
File-Based Databases
 |
File-Based Databases |
In Lesson 1, to get a list of items, we created and stored it in a variable-based list. The user had no way of storing items in the computer. This meant that once the computer was shut down or the application was closed, the information created while using the application was lost. In list-oriented business applications, to make sure that the same information is not entered over and over again, any new information can be saved and stored somewhere. Such a type of file-based application can be used to create new items, save them, and process them the next time they are needed. This is the basis of databases. A database is a information created as a list and stored somewhere so the list can be better managed. This means that the person using the database should be able to add information to the database, to retrieve information from the database, to change the information stored in the database, to manipulate it, to manage the database as an ensemble, and to save new or changed information.
There are various types of databases used with different goals. The .NET Framework provides various means of creating and managing such various types of databases. Those we will review are categorized as follows:
As mentioned above, a file-based database consists of creating one or more files that can be used as a database. To do this, you can create an array of a list of objects as we learned in Lesson 1. The problem with arrays is that they have a fixed size and you must know from the beginning the number of items that can created in the list. The alternative is to use a linked-list. As seen in Lesson 1, this is easily supported through the ArrayList class. |
|
|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
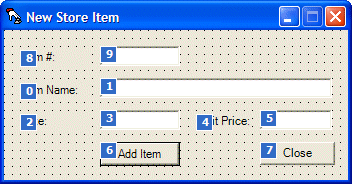
Dim lstStoreItems As ArrayList
Private Sub NewStoreItem_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
lstStoreItems = New ArrayList
End Sub
|
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnClose.Click
Close()
End Sub
|
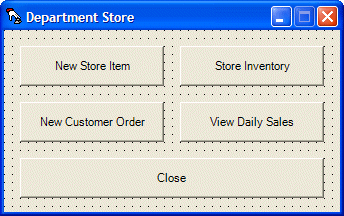
Private Sub btnNewStoreItem_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnNewStoreItem.Click
Dim frmNewItem As New NewStoreItem
frmNewItem.Show()
End Sub
|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnClose.Click
Close()
End Sub
|
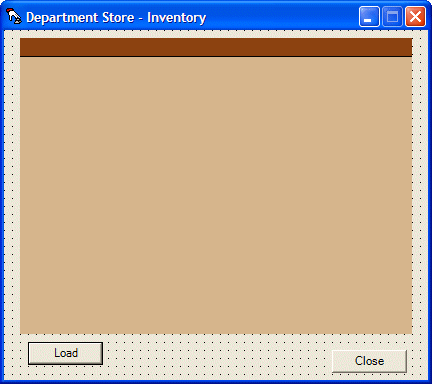
Private Sub btnStoreInventory_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnStoreInventory.Click
Dim frmInventory As New StoreInventory
frmInventory.Show()
End Sub
|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnClose.Click
Close()
End Sub
|
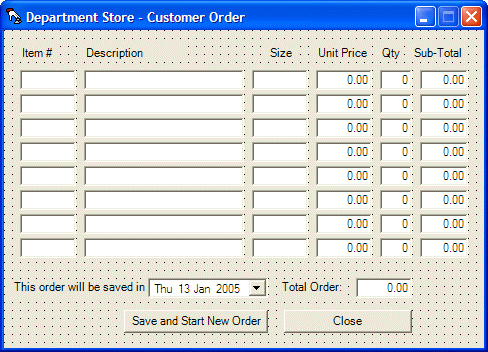
Private Sub btnNewOrder_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnNewOrder.Click
Dim frmOrder As New CustomerOrder
frmOrder.Show()
End Sub
|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnClose.Click
Close()
End Sub
|
Private Sub btnDailySales_Click(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnDailySales.Click
Dim frmSales As New DailySales
frmSales.Show()
End Sub
|
Private Sub btnClose_Click(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnClose.Click
End
End Sub
|
|
File Processing |
|
Introduction |
|
A file-based database is primarily a technique of storing values in files so they can be retrieved when needed. Based on this, the files are created like any other and they can have any extension of your choice. When a file is created, its contents can be stored in a portable medium such as a hard disc, a floppy disc, a compact disc, or any valid and supported type of storage. File processing is support in the .NET Framework through the System.IO namespace that contains many different classes to handle almost any type of file operation you may need to perform.
When creating a file-base application, you should know where the files are located, even if you don't explicitly communicate this to the user. This means that you may need to create a folder that would hold the files of your database. In some cases you can create a new folder on the C: drive, under the the Program Files folder or in the My Documents folder. In some other cases, you may use a network shared folder as the repository of users files. These are decisions you can make when planning the deployment. Once the application has been installed, you can allow the user to directly save the files to default or selected folder without being prompted to specify the name or path of the file.
