Introduction to Built-In Collection Classes
Introduction to Built-In Collection Classes
Introduction to List Classes
Overview
To support the creation of any kind of list, the .NET Framework provides the ArrayList and the generic List<> classes.
The ArrayList class is defined in the System.Collections namespace while the generic List<> class is part of the System.Collections.Generic namespace.
The ArrayList class implements the IList, the ICollection, and the IEnumerable interfaces. The generic List<> class implements the generic IList<>, the generic ICollection<>, the generic IEnumerable<>, the IList, the ICollection, and the IEnumerable interfaces.
The ArrayList class starts as follows:
public class ArrayList : IList, ICollection, IEnumerable, ICloneable
The generic List<> class starts as follows:
public class List<T> : IList<T>, ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IList, ICollection, IEnumerable
You can use either the ArrayList or the generic List<> class to create and manage values for a list. Here is an example of declaring an ArrayList variable:
A Variable for a List
The primary way to use a list is to declare a variable for it. For the ArrayList class, you can just declare a variable like any other. Here are various examples of declaring ArrayList variables:
using System.Collections; namespace Numerotation { public partial class Exercise : Form { public Exercise() { InitializeComponent(); } private void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Classic variable declaration ArrayList alNames = new ArrayList(); // Declaring the variable by name ArrayList alNumbers = new(); // Declaring the variable using the var keyword var alValues = new ArrayList(); // Declaring the variable using the dynamic keyword dynamic alDynamics = new ArrayList(); } } }
You can also declare a variable for the List<> class. Because List<> is a generic class, when using it, such as when declaring a variable for it, you must specify its parameter type. Here are examples of declaring List<> variables:
namespace Numerotation
{
public partial class Exercise : Form
{
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Classic variable declaration
List<string> alNames = new List<string>();
// Declaring the variable by name
List<double> alNumbers = new();
// Declaring the variable using the var keyword
var alValues = new List<decimal>();
// Declaring the variable using the dynamic keyword
dynamic alDynamics = new List<char>();
}
}
}
Both classes can deal with various types of values. Again, you must indicate the parameter type of a List<> variable. Therefore, if you are creating a list of objects using a List<> variable, specif the class of those objects as the parameter type.
Primary Characteristics of a List
The Capacity of a List
After declaring an ArrayList or a List<> variable, it is empty. As objects are added to it, the list grows. The list can grow tremendously as you wish. The number of items of the list is managed through the memory it occupies and this memory grows as needed. The number of items that the memory allocated is currently using is represented by a property named Capacity. Here is an example of accessing the ArrayList.Capacity property:
public class Exercise : Form
{
ArrayList lstNames;
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
lstNames = new ArrayList();
Text = "List Capacity: " + lstNames.Capacity.ToString();
}
}
This would produce:

The capacity of a list will usually be the least of your concerns. If for some reason, you want to intervene and control the number of items that your list can contain, you can manipulate the Capacity property. For example, you can assign it a constant to set the maximum value that the list can contain. Instead of specifying the capacity after the list has been created, when declaring the list variable, you can specify its maximum capacity. To support this, both the ArrayList and the List<> classes are equipped with an additional constructor as follows:
public ArrayList(int capacity); public List<>(int capacity);
Once again, you will hardly have any reason to use the Capacity property: the compiler knows what to do with it.
The Number of Items in the List
When using a list, at any time, you should be able to know the number of items that the list contains. This information is provided by a read-only property named Count. Here is the property for the ArrayList class:
public virtual int Count { get; }
Here is the property for the List<> class:
public int Count { get; }
The Capacity and the Count properties have this in common: the value of each increases as the list grows and the same value decreases if the list shrinks. It is important to know that there are various differences between the capacity of a list and the number of items it contains. Capacity is a read/write property. This means that you can assign a value to the capacity to fix the number of items that the list can contain. You can also retrieve the value of the Capacity. The Count property is read-only because it is used by the compiler to count the current number of values of the list and this counting is performed without your intervention.
A Read-Only List
One of the reasons for creating a list is to be able to add values to it, edit its values, get a value, or delete values from it. These are the default operations. You can still limit these operations as you judge them unnecessary. For example, you may create a list and then initialize it with the values that you want the list to only have. If you don't want to have the user adding values to your list, you can create the list as read-only. To do this, you can call the ArrayList.ReadOnly() method. It is overloaded with two versions whose syntaxes are:
public static ArrayList ReadOnly(ArrayList list) public static IList ReadOnly(IList list)
Some operations cannot be performed on a read-only list. To perform such operations, you can first find out whether an ArrayList list is read-only. This is done by checking its IsReadOnly property.
Populating a List
Adding a Value or an Object to a List
The primary operation performed on a list is to create one or more values. To do this, you have various alternatives. Both the ArrayList and the List<> classes are equipped with a method named Add. The syntax of the System.Collections.ArrayList.Add() method is:
public virtual int Add(object value);
The syntax of the System.Collections.Generic.List.Add() method is:
public void Add(T value);
The argument of the method is the value or object to add to the list. If the method succeeds with the addition, it returns the position where the value was added in the list. Here are example for an ArrayList variable:
void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Text = "Employees Records";
lstNames = new ArrayList();
lstNames.Add("Christine Kingston");
lstNames.Add("Hermine Paulson");
lstNames.Add("William Harrison");
lstNames.Add("Ursula Morales");
lstNames.Add("Evan Lancos");
}
If the method fails to add the value and if you are using the ArrayList class, the compiler would throw an error. One of the errors that could result from the ArrayList's failure of this operation would be based on the fact that either a new value cannot be added to the list because the list is read-only, or the list was already full prior to adding the new value. Normally, a list can be full only if you had specified the maximum number of items it can contain using the ArrayList.Capacity property. As mentioned above, the list can be made read-only by passing its variable to the ArrayList.ReadOnly() method.
Adding a Range of Items
Instead of adding one values at a time, you can first create a list of values and add that whole list at once. To support this operation, both the ArrayList and the List<> classes are equipped with a method named AddRange.
The syntax of the ArrayList.AddRange() method is:
public virtual