub chkIncludesSportsPackage_Click()
If chkIncludesSportsPackage.Value = True Then
txtSportsPackageFee.Visible = True
txtSportsPackageFee = "10.55"
Else
txtSportsPackageFee.Visible = False
txtSportsPackageFee = "0.00"
End If
End SubPrivate Sub chkIncludesModemLease_Click()
If chkIncludesModemLease.Value = False Then
txtModemFee.Visible = False
txtModemFee = "0.00"
Else
txtModemFee.Visible = True
txtModemFee = "5.75"
End If
End SubIntroduction to Toggle Buttons
Overview
A toggle button is a variant of a command button, a radio button, and a check box. This means that a toggle button has the ability to behave like any of those controls. In Microsoft Windows (that is, in Win32), the toggle button is created by setting some of the characteristics of either the radio button or the check box.
Creating a Toggle Button
Microsoft Access has its own support of the toggle button with a formal control of that name. In Microsoft Access, the toggle button is managed by a class named ToggleButton.
In the Microsoft Access database environment, the way you create a toggle button depends on how you are planning to use it. To create a toggle button that will behave like a general button, display a form or report in the Design View
(it is not particularly useful to add a toggle button to a report). In the Controls section of the Ribbon, click the Toggle Button control ![]() and click the form
(or report).
and click the form
(or report).
Characteristics of Toggle Buttons
The Caption of a Toggle Button
Most of time, the toggle button doesnít use a caption. Still, if you want it to indicate what it is used for, you can add a caption to it. This is managed by the Caption property.
Toggle Buttons as a Group of Radio Buttons
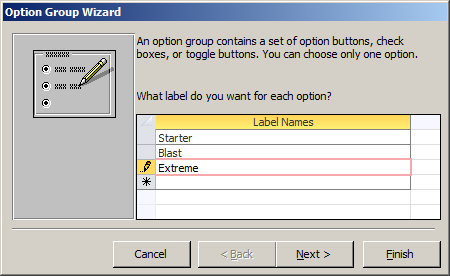
Toggle buttons can be used in a group like radio buttons. You create the group as it is done for radio buttons. If you click the Option Group button from the Controls section of the Ribbon and click a form (or report) in the Design View, a wizard may start. The fourth page of the wizard is the real difference. This is where you should click the Toggle Buttons option.
You can create a group of toggle buttons without using a wizard. To do this, from the Controls section of the Ribbon, click the Option Group button and click a form in the Design View. If the wizard starts, click Cancel. In the Controls section of the Ribbon, click the Toggle Button control and click inside the group box on the form. Add as many toggle buttons as you need. You can create a group of toggle buttons without using a wizard. To do this, from the Controls section of the Ribbon, click the Option Group button and click a form in the Design View. If the wizard starts, click Cancel. In the Controls section of the Ribbon, click the Toggle Button control and click inside the group box on the form. Add as many toggle buttons as you need.
If you create a group of toggle buttons, as mentioned for radio buttons, they are managed by the group box that in fact holds their common Control Source. As a result, when one of the toggle buttons is clicked, to find out which one is active, get the Value property of the group box. To specify one of the toggle buttons is primarily clicked, set the Default Value of the group box.
![]() Practical Learning: Introducing
Toggle Buttons
Practical Learning: Introducing
Toggle Buttons



| Control | Caption | Name | |
| Option Group |
|
Speed Requested | fraInternetSpeedApplied |
A Toggle Button like a Check Box
As mentioned above, when creating or a group of toggle buttons, you should know how you are planning to use it. If you want to use it as a check box, add it to a form or a rectangle. In this case, the toggle button would be equipped with a Control Source property that you can use to bind the control to a field of a table, query, or SQL expression.
A toggle button that is created to behave like a check box has the same properties and events as the check box.
When the toggle button is clicked, to let you get its state, use its Value property. When the toggle value is displaying normally, which is equivalent to an empty check box, the Value of the toggle button is 0. When the control is clicked, its value becomes -1. At any time, to find out the state of the toggle button, you can inquire about its Value.
To let you specify how the toggle button should primarily display, the control is equipped with the Default Value property.
The Background Colors of a Toggle Button
A toggle button added directly to a form, to a report, or inside a rectangle behaves, by default, like a check box. This means that it first comes up with a default color (deep blue, close to Navy). When clicked, its changes its appearance to a light blue color. As mentioned for command buttons, you can specify what color should paint the toggle button:
These aspects can also be enhanced with the border colors.
 Practical
Learning: Ending the Lesson
Practical
Learning: Ending the Lesson

| Control | Name | Caption | |
| Button |
|
cmdCreateNewCustomerAccount | Create New Customer Account |
| Button |
|
cmdPrepareCustomerBill | Prepare Customer Bill |
| Button |
|
cmdClose | Close |
Private Sub cmdCreateNewCustomerAccount_Click()
DoCmd.OpenForm "New Customer Account"
End SubPrivate Sub cmdPrepareCustomerBill_Click()
DoCmd.OpenForm "New Customer Bill"
End SubPrivate Sub cmdClose_Click()
DoCmd.Close
End Sub|
|
||
| Previous | Copyright © 2010-2022, FunctionX, Inc. | Next |
|
|
||