|
|
A label is a control that serves as a guide to the user.
It provides static text that the user cannot change but can read to get
information on a form. The programmer can also use it to display simple
information to the user. Most controls on the form are not explicit at first
glance and the user may not know what they are used for. Therefore, you can
assign a label to a control as a help to the user.
|
To add a label to a container, click the Label button
 from the Toolbox and click the object that would host it.
from the Toolbox and click the object that would host it.
To programmatically create a label, declare a handle
to Label, initialize it using its default constructor, and add it
to the Controls property of the form. Here is an example:
#include <windows.h>
#using <System.dll>
#using <System.Windows.Forms.dll>
using namespace System;
using namespace System::Windows::Forms;
public ref class CExercise : public Form
{
private:
Label ^ lblMessage;
public:
CExercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
void InitializeComponent()
{
lblMessage = gcnew Label;
Controls->Add(lblMessage);
}
};
int APIENTRY WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance,
HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPSTR lpCmdLine,
int nCmdShow)
{
Application::Run(gcnew CExercise());
return 0;
}
|
 Practical
Learning: Introducing Labels Practical
Learning: Introducing Labels
|
|
- Start Microsoft Visual C++
- Create a Window Forms Application named ElementaryAddition1
- From the Common Control section of the Toolbox, click Label and
click the form
- From the Common Control section of the Toolbox, click the Label
again and click the form
- From the Common Control section of the Toolbox, click the Label
again and click the form
|
Characteristics of a Label
|
|
The most important characteristic of a label control
is the text it displays. That text is also referred to as its caption and
this is what the user would read. The text of a label is its Text
property and is its default. To set a label's caption,
after adding the control to a container, click Text in the
Properties window and type the desired value. As we mentioned when
studying controls characteristics, at design time, the text you type in
the Text field is considered "as is".
If you want to create a more elaborate and formatted string, you would
have to do it programmatically. Here is an example:
public ref class CExercise : public Form
{
private:
Label ^ lblMessage;
public:
CExercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
void InitializeComponent()
{
lblMessage = gcnew Label;
lblMessage->Location = Point(20, 20);
lblMessage->Text = DateTime::Now.ToString();
Controls->Add(lblMessage);
}
};
After specifying the caption of a label, by default,
it is positioned to the left of its confined rectangle. You can change
this alignment to the center or the right sides. To do this, you can
specify the value of the TextAlign property.
When it comes to its caption, one of the most valuable
characteristics of the text of a label is the variance of the font. When
designing a caption. you can change the default font to make it more
attractive.
|
 Practical
Learning: Captioning the Labels Practical
Learning: Captioning the Labels
|
|
- On the form, click the first label
- In the Properties window, click Text and type 00
- Click (Name) and type lblOperand1
- Click TextAlign and the arrow of its combo box to select
MiddleCenter
- Click the + button of the Font field and change the
characteristics as follows:
Name: Tahoma
Font Style: Bold
Size: 48
- On the form, click the second label and, in the Properties window,
change its characteristics as follows:
Text: +
TextAlign:
MiddleCenter
(Name): lblOPeration
Font -> Name: Arial
Font -> Font Style: Bold
Font -> Size: 48
- On the form, click the third label and, in the Properties window,
change its characteristics as follows:
Text: 00
TextAlign: MiddleCenter
(Name): lblOperand2
Font -> Name:
Arial
Font -> Font Style: Bold
Font -> Size: 48
|
Automatically Sizing a Label
|
|
After adding a label to a form, by default, it
receives a fixed size. If you type its caption and press Enter, the text
you provided would be confined to the allocated dimensions of the control.
If the text is too long, part of it may disappear. You can then resize the
label to provide more area. Another solution is to automatically resize
the label to accommodate the length of the string you typed. This is
aspects is controlled by the Boolean AutoSize property. Its default
value is False. If you set this property to True, at design time, a
rectangular border appears around it. If you type a string in the Text
field and press Enter, the control would be resized to show the whole
string but using only the necessary space.
If you programmatically create a label, it assumes a
default size. If you assign it a string that is too long for that default
size, part of the string may appear on a subsequent line. If you want the
whole string to appear on the same line, you can set the AutoSize
to true. Here is an example:
public ref class CExercise : public Form
{
private:
Label ^ lblMessage;
public:
CExercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
void InitializeComponent()
{
lblMessage = gcnew Label;
lblMessage->Location = Point(20, 20);
lblMessage->Text = DateTime::Now.ToString();
lblMessage->AutoSize = true;
Controls->Add(lblMessage);
}
};
|
 Practical
Learning: Using AutoSize Practical
Learning: Using AutoSize
|
|
- Click an unoccupied area of the form and press Ctrl+A to select
all three labels
- In the Properties window, double-click AutoSize to set the value
to False
After typing the caption of a label whose AutoSize
property is set to False, you can resize its allocated space to your
liking. This is because a string occupies a rectangular area. Here is an
example:
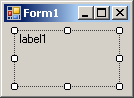
By default, the caption of a
label is positioned starting on the middle-left side of its allocated
rectangle. Alternatively, you can position it to one of the nine available
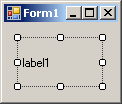
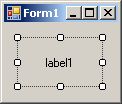
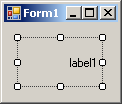
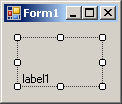
positions. The position of the caption of a label is controlled by the
TextAlign property which is based on the ContentAlignment
enumerator:
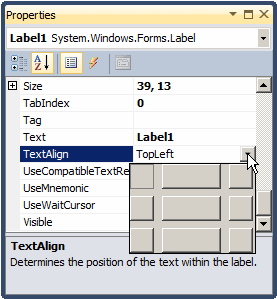
It can have the following values:
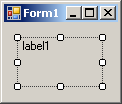
| TopLeft |
TopCenter |
TopRight |
 |
 |
 |
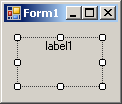
| MiddleLeft |
MiddleCenter |
MiddleRight |
 |
 |
 |
| BottomLeft |
BottomCenter |
BottomRight |
 |
 |
 |