 |
Visual C++/CLI Collections: Dictionary-Based Collection Classes |
|
|
|
A dictionary is a list of items with the following two rules:
|
- Each item is a combination of a key and a value. An item can be made of three parts: a key, a value, and a correspondence between them. The correspondence can be represented by the assignment operator: Key=Value. In some environments, the = operator is used. In some others, the : operator is used. Yet in some others, there is no actual operator that joins both sides but you must know that the key and the value go in pair
- As each item is a combination of a key and a value, each key must be unique. The list of items in the dictionary can be very huge, sometimes in the thousands or even millions. Among
the items, each key must be distinct from any other key in the dictionary
In some cases, in addition to these two rules, the items should - in some cases must - be ordered. To order the items, the keys are used. Because in most cases a dictionary is made of words, the keys are ordered in alphabetical order. A dictionary can also be made of items whose keys are date values. In this case, the items would be ordered in chronological order.
There are various types of dictionary types of list used in
daily life. The word "dictionary" here does not imply the traditional
dictionary that holds the words and their meanings in the English language.
The concept is applied in various scenarios.
|
 Practical
Learning: Introducing Dictionary Collections Practical
Learning: Introducing Dictionary Collections
|
|
- Start Microsoft Visual Studio
- Create a new Windows Application named BethesdaCarRental1
- To add a new form to the project, in the Solution Explorer, right-click
BethesdaCarRental1 -> Add -> New Item...
- Click Windows Form.
- Set the Name to RentalRates and press Enter
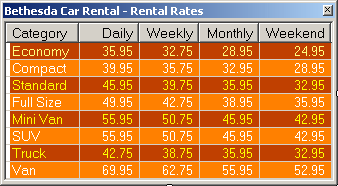
- Add a ListView to the form and create its Columns as follows:
| (Name) |
Text |
TextAlign |
Width |
| colCategory |
Category |
|
90 |
| colDaily |
Daily |
Right |
|
| colWeekly |
Weekly |
Right |
|
| colMonthly |
Monthly |
Right |
|
| colWeekend |
Weekend |
Right |
|
- Create its Items as follows:
| ListViewItem |
SubItems |
SubItems |
SubItems |
SubItems |
| |
Text |
Text |
Text |
Text |
| Economy |
35.95 |
32.75 |
28.95 |
24.95 |
| Compact |
39.95 |
35.75 |
32.95 |
28.95 |
| Standard |
45.95 |
39.75 |
35.95 |
32.95 |
| Full Size |
49.95 |
42.75 |
38.95 |
35.95 |
| Mini Van |
55.95 |
50.75 |
45.95 |
42.95 |
| SUV |
55.95 |
50.75 |
45.95 |
42.95 |
| Truck |
42.75 |
38.75 |
35.95 |
32.95 |
| Van |
69.95 |
62.75 |
55.95 |
52.95 |
- Complete the design of the form as follows:
- To add a new form to the application, in the Solution Explorer, right-click
BethesdaCarRental1 -> Add -> New Item...
- Click Windows Form and set the Name to Employees
- Click Add
- From the Toolbox, add a ListView to the form
- While the new list view is still selected, in the Properties window, click
the ellipsis button of the Columns field and create the columns as follows:
| (Name) |
Text |
TextAlign |
Width |
| colEmployeeNumber |
Empl # |
|
45 |
| colFirstName |
First Name |
|
65 |
| colLastName |
Last Name |
|
65 |
| colFullName |
Full Name |
|
140 |
| colTitle |
Title |
|
120 |
| colHourlySalary |
Hourly Salary |
Right |
75 |
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Other Properties |
| ListView |
|
lvwEmployees |
Anchor: Top, Bottom, Left, Right
FullRowSelect: True
GridLines: True
View: Details |
| Button |
New Employee... |
btnNewEmployee |
|
| Button |
Close |
btnClose |
|
|
- To add another form to the application, in the Solution Explorer, right- click
BethesdaCarRental1
-> Add -> New Item...