Before saving a file, you may first want to check its existence. This can be done by calling the File.Exists() method. Once you have decided to save a file, you can specify the type of operation using the FileMode option of the Stream-based class you are using. The options of the FileMode are FileMode.Append, FileMode.Create, FileMode.CreateNew, FileMode.Open, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, and FileMode.Truncate. The FileAccess option allows you to specify the type of access the user will need when saving the file. The options are FileAccess.Write, FileAccess.Read, and FileAccess.ReadWrite. The FileShare allows you to decide whether or how other users (actually, processes) can access the file while it is being accessed. The options of the FileShare are FileShare.Inheritable, FileShare.None, FileShare.Read, FileShare.Write, and FileShare.ReadWrite.
|
|
Object Serialization |
|
Binary Serialization |
|
The .NET Framework provides all means of serializing any managed class through a concept referred to as binary serialization. To proceed with object serialization, you must first specify the object you would use. As with any other program, you can either use one of the classes built-in the .NET Framework or you can use your own programmer-created class. If you decide to use your own class, you can specify whether the whole class or just some parts of the class can be saved. Binary serialization consists of saving an object. This object is usually a class that either you create or is provided through the .NET Framework. For a class to be serializable, it must be marked with the Serializable attribute. This means that, when checking the MSDN documentation, any class you see with this attribute is already configured to be serialized. This is the case for almost all list-oriented classes such as Array, ArrayList, etc, including many of the classes we will use when we start studying ADO .NET and relational databases. If you create your own class and want to be able to save values from its variables, you can (must) mark the class with the Serializable attribute. To do this, type [Serializable] before starting to create the class. The Serializable attribute informs the compiler that values from the class can be serialized. When creating a serializable class, you have the ability to specify whether all of the member variables of the class can be serialized or just some of them. |
|
|
<Serializable()> Public Class CStoreItem
Private nbr As String
Private nm As String
Private sz As String
Private uprice As Double
Public Sub New()
nbr = ""
nm = ""
sz = ""
uprice = 0.0
End Sub
Public Sub New(ByVal number As String, ByVal name As String, _
ByVal size As String, ByVal price As Double)
nbr = number
nm = name
size = sz
uprice = price
End Sub
Public Property ItemNumber() As String
Get
Return nbr
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As String)
nbr = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property ItemName() As String
Get
Return nm
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As String)
nm = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property ItemSize() As String
Get
Return sz
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As String)
sz = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property UnitPrice() As Double
Get
Return uprice
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As Double)
uprice = Value
End Set
End Property
End Class
|
Private Sub NewStoreItem_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
lstStoreItems = New ArrayList
Dim tmeNow As Date = Now
' Get ready to create a random number
Dim strItemNumber As String = "000000"
Dim mls As Integer = tmeNow.Millisecond
' Generate two random numbers between 100 and 999
Dim rndNumber As New Random(mls)
Dim NewNumber1 As Integer = rndNumber.Next(100, 999)
Dim NewNumber2 As Integer = rndNumber.Next(100, 999)
' Create an item number from the random numbers
strItemNumber = NewNumber1.ToString() + "-" + NewNumber2.ToString()
' Display the created item number in the Item # text box
Me.txtItemNumber.Text = strItemNumber
End Sub
|
Private Function LocateStoreItem(ByVal ItemNumber As String) As StoreItemR2.CStoreItem
Dim item As New StoreItemR2.CStoreItem
Dim i As Integer
' Get a list of all items in the store
For i = 0 To lstAvailableItems.Count Step 1
' Get a reference to the current item
item = lstAvailableItems(i)