- Click Windows Form and set the Name to EmployeeEditor
- Click Add
- Design the form as follows:
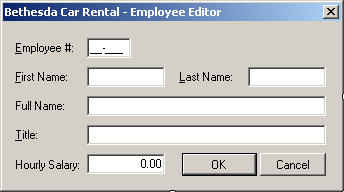 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Properties |
| Label |
&Employee #: |
|
|
| MaskedTextBox |
|
txtEmployeeNumber |
Mask: 00-000
Modifiers: public |
| Label |
First Name: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtFirstName |
Modifiers: public |
| Label |
Last Name: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtLastName |
Modifiers: public |
| Label |
Full Name: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtFullName |
Enabled: False
Modifiers: public |
| Label |
Title: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtTitle |
Modifiers: public |
| Label |
Hourly Salary: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtHourlySalary |
Modifiers: public
TextAlign: Right |
| Button |
OK |
btnOK |
DialogResult: OK |
| Button |
Cancel |
btnCancel |
DialogResult: Cancel |
| Form |
|
|
AcceptButton: btnOK
CancelButton: btnCancel
FormBorderStyle: FixedDialog
MaximizeBox: False
MinimizeBox: False
ShowInTaskbar: False |
|
- Click the Last Name text box
- In the Properties window, click the Events button and double-click Leave
- Implement the event as follows:
// This code is used to create and display the customer's full name
System::Void txtLastName_Leave(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
String ^ strFirstName = txtFirstName->Text;
String ^ strLastName = txtLastName->Text;
String ^ strFullName;
if (strFirstName->Length == 0)
strFullName = strLastName;
else
strFullName = strLastName + L", " + strFirstName;
txtFullName->Text = strFullName;
}
|
- To add a new class to the project, in the Class View, right- click
BethesdaCarRental1
-> Add -> Class...
- Click C++ Class
- Click Add
- Set the Class Name to CEmployee
- Click Finish
- Change the header file as follows:
#pragma once
using namespace System;
[Serializable]
public ref class CEmployee
{
public:
String ^ FirstName;
String ^ LastName;
String ^ Title;
double HourlySalary;
property String ^ FullName
{
String ^ get()
{
return LastName+ L", " + FirstName;
}
}
public:
CEmployee(void);
CEmployee(String ^ fname, String ^ lname,
String ^ title, double salary);
};
|
- Change the source file as follows:
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Employee.h"
// This default constructor says that
// the employee is not defined
CEmployee::CEmployee(void)
: FirstName(L"Unknown"),
LastName(L"Unknown"),
Title(L"N/A"),
HourlySalary(0.00)
{
}
// This constructor completely defines an employee
CEmployee::CEmployee(System::String ^fname,
System::String ^lname,
System::String ^title,
double salary)
: FirstName(fname),
LastName(lname),
Title(title),
HourlySalary(salary)
{
}
|
- To add a new form to the application, on the main menu, click Project
-> Add New Item...
- Click Windows Forms
- Set the Name to Customers
- Press Enter
- From the Toolbox, add a ListView to the form
- While the new list view is still selected, in the Properties window, click
the ellipsis button of the Columns field and create the columns as follows:
| (Name) |
Text |
Width |
| colDrvLicNbr |
Driver's Lic. # |
100 |
| colFullName |
Full Name |
100 |
| colAddress |
Address |
160 |
| colCity |
City |
100 |
| colState |
State |
38 |
| colZIPCode |
ZIPCode |
|
- Design the form as follows:
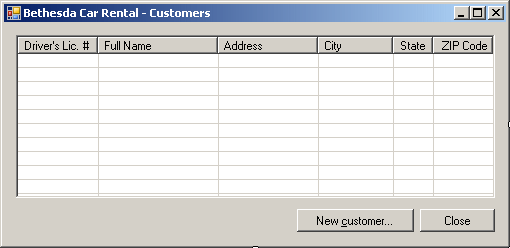 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Other Properties |
| ListView |
|
lvwCustomers |
View: Details
GridLines: True
FullRowSelect: True |
| Button |
New Customer... |
btnNewCustomer |
|
| Button |
Close |
btnClose |
|
|
- To add another form to the application, on the main menu, click Project
-> Add New Item...
- Click Windows Forms and cet the Name to CustomerEditor
- Click Add
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Properties |
| Label |
Driver's Lic. #: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtDrvLicNbr |
Modifiers: Public |
| Label |
State: |
|
|
| ComboBox |
|
cbxStates |
Modifiers: Public
Items: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, DC, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL,
IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH,
NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT,
VA, WA, WV, WI, WY |
| Label |
Full Name: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtFullName |
Modifiers: Public |
| Label |
Address: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtAddress |
Modifiers: Public |
| Label |
City: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtCity |
Modifiers: Public |
| Label |
ZIP Code: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtZIPCode |
Modifiers: Public |
| Button |
OK |
btnOK |
DialogResult: OK |
| Button |
Close |
btnCancel |
DialogResult: Cancel |
| Form |
|
|
AcceptButton: btnOK
CancelButton: btnCancel
FormBorderStyle: FixedDialog
MaximizeBox: False
MinimizeBox: False
ShowInTaskbar: False |
|
- To add a new class to the project, in the Class View, right-click
BethesdaCarRental1 -> Add -> Class...
- Click C++ Class
- Click Add
- Set the Class Name to CCustomer
- Click Finish
- Change the header file as follows:
#pragma once
using namespace System;
[Serializable]
public ref class CCustomer
{
public:
String ^ FullName;
String ^ Address;
String ^ City;
String ^ State;
String ^ ZIPCode;
public:
CCustomer(void);
CCustomer(String ^ fName,
String ^ adr, String ^ ct,
String ^ ste, String ^ zip);
};
|
- Change the source file as follows:
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Customer.h"
CCustomer::CCustomer(void)
: FullName(L""),
Address(L""),
City(L""),
State(L""),
ZIPCode(L"")
{
}
// This constructor defines a customer
CCustomer::CCustomer(String ^ fName,
String ^ adr, String ^ ct,
String ^ ste, String ^ zip)
: FullName(fName),
Address(adr),
City(ct),
State(ste),
ZIPCode(zip)
{
}
|
- Save all
- Copy the following pictures to any folder somewhere on your computer (this
is simply an example of preparing the pictures of cars you would include in
your database application):
 |
 |
| BMW: 335i |
Chevrolet Avalanche |
 |
 |
| Honda Accord |
Mazda Miata |
 |
 |
| Chevrolet Aveo |
Ford E150XL |
 |
 |
| Buick Lacrosse |
Honda Civic |
 |
 |
| Ford F-150 |
Mazda Mazda5 |
 |
 |
| Volvo S40 |
Land Rover LR3 |
- Return to your programming environment
- To add a new form to the application, in the Solution Explorer, right-click
BethesdaCarRental1
-> Add -> New Item...