' If the Item Number of the current item matches the argument,
' then return it
If item.ItemNumber = ItemNumber Then
Return item
End If
Next
' If the item was not found, then return nothing;
Return Nothing
End Function
|
Private Sub CalculateTotalOrder()
Dim subTotal1 As Double
Dim subTotal2 As Double
Dim subTotal3 As Double
Dim subTotal4 As Double
Dim subTotal5 As Double
Dim subTotal6 As Double
Dim subTotal7 As Double
Dim subTotal8 As Double
Dim orderTotal As Double
' Retrieve the value of each sub total
subTotal1 = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal1.Text)
subTotal2 = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal2.Text)
subTotal3 = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal3.Text)
subTotal4 = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal4.Text)
subTotal5 = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal5.Text)
subTotal6 = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal6.Text)
subTotal7 = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal7.Text)
subTotal8 = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal8.Text)
' Calculate the total value of the sub totals
orderTotal = subTotal1 + subTotal2 + subTotal3 + _
subTotal4 + subTotal5 + subTotal6 + _
subTotal7 + subTotal8
' Display the total order in the appropriate text box
Me.txtTotalOrder.Text = orderTotal.ToString("F")
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtItemNumber1_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtItemNumber1.Leave
Dim strItemNumber As String = Me.txtItemNumber1.Text
Dim objItem As New CStoreItem
objItem = LocateStoreItem(strItemNumber)
If Not IsNothing(objItem) Then
Me.txtDescription1.Text = objItem.ItemName
Me.txtSize1.Text = objItem.ItemSize
Me.txtUnitPrice1.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
Me.txtQuantity1.Text = "1"
Me.txtSubTotal1.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
CalculateTotalOrder()
Else
Me.txtItemNumber1.Text = ""
Me.txtDescription1.Text = ""
Me.txtSize1.Text = ""
Me.txtUnitPrice1.Text = "0.00"
Me.txtQuantity1.Text = "0"
Me.txtSubTotal1.Text = "0.00"
End If
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtItemNumber2_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtItemNumber2.Leave
Dim strItemNumber As String = Me.txtItemNumber2.Text
Dim objItem As New CStoreItem
objItem = LocateStoreItem(strItemNumber)
If Not IsNothing(objItem) Then
Me.txtDescription2.Text = objItem.ItemName
Me.txtSize2.Text = objItem.ItemSize
Me.txtUnitPrice2.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
Me.txtQuantity2.Text = "1"
Me.txtSubTotal2.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
CalculateTotalOrder()
Else
Me.txtItemNumber2.Text = ""
Me.txtDescription2.Text = ""
Me.txtSize2.Text = ""
Me.txtUnitPrice2.Text = "0.00"
Me.txtQuantity2.Text = "0"
Me.txtSubTotal2.Text = "0.00"
End If
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtItemNumber3_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtItemNumber3.Leave
Dim strItemNumber As String = Me.txtItemNumber3.Text
Dim objItem As New CStoreItem
objItem = LocateStoreItem(strItemNumber)
If Not IsNothing(objItem) Then
Me.txtDescription3.Text = objItem.ItemName
Me.txtSize3.Text = objItem.ItemSize
Me.txtUnitPrice3.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
Me.txtQuantity3.Text = "1"
Me.txtSubTotal3.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
CalculateTotalOrder()
Else
Me.txtItemNumber3.Text = ""
Me.txtDescription3.Text = ""
Me.txtSize3.Text = ""
Me.txtUnitPrice3.Text = "0.00"
Me.txtQuantity3.Text = "0"
Me.txtSubTotal3.Text = "0.00"
End If
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtItemNumber4_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtItemNumber4.Leave
Dim strItemNumber As String = Me.txtItemNumber4.Text
Dim objItem As New CStoreItem
objItem = LocateStoreItem(strItemNumber)
If Not IsNothing(objItem) Then
Me.txtDescription4.Text = objItem.ItemName
Me.txtSize4.Text = objItem.ItemSize
Me.txtUnitPrice4.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
Me.txtQuantity4.Text = "1"
Me.txtSubTotal4.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
CalculateTotalOrder()
Else
Me.txtItemNumber4.Text = ""
Me.txtDescription4.Text = ""
Me.txtSize4.Text = ""
Me.txtUnitPrice4.Text = "0.00"
Me.txtQuantity4.Text = "0"
Me.txtSubTotal4.Text = "0.00"
End If
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtItemNumber5_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtItemNumber5.Leave