- Click Windows Forms if necessary and set the Name to CarEditor
- Click Add
- Design the form as follows:
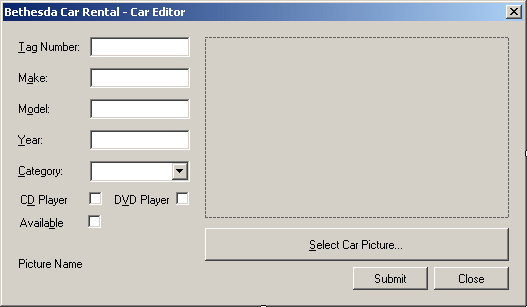 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Other Properties |
| Label |
Text # |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtTagNumber |
|
| Label |
Make: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtMake |
|
| Label |
Model: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtModel |
|
| Label |
Year: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtYear |
|
| Label |
Category: |
|
|
| ComboBox |
|
cboCategories |
DropDownStyle: DropDownList |
| Items: |
Economy
Compact
Standard
Full Size
Mini Van
SUV
Truck
Van |
| PictureBox |
|
pbxCar |
SizeMode: Zoom |
| CheckBox |
CD Player |
chkCDPlayer |
CheckAlign: MiddleRight |
| CheckBox |
DVD Player |
chkDVDPlayer |
CheckAlign: MiddleRight |
| Button |
Select Car Picture... |
btnSelectPicture |
|
| CheckBox |
Available |
chkAvailable |
CheckAlign: MiddleRight |
| Label |
Picture Name |
lblPictureName |
|
| Button |
Submit |
btnSubmit |
|
| Button |
Close |
btnClose |
DialogResult: Cancel |
| OpenFileDialog |
(Name): dlgOpen
Title: Select Item Picture
DefaultExt: jpg
Filter: JPEG Files (*.jpg,*.jpeg)|*.jpg|GIF Files (*.gif)|*.gif|Bitmap Files
(*.bmp)|*.bmp|PNG Files (*.png)|*.png |
| Form |
|
|
FormBorderStyle: FixedDialog
MaximizeBox: False
MinimizeBox: False
ShowInTaskbar: False |
|
- Double-click the Select Car Picture button and implement its event as
follows:
System::Void btnSelectPicture_Click(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
if (dlgPicture->ShowDialog() == System::Windows::Forms::DialogResult::OK)
{
lblPictureName->Text = dlgPicture->FileName;
pbxCar->Image = Image::FromFile(lblPictureName->Text);
}
}
|
- To add a new class to the project, in the Class View, right-click
BethedaCarRental1 -> Add -> Class...
- Click C++ Click
- Click Add
- Set the Class Name to CCar
- Click Add
- Change the header file as follows:
#pragma once
using namespace System;
[Serializable]
public ref class CCar
{
public:
String ^ Make;
String ^ Model;
int Year;
String ^ Category;
bool HasCDPlayer;
bool HasDVDPlayer;
bool IsAvailable;
public:
CCar(void);
CCar(String ^ mk, String ^ mdl,
int yr, String ^ cat, bool cd,
bool dvd, bool avl);
};
|
- Change the source file as follows:
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Car.h"
CCar::CCar(void)
: Make(L""),
Model(L""),
Year(0),
Category(L""),
HasCDPlayer(false),
HasDVDPlayer(false),
IsAvailable(false)
{
}
CCar::CCar(System::String ^mk, System::String ^mdl,
int yr, System::String ^cat, bool cd,
bool dvd, bool avl)
: Make(mk),
Model(mdl),
Year(yr),
Category(cat),
HasCDPlayer(cd),
HasDVDPlayer(dvd),
IsAvailable(avl)
{
}
|
- To add a new class to the project, in the Class View, right-click
BethesdaCarRental -> Add -> Class...
- Click C++ Class and click Add
- Set the Class Name to CRentalOrder
- Press Enter
- Change the header file as follows:
#pragma once
using namespace System;
[Serializable]
public ref class CRentalOrder
{
public:
String ^ EmployeeNumber;
// The following flag will allow us to update/know whether
// * The car is currently being used by the customer.
// That is, if the car has been picked up by the customer
// * The customer has brought the car back
String ^ OrderStatus;
// Because every car has a tag number
// and that tag number will not change
// during the lifetime of a car (while the car remains with our
// car rental company, we will
// use only the tag number here.
// The other pieces of information will
// be retrieved from the list of cars
String ^ CarTagNumber;
// We will identify the customer by the number
// and the name on his or her driver's license
String ^ CustomerDrvLicNbr;
String ^ CustomerName;
// Although he or she may keep the same driver's
// license number for a lifetime, a customer who
// rents cars at different times with this company
// over months or years may have different addresses.
// Therefore, although we will primarily retrieve the
// customer's address from the list of customers,
// we will give the clerk the ability to change this
// information on a rental order. This means that the
// same customer could have different information on
// different rental orders.
// For this reason, each rental order will its own set
// of these pieces of information
String ^ CustomerAddress;
String ^ CustomerCity;
String ^ CustomerState;
String ^ CustomerZIPCode;
String ^ CarCondition;
String ^ TankLevel;
// This information will be entered when the car is being rented
int MileageStart;
// This information will be entered when the car is brought back
int MileageEnd;
// This information will be entered when the car is being rented
DateTime DateStart;
// This information will be entered when the car is brought back
DateTime DateEnd;
int Days;
// This information will be entered when the car is being rented
double RateApplied;
// This calculation should occur when the car is brought back
double SubTotal;
double TaxRate;
double TaxAmount;
double OrderTotal;
public:
CRentalOrder(void);
};
|
- To add a new form to the project, in the Solution Explorer, right-click
BethesdaCarRenat1 -> Add -> New Item...
- Click Windows Form
- Set the Name to OrderProcessing
- Press Enter
- Design the form as follows:
 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
Other Properties |
| Label |
Processed By: |
|
AutoSize: False
BackColor: Gray
BorderStyle: FixedSingle
ForeColor: White
TextAlign: MiddleLeft |
| Label |
Employee #: |
|
|
| MaskedTextBox |
|
txtEmployeeNumber |
Mask: 00-000 |
| Label |
Employee Name: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtEmployeeName |
|
| Label |
Processed For |
|
AutoSize: False
BackColor: Gray
BorderStyle: FixedSingle
ForeColor: White
TextAlign: MiddleLeft |
| Label |
Driver's Lic #: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtDrvLicNumber |
|
| Label |
Cust Name: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtCustomerName |
|
| Label |
Address: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtCustomerAddress |
|
| Label |
City: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtCustomerCity |
|
| Label |
State: |
|
|
| ComboBox |
|
cbxCustomerStates |
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Sorted: True
Items: AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, DC, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL,
IN, IA, KS, KY, LA, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, MS, MO, MT, NE, NV, NH,
NJ, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT,
VA, WA, WV, WI, WY |
| Label |
ZIP Code |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtCustomerZIPCode |
|
| Label |
Car Selected |
|
AutoSize: False
BackColor: Gray
BorderStyle: FixedSingle
ForeColor: White
TextAlign: MiddleLeft |
| Label |
Tag Number: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtTagNumber |
|
| Label |
Car Condition: |
|
|
| ComboBox |
|
cbxCarConditions |
Sorted: True
Items:
Needs Repair
Drivable
Excellent |
| Label |
Make: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtMake |
|
| Label |
Model: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtModel |
|
| Label |
Year: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtCarYear |
|
| label |
Tank Level: |
|
|
| ComboBox |
|
cbxTankLevels |
Empty
1/4 Empty
1/2 Full
3/4 Full
Full |
| Label |
Mileage Start: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtMileageStart |
TextAlign: Right |
| Label |
Mileage End: |
|
|
| TextBox |
|
txtMileageEnd |
TextAlign: Right |
| Label |
Order Timing |
|
AutoSize: False
BackColor: Gray
BorderStyle: FixedSingle
ForeColor: White
TextAlign: MiddleLeft |
| Label |
Start Date: |
|
|
| DateTimePicker |
|
dtpStartDate |
|
| Label |
End Date: |
|
|
| DateTimePicker |
|
dtpEndDate |
|
| Label |
Days: |
|
|
| TextBox |
0 |
txtDays |
TextAlign: Right |
| Label |
Order Status |
|
|
| ComboBox |
|
cbxOrderStatus |
Items:
Car On Road
Car Returned
Order Reserved |
| Label |
Order Evaluation |
|
AutoSize: False
BackColor: Gray
BorderStyle: FixedSingle
ForeColor: White
TextAlign: MiddleLeft |
| Label |
Rate Applied: |
|
|
| TextBox |
0.00 |
txtRateApplied |
TextAlign: Right |
| Button |
Rental Rates |
btnRentalRates |
|
| Label |
Sub-Total: |
|
|
| TextBox |
0.00 |
txtSubTotal |
TextAlign: Right |
| Button |
Calculate |
btnCalculate |
|
| Label |
Tax Rate: |
|
|
| TextBox |
7.75 |
txtTaxRate |
TextAlign: Right |
| Label |
% |
|
|
| Button |
Save |
btnSave |
|
| Label |
Tax Amount: |
|
|
| TextBox |
0.00 |
txtTaxAmount |
TextAlign: Right |
| Button |
Print... |
btnPrint |
|
| Label |
Order Total: |
|
|
| TextBox |
0.00 |
txtOrderTotal |
TextAlign: Right |
| Button |
Print Preview... |
btnPrintPreview |
|
| Label |
Receipt #: |
|
|
| TextBox |
0 |
txtReceiptNumber |
|
| Button |
Open |
btnOpen |
|
| Button |
New Rental Order/Reset |
btnNewRentalOrder |
|
| Button |
Close |
btnClose |
|
|
- On the Order Processing form, double-click the Start Date date time picker control
- Implement the event as follows:
System::Void dtpStartDate_ValueChanged(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
dtpEndDate->Value = dtpStartDate->Value;
}
|
- Return to the Order Processing form and double-click the End Date control
- Implement its Click event as follows:
// This event approximately evaluates the number of days as a
// difference between the end date and the starting date
System::Void dtpEndDate_ValueChanged(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
int days;
DateTime dteStart = this->dtpStartDate->Value;
DateTime dteEnd = this->dtpEndDate->Value;
// Let's calculate the difference in days
TimeSpan tme = dteEnd - dteStart;
days = tme.Days;
// If the customer returns the car the same day,
// we consider that the car was rented for 1 day
if (days == 0)
days = 1;
txtDays->Text = days.ToString();
// At any case, we will let the clerk specify the actual number of days
}
|
- Scroll up on the document
- Include the header file for the RentalRates:
#pragma once
#include "RentalRates.h"
using namespace System;
using namespace System::ComponentModel;
using namespace System::Collections;
using namespace System::Windows::Forms;
using namespace System::Data;
using namespace System::Drawing;
|
- Return to the Order Processing form and double-click the Rental Rates button
- Implement its event as follows:
System::Void btnRentalRates_Click(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
RentalRates ^ wndRates = gcnew RentalRates;
wndRates->Show();
}
|
- Return to the Order Processing form and double-click the Calculate button
- Implement its event as follows:
System::Void btnCalculate_Click(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
int Days = 0;
double RateApplied = 0.00;
double SubTotal = 0.00;
double TaxRate = 0.00;
double TaxAmount = 0.00;
double OrderTotal = 0.00;
try
{
Days = int::Parse(this->txtDays->Text);
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
MessageBox::Show(L"Invalid Number of Days");
}
try
{
RateApplied = double::Parse(txtRateApplied->Text);
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
MessageBox::Show(L"Invalid Amount for Rate Applied");
}
SubTotal = Days * RateApplied;
txtSubTotal->Text = SubTotal.ToString(L"F");
try
{
TaxRate = double::Parse(txtTaxRate->Text);
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
MessageBox::Show(L"Invalid Tax Rate");
}
TaxAmount = SubTotal * TaxRate / 100;
txtTaxAmount->Text = TaxAmount.ToString(L"F");
OrderTotal = SubTotal + TaxAmount;
txtOrderTotal->Text = OrderTotal.ToString(L"F");
}
|
- Return to the Order Processing form
- From the Printing section of the Toolbox, click PrintDocument and click
the form
- In the Properties window, set its (Name) to docPrint and press Enter
- Under the form, double-click docPrint and implement its event as follows:
System::Void docPrint_PrintPage(System::Object^ sender,
System::Drawing::Printing::PrintPageEventArgs^ e)
{
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 2), 80, 90, 750, 90);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1), 80, 93, 750, 93);
String ^ strDisplay = L"Bethesda Car Rental";
System::Drawing::Font ^ fntString =
gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 28,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(strDisplay, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 240, 100);
strDisplay = L"Car Rental Order";
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 22,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(strDisplay, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 320, 150);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1), 80, 187, 750, 187);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 2), 80, 190, 750, 190);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Receipt #: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 220);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtReceiptNumber->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 260, 220);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1), 100, 240, 380, 240);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Processed By: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 420, 220);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtEmployeeName->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 550, 220);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1), 420, 240, 720, 240);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->FillRectangle(Brushes::Gray,
Rectangle(100, 260, 620, 20));
e->Graphics->DrawRectangle(Pens::Black,
Rectangle(100, 260, 620, 20));
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Customer", fntString,
Brushes::White, 100, 260);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Driver's License #: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 300);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Name: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 420, 300);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtDrvLicNumber->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 260, 300);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtCustomerName->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 540, 300);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1), 100, 320, 720, 320);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Address: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 330);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtCustomerAddress->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 260, 330);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