Dim strItemNumber As String = Me.txtItemNumber5.Text
Dim objItem As New CStoreItem
objItem = LocateStoreItem(strItemNumber)
If Not IsNothing(objItem) Then
Me.txtDescription5.Text = objItem.ItemName
Me.txtSize5.Text = objItem.ItemSize
Me.txtUnitPrice5.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
Me.txtQuantity5.Text = "1"
Me.txtSubTotal5.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
CalculateTotalOrder()
Else
Me.txtItemNumber5.Text = ""
Me.txtDescription5.Text = ""
Me.txtSize5.Text = ""
Me.txtUnitPrice5.Text = "0.00"
Me.txtQuantity5.Text = "0"
Me.txtSubTotal5.Text = "0.00"
End If
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtItemNumber6_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtItemNumber6.Leave
Dim strItemNumber As String = Me.txtItemNumber6.Text
Dim objItem As New CStoreItem
objItem = LocateStoreItem(strItemNumber)
If Not IsNothing(objItem) Then
Me.txtDescription6.Text = objItem.ItemName
Me.txtSize6.Text = objItem.ItemSize
Me.txtUnitPrice6.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
Me.txtQuantity6.Text = "1"
Me.txtSubTotal6.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
CalculateTotalOrder()
Else
Me.txtItemNumber6.Text = ""
Me.txtDescription6.Text = ""
Me.txtSize6.Text = ""
Me.txtUnitPrice6.Text = "0.00"
Me.txtQuantity6.Text = "0"
Me.txtSubTotal6.Text = "0.00"
End If
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtItemNumber7_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtItemNumber7.Leave
Dim strItemNumber As String = Me.txtItemNumber7.Text
Dim objItem As New CStoreItem
objItem = LocateStoreItem(strItemNumber)
If Not IsNothing(objItem) Then
Me.txtDescription7.Text = objItem.ItemName
Me.txtSize7.Text = objItem.ItemSize
Me.txtUnitPrice7.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
Me.txtQuantity7.Text = "1"
Me.txtSubTotal7.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
CalculateTotalOrder()
Else
Me.txtItemNumber7.Text = ""
Me.txtDescription7.Text = ""
Me.txtSize7.Text = ""
Me.txtUnitPrice7.Text = "0.00"
Me.txtQuantity7.Text = "0"
Me.txtSubTotal7.Text = "0.00"
End If
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtItemNumber8_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtItemNumber8.Leave
Dim strItemNumber As String = Me.txtItemNumber8.Text
Dim objItem As New CStoreItem
objItem = LocateStoreItem(strItemNumber)
If Not IsNothing(objItem) Then
Me.txtDescription8.Text = objItem.ItemName
Me.txtSize8.Text = objItem.ItemSize
Me.txtUnitPrice8.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
Me.txtQuantity8.Text = "1"
Me.txtSubTotal8.Text = objItem.UnitPrice.ToString("F")
CalculateTotalOrder()
Else
Me.txtItemNumber8.Text = ""
Me.txtDescription8.Text = ""
Me.txtSize8.Text = ""
Me.txtUnitPrice8.Text = "0.00"
Me.txtQuantity8.Text = "0"
Me.txtSubTotal8.Text = "0.00"
End If
End Sub
|
Private Function CalculateSubTotal(ByVal strPrice As String, ByVal strQuantity As String) As Double
Dim qty As Integer = 0
Dim unitPrice As Double = 0.0
Dim subTotal As Double
Try
' Get the quantity of the current item
qty = CInt(strQuantity)
Catch ex As FormatException
MsgBox("The value you provided for the quantity of the item is invalid" _
+ vbCrLf + "Please try again")
End Try
Try
' Get the unit price of the current item
unitPrice = CDbl(strPrice)
Catch ex As FormatException
MsgBox("The unit price you provided for item is invalid" _
+ vbCrLf + "Please try again")
End Try
' Calculate the current sub total
subTotal = qty * unitPrice
Return subTotal
End Function
|
Private Sub txtQuantity1_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtQuantity1.Leave
Dim strUnitPrice As String
Dim strQty As String
Dim subTotal As Double
strUnitPrice = Me.txtUnitPrice1.Text
strQty = Me.txtQuantity1.Text
subTotal = Me.CalculateSubTotal(strUnitPrice, strQty)
' Display the new sub total in the corresponding text box
Me.txtSubTotal1.Text = subTotal.ToString("F")
' Update the order
CalculateTotalOrder()
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtQuantity2_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtQuantity2.Leave
Dim strUnitPrice As String
Dim strQty As String
Dim subTotal As Double
strUnitPrice = Me.txtUnitPrice2.Text
strQty = Me.txtQuantity2.Text
subTotal = Me.CalculateSubTotal(strUnitPrice, strQty)
' Display the new sub total in the corresponding text box
Me.txtSubTotal2.Text = subTotal.ToString("F")
' Update the order
CalculateTotalOrder()