100, 350, 720, 350);
strDisplay = txtCustomerCity->Text+ L" " +
cbxCustomerStates->Text+ L" " +
txtCustomerZIPCode->Text;
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman",
12, FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(strDisplay, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 260, 360);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
260, 380, 720, 380);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->FillRectangle(Brushes::Gray,
Rectangle(100, 410, 620, 20));
e->Graphics->DrawRectangle(Pens::Black,
Rectangle(100, 410, 620, 20));
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Car Information", fntString,
Brushes::White, 100, 410);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Tag #: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 450);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtTagNumber->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 260, 450);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
100, 470, 380, 470);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Year: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 420, 450);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtCarYear->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 530, 450);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
420, 470, 720, 470);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Make: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 480);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtMake->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 260, 480);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
100, 500, 380, 500);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Model: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 420, 480);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtModel->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 530, 480);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
420, 500, 720, 500);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Car Condition: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 510);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(cbxCarConditions->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 260, 510);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
100, 530, 380, 530);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Tank Level: ", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 420, 510);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(cbxTankLevels->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 530, 510);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
420, 530, 720, 530);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Mileage Start:", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 540);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtMileageStart->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 260, 540);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
100, 560, 380, 560);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Mileage End:", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 420, 540);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtMileageEnd->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 530, 540);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
420, 560, 720, 560);
e->Graphics->FillRectangle(Brushes::Gray,
Rectangle(100, 590, 620, 20));
e->Graphics->DrawRectangle(Pens::Black,
Rectangle(100, 590, 620, 20));
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Order Timing Information", fntString,
Brushes::White, 100, 590);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Start Date:", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 620);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(dtpStartDate->Value.ToString(L"D"),
fntString, Brushes::Black, 260, 620);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
100, 640, 720, 640);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"End Date:", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 650);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(dtpEndDate->Value.ToString(L"D"), fntString,
Brushes::Black, 260, 650);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
100, 670, 520, 670);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Days:", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 550, 650);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtDays->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 640, 650);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
550, 670, 720, 670);
e->Graphics->FillRectangle(Brushes::Gray,
Rectangle(100, 700, 620, 20));
e->Graphics->DrawRectangle(Pens::Black,
Rectangle(100, 700, 620, 20));
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Order Evaluation", fntString,
Brushes::White, 100, 700);
StringFormat ^ fmtString = gcnew StringFormat;
fmtString->Alignment = StringAlignment::Far;
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Rate Applied:", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 740);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtRateApplied->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 300, 740, fmtString);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
100, 760, 380, 760);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Tax Rate:", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 420, 740);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtTaxRate->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 640, 740, fmtString);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"%", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 640, 740);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
420, 760, 720, 760);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Sub-Total:", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 100, 770);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtSubTotal->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 300, 770, fmtString);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
100, 790, 380, 790);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Tax Amount:", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 420, 770);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtTaxAmount->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 640, 770, fmtString);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
420, 790, 720, 790);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Bold);
e->Graphics->DrawString(L"Order Total:", fntString,
Brushes::Black, 420, 800);
fntString = gcnew System::Drawing::Font(L"Times New Roman", 12,
FontStyle::Regular);
e->Graphics->DrawString(txtOrderTotal->Text, fntString,
Brushes::Black, 640, 800, fmtString);
e->Graphics->DrawLine(gcnew Pen(Color::Black, 1),
420, 820, 720, 820);
}
|
- Return to the Order Processing form
- From the Printing section of the Toolbox, click PrintDialog and click the
form
- In the Properties window, change its Name to dlgPrint
- Still in the Properties windows, set its Document property to docPrint
- On the Order Processing form, double-click the Print button and implement its event as
follows:
System::Void btnPrint_Click(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
if (dlgPrint->ShowDialog() == System::Windows::Forms::DialogResult::OK)
docPrint->Print();
}
|
- Return to the Order Processing form
- From the Printing section of the Toolbox, click PrintPreviewDialog and
click the form
- In the Properties window, change its (Name) to dlgPrintPreview
- Still in the Properties windows, set its Document property to docPrint
- On the Order Processing form, double-click the Print Preview button
- Implement the event as follows:
System::Void btnPrintPreview_Click(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
dlgPrintPreview->ShowDialog();
}
|
- Access the Form1 form and design it as follows:
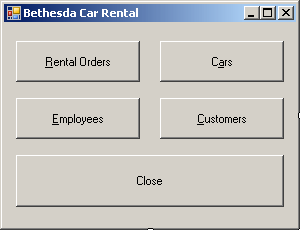 |
| Control |
Text |
Name |
| Button |
Customers &Rental Orders |
btnRentalOrders |
| Button |
C&ars |
btnCars |
| Button |
&Employees |
btnEmployees |
| Button |
&Customers |
btnCustomers |
| Button |
C&lose |
btnClose |
|
- Right-click the form and click View Code
- In the top section of the file, include the header files of the other
forms:
#pragma once
#include "OrderProcessing.h"
#include "CarEditor.h"
#include "Employees.h"
#include "Customers.h"
namespace BethesdaCarRental1 {
using namespace System;
using namespace System::ComponentModel;
using namespace System::Collections;
using namespace System::Windows::Forms;
using namespace System::Data;
using namespace System::Drawing;
|
- Return to the Form1 form
- Double-click the Order Processing button and implement its event as follows:
System::Void btnOrderProcessing_Click(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
OrderProcessing ^ dlgOrder = gcnew OrderProcessing;
dlgOrder->ShowDialog();
}
|
- Return to the Form1 form
- Double-click the Car Editor button and implement its event as follows:
System::Void btnCarEditor_Click(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
CarEditor ^ dlgCars = gcnew CarEditor;
dlgCars->ShowDialog();
}
|
- Return to the Form1 form
- Double-click the Employees button and implement its event as follows:
System::Void btnEmployees_Click(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
Employees ^ dlgEmployees = gcnew Employees;
dlgEmployees->ShowDialog();
}
|
- Return to the Form1 form
- Double-click the Customers button and implement its event as follows:
System::Void btnCustomers_Click(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
Customers ^ dlgCustomers = gcnew Customers;
dlgCustomers->ShowDialog();
}
|
- Return to the Form1 form
- Double-click the Close button and implement its event as follows:
System::Void btnClose_Click(System::Object^ sender,
System::EventArgs^ e)
{
Close();
}
|
- Save all
|
|