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtQuantity3_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtQuantity3.Leave
Dim strUnitPrice As String
Dim strQty As String
Dim subTotal As Double
strUnitPrice = Me.txtUnitPrice3.Text
strQty = Me.txtQuantity3.Text
subTotal = Me.CalculateSubTotal(strUnitPrice, strQty)
' Display the new sub total in the corresponding text box
Me.txtSubTotal3.Text = subTotal.ToString("F")
' Update the order
CalculateTotalOrder()
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtQuantity4_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtQuantity4.Leave
Dim strUnitPrice As String
Dim strQty As String
Dim subTotal As Double
strUnitPrice = Me.txtUnitPrice4.Text
strQty = Me.txtQuantity4.Text
subTotal = Me.CalculateSubTotal(strUnitPrice, strQty)
' Display the new sub total in the corresponding text box
Me.txtSubTotal4.Text = subTotal.ToString("F")
' Update the order
CalculateTotalOrder()
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtQuantity5_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtQuantity5.Leave
Dim strUnitPrice As String
Dim strQty As String
Dim subTotal As Double
strUnitPrice = Me.txtUnitPrice5.Text
strQty = Me.txtQuantity5.Text
subTotal = Me.CalculateSubTotal(strUnitPrice, strQty)
' Display the new sub total in the corresponding text box
Me.txtSubTotal5.Text = subTotal.ToString("F")
' Update the order
CalculateTotalOrder()
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtQuantity6_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtQuantity6.Leave
Dim strUnitPrice As String
Dim strQty As String
Dim subTotal As Double
strUnitPrice = Me.txtUnitPrice6.Text
strQty = Me.txtQuantity6.Text
subTotal = Me.CalculateSubTotal(strUnitPrice, strQty)
' Display the new sub total in the corresponding text box
Me.txtSubTotal6.Text = subTotal.ToString("F")
' Update the order
CalculateTotalOrder()
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtQuantity7_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtQuantity7.Leave
Dim strUnitPrice As String
Dim strQty As String
Dim subTotal As Double
strUnitPrice = Me.txtUnitPrice7.Text
strQty = Me.txtQuantity7.Text
subTotal = Me.CalculateSubTotal(strUnitPrice, strQty)
' Display the new sub total in the corresponding text box
Me.txtSubTotal7.Text = subTotal.ToString("F")
' Update the order
CalculateTotalOrder()
End Sub
|
Private Sub txtQuantity8_Leave(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles txtQuantity8.Leave
Dim strUnitPrice As String
Dim strQty As String
Dim subTotal As Double
strUnitPrice = Me.txtUnitPrice8.Text
strQty = Me.txtQuantity8.Text
subTotal = Me.CalculateSubTotal(strUnitPrice, strQty)
' Display the new sub total in the corresponding text box
Me.txtSubTotal8.Text = subTotal.ToString("F")
' Update the order
CalculateTotalOrder()
End Sub
|
|
The Process of Serializing |
|
To support serialization of an object, the .NET Framework provides the BinaryFormatter class from the System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary namespace. This class is derived from Object but implements the IRemotingFormatter and the IFormatter interfaces. One of the methods of this class is called Serialize. This method is overloaded with two versions. The syntax of the first version is: Overloads Public Overridable Sub Serialize( _ ByVal serializationStream As Stream, _ ByVal graph As Object _ ) Implements IFormatter.Serialize The first argument of this method is a stream object that will carry the details of the streaming process. It must be a class derived from Stream. The second argument is a variable that carries the value(s) to be saved. It can be an instance of a class you created or a variable declared from a .NET Framework serializable class. |
|
|
Private Sub NewStoreItem_Deactivate(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Deactivate
Dim strFilename As String = "StoreItems.sti"
Dim fStream As New FileStream(strFilename, FileMode.Create)
Dim binFormat As New BinaryFormatter
Try
binFormat.Serialize(fStream, Me.lstStoreItems)
Catch anex As ArgumentNullException
MsgBox("The inventory could not be accessed")
Catch serex As SerializationException
MsgBox("The inventory could not be saved")
Finally
fStream.Close()
End Try
End Sub
|
|
Object Deserialization |
|
The opposite of serialization is deserialization. Deserialization is the process of retrieving an object that was serialized. When this is done, an exact copy of the object that was saved is created and restored as the origin. To support deserialization, the BinaryFormatter class provides the Deserialize() method, which is overloaded in two versions. The syntax of the first version: Overloads Public Overridable Function Deserialize( _ ByVal serializationStream As Stream _ ) As Object Implements IFormatter.Deserialize This method as argument the object that holds the file and the details on how the file will be opened. |
|
|
imports System.IO imports System.Runtime.Serialization imports System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary Imports StoreItemR2 |
Dim lstStoreItems As ArrayList
Private Sub NewStoreItem_Activated(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Activated
' This file holds the items sold in the store
Dim strFilename As String
Dim fStream As FileStream
strFilename = "StoreItems.sti"
If File.Exists(strFilename) Then
Try
' Create a stream of store items
fStream = New FileStream(strFilename, FileMode.Open)
Dim binFormat As New BinaryFormatter
lstStoreItems = binFormat.Deserialize(fStream)
Catch anex As ArgumentNullException
MsgBox("The inventory could not be accessed")
Catch ex As SerializationException
MsgBox("The application failed to retrieve the inventory")
Finally
fStream.Close()
End Try
else
Return
End If
End Sub
|
Private Sub btnAddItem_Click(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnAddItem.Click
Dim objItem As New StoreItemR2.CStoreItem
' Make sure the record is complete before attempting to add it
If Me.txtItemNumber.Text = "" Then Exit Sub
If Me.txtItemName.Text = "" Then Exit Sub
If Me.txtUnitPrice.Text = "" Then Exit Sub
' Now the record seems to be ready: build it
objItem.ItemNumber = Me.txtItemNumber.Text
objItem.ItemName = Me.txtItemName.Text
objItem.ItemSize = Me.txtSize.Text
objItem.UnitPrice = CDbl(Me.txtUnitPrice.Text)
' Add the record
Me.lstStoreItems.Add(objItem)
' Get ready to create a unique item number
Dim tmeNow As Date = Now
' Get ready to create a unique item number
Dim FoundUniqueNumber As Boolean = False
Dim strItemNumber As String = "000000"
Dim mls As Integer = tmeNow.Millisecond
' Generate two random numbers between 100 and 999
Dim rndNumber As New Random(mls)
Dim NewNumber1 As Integer = rndNumber.Next(100, 999)
Dim NewNumber2 As Integer = rndNumber.Next(100, 999)
' Create an item number from the random numbers
strItemNumber = NewNumber1.ToString() + "-" + NewNumber2.ToString()
' Reset the form for a new record
Me.txtItemNumber.Text = strItemNumber
Me.txtItemName.Text = ""
Me.txtSize.Text = ""
Me.txtUnitPrice.Text = ""
Me.txtItemName.Focus()
End Sub
|
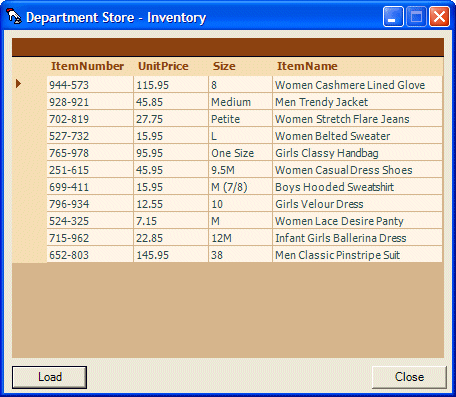
| Item Name | Size | Unit Price |
| Women Cashmere Lined Glove | 8 | 115.95 |
| Men Trendy Jacket | Medium | 45.85 |
| Women Stretch Flare Jeans | Petite | 27.75 |
| Women Belted Sweater | L | 15.95 |
| Girls Classy Handbag | One Size | 95.95 |
| Women Casual Dress Shoes | 9.5M | 45.95 |
| Boys Hooded Sweatshirt | M (7/8) | 15.95 |
| Girls Velour Dress | 10 | 12.55 |
| Women Lace Desire Panty | M | 7.15 |
| Infant Girls Ballerina Dress | 12M | 22.85 |
| Men Classic Pinstripe Suit | 38 | 145.95 |
Imports System.IO Imports System.Runtime.Serialization Imports System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary |
Private Sub btnLoad_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnLoad.Click
Dim lstItems As ArrayList = New ArrayList
Dim strFilename As String
Dim fStream As FileStream
Dim binFormat As BinaryFormatter
strFilename = "StoreItems.sti"
If File.Exists(strFilename) Then
fStream = New FileStream(strFilename, FileMode.Open)
Try
lstItems = binFormat.Deserialize(fStream)
Me.dataGrid1.DataSource = Nothing
Me.dataGrid1.DataSource = lstItems
Catch anex As ArgumentNullException
MsgBox("The inventory could not be accessed")
Catch serex As SerializationException
MsgBox("The application failed to retrieve the inventory")
Finally
fStream.Close()
End Try
End If
End Sub
|
Imports System.IO Imports System.Runtime.Serialization Imports System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary |
Private Sub CustomerOrder_Activated(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Activated
lstAvailableItems = New ArrayList
Dim strFilename As String
Dim binFormat As BinaryFormatter = New BinaryFormatter
' This file holds the items sold in the store
strFilename = "StoreItems.sti"
Dim fStream As FileStream
If File.Exists(strFilename) Then
Try
' Create a stream of store items
fStream = New FileStream(strFilename, FileMode.Open)
lstAvailableItems = binFormat.Deserialize(fStream)
Catch anex As ArgumentNullException
MsgBox("The inventory could not be accessed")
Catch serex As SerializationException
MsgBox("The application failed to retrieve the inventory")
Finally
fStream.Close()
End Try
else
Exit Sub
End If
End Sub
|
<Serializable()> Public Class CSaleInventory
Private nbr As String
Private nm As String
Private sz As String
Private uprice As Double
Private iQty As Integer
Private stotal As Double
Public Sub New()
nbr = ""
nm = ""
sz = ""
uprice = 0.0
iQty = 0
stotal = 0.0
End Sub
Public Sub New(ByVal number As String, ByVal name As String, _
ByVal size As String, ByVal price As Double, _
ByVal qty As Integer, ByVal total As Double)
nbr = number
nm = name
size = sz
uprice = price
iQty = qty
stotal = total
End Sub
Public Property ItemNumber() As String
Get
Return nbr
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As String)
nbr = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property ItemName() As String
Get
Return nm
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As String)
nm = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property ItemSize() As String
Get
Return sz
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As String)
sz = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property UnitPrice() As Double
Get
Return uprice
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As Double)
uprice = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property Quantity() As Integer
Get
Return iQty
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As Integer)
iQty = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property SubTotal() As Double
Get
Return stotal
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As Double)
stotal = Value
End Set
End Property
End Class
|
Private Sub btnSaveOrder_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnSaveOrder.Click
Dim dteCurrent As DateTime = Me.dtpSaleDate.Value
Dim strFilename As String
Dim lstCurrentSoldItems As ArrayList
Dim curOrder As SalesInventory.CSaleInventory
Dim fStream As FileStream
Dim binFormat As BinaryFormatter = New BinaryFormatter
Dim month As Integer = dteCurrent.Month
Dim day As Integer = dteCurrent.Day
Dim year As Integer = dteCurrent.Year
strFilename = month.ToString() + "-" + day.ToString() + _
"-" + year.ToString() + ".dly"
lstCurrentSoldItems = New ArrayList
' If this is not the first order of this file, then first open the file
' and store its orders in a temporary list
If File.Exists(strFilename) Then
Try
' Create a stream of store items
fStream = New FileStream(strFilename, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read)
lstCurrentSoldItems = binFormat.Deserialize(fStream)
Catch anex As ArgumentNullException
MsgBox("The inventory could not be accessed")
Catch serex As SerializationException
MsgBox("The application failed to retrieve the inventory")
Finally
fStream.Close()
End Try
End If
' Whether the file existed already or not, add the current items to the list
If Me.txtItemNumber1.Text <> "" Then
curOrder = New SalesInventory.CSaleInventory
curOrder.ItemNumber = Me.txtItemNumber1.Text
curOrder.ItemName = Me.txtDescription1.Text
curOrder.ItemSize = Me.txtSize1.Text
curOrder.UnitPrice = CDbl(Me.txtUnitPrice1.Text)
curOrder.Quantity = CInt(Me.txtQuantity1.Text)
curOrder.SubTotal = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal1.Text)
lstCurrentSoldItems.Add(curOrder)
End If
If Me.txtItemNumber2.Text <> "" Then
curOrder = New SalesInventory.CSaleInventory
curOrder.ItemNumber = Me.txtItemNumber2.Text
curOrder.ItemName = Me.txtDescription2.Text
curOrder.ItemSize = Me.txtSize2.Text
curOrder.UnitPrice = CDbl(Me.txtUnitPrice2.Text)
curOrder.Quantity = CInt(Me.txtQuantity2.Text)
curOrder.SubTotal = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal2.Text)
lstCurrentSoldItems.Add(curOrder)
End If
If Me.txtItemNumber3.Text <> "" Then
curOrder = New SalesInventory.CSaleInventory
curOrder.ItemNumber = Me.txtItemNumber3.Text
curOrder.ItemName = Me.txtDescription3.Text
curOrder.ItemSize = Me.txtSize3.Text
curOrder.UnitPrice = CDbl(Me.txtUnitPrice3.Text)
curOrder.Quantity = CInt(Me.txtQuantity3.Text)
curOrder.SubTotal = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal3.Text)
lstCurrentSoldItems.Add(curOrder)
End If
If Me.txtItemNumber4.Text <> "" Then
curOrder = New SalesInventory.CSaleInventory
curOrder.ItemNumber = Me.txtItemNumber4.Text
curOrder.ItemName = Me.txtDescription4.Text
curOrder.ItemSize = Me.txtSize4.Text
curOrder.UnitPrice = CDbl(Me.txtUnitPrice4.Text)
curOrder.Quantity = CInt(Me.txtQuantity4.Text)
curOrder.SubTotal = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal4.Text)
lstCurrentSoldItems.Add(curOrder)
End If
If Me.txtItemNumber5.Text <> "" Then
curOrder = New SalesInventory.CSaleInventory
curOrder.ItemNumber = Me.txtItemNumber5.Text
curOrder.ItemName = Me.txtDescription5.Text
curOrder.ItemSize = Me.txtSize5.Text
curOrder.UnitPrice = CDbl(Me.txtUnitPrice5.Text)
curOrder.Quantity = CInt(Me.txtQuantity3.Text)
curOrder.SubTotal = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal5.Text)
lstCurrentSoldItems.Add(curOrder)
End If
If Me.txtItemNumber6.Text <> "" Then
curOrder = New SalesInventory.CSaleInventory
curOrder.ItemNumber = Me.txtItemNumber6.Text
curOrder.ItemName = Me.txtDescription6.Text
curOrder.ItemSize = Me.txtSize6.Text
curOrder.UnitPrice = CDbl(Me.txtUnitPrice6.Text)
curOrder.Quantity = CInt(Me.txtQuantity6.Text)
curOrder.SubTotal = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal6.Text)
lstCurrentSoldItems.Add(curOrder)
End If
If Me.txtItemNumber7.Text <> "" Then
curOrder = New SalesInventory.CSaleInventory
curOrder.ItemNumber = Me.txtItemNumber7.Text
curOrder.ItemName = Me.txtDescription7.Text
curOrder.ItemSize = Me.txtSize7.Text
curOrder.UnitPrice = CDbl(Me.txtUnitPrice7.Text)
curOrder.Quantity = CInt(Me.txtQuantity7.Text)
curOrder.SubTotal = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal7.Text)
lstCurrentSoldItems.Add(curOrder)
End If
If Me.txtItemNumber8.Text <> "" Then
curOrder = New SalesInventory.CSaleInventory
curOrder.ItemNumber = Me.txtItemNumber8.Text
curOrder.ItemName = Me.txtDescription8.Text
curOrder.ItemSize = Me.txtSize8.Text
curOrder.UnitPrice = CDbl(Me.txtUnitPrice8.Text)
curOrder.Quantity = CInt(Me.txtQuantity8.Text)
curOrder.SubTotal = CDbl(Me.txtSubTotal8.Text)
lstCurrentSoldItems.Add(curOrder)
End If
fStream = New FileStream(strFilename, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write, FileShare.None)
Try
binFormat.Serialize(fStream, lstCurrentSoldItems)
Catch anex As ArgumentNullException
MessageBox.Show("The customer order could not be accessed")
Catch serex As SerializationException
MessageBox.Show("The customer order could not be saved")
End
Finally
fStream.Close()
End Try
' Reset the order
Me.txtItemNumber1.Text = ""
Me.txtItemNumber2.Text = ""
Me.txtItemNumber3.Text = ""
Me.txtItemNumber4.Text = ""
Me.txtItemNumber5.Text = ""
Me.txtItemNumber6.Text = ""
Me.txtItemNumber7.Text = ""
Me.txtItemNumber8.Text = ""
Me.txtItemNumber1_Leave(sender, e)
Me.txtItemNumber2_Leave(sender, e)
Me.txtItemNumber3_Leave(sender, e)
Me.txtItemNumber4_Leave(sender, e)
Me.txtItemNumber5_Leave(sender, e)
Me.txtItemNumber6_Leave(sender, e)
Me.txtItemNumber7_Leave(sender, e)
Me.txtItemNumber8_Leave(sender, e)
Me.txtTotalOrder.Text = "0.00"
Me.dtpSaleDate.Value = DateTime.Today
Me.txtItemNumber1.Focus()
End Sub
|
Imports System.IO Imports System.Runtime.Serialization Imports System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary |
Private Sub dtpSaleDate_ValueChanged(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles dtpSaleDate.ValueChanged
Dim dteCurrent As DateTime
Dim strFilename As String
Dim lstDaySoldItems As ArrayList = New ArrayList
Dim binFormat As BinaryFormatter = New BinaryFormatter
dteCurrent = Me.dtpSaleDate.Value
Dim month As Integer = dteCurrent.Month
Dim day As Integer = dteCurrent.Day
Dim year As Integer = dteCurrent.Year
strFilename = month.ToString() + "-" + day.ToString() + "-" + year.ToString() + ".dly"
' Find out if the file exists, that is, if some orders were placed on that day
If File.Exists(strFilename) Then
Dim fStream As FileStream = New FileStream(strFilename, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read)
Try
binFormat = New BinaryFormatter
lstDaySoldItems = binFormat.Deserialize(fStream)
Me.dataGrid1.DataSource = Nothing
Me.dataGrid1.DataSource = lstDaySoldItems
Catch anex As ArgumentNullException
MsgBox("The inventory could not be accessed")
Catch serex As SerializationException
MsgBox("The application failed to retrieve the inventory")
Finally
fStream.Close()
End Try
Else
Me.dataGrid1.DataSource = Nothing
End If
End Sub
|
|
|
||
| Home | Copyright © 2005-2016, FunctionX | |
|
|
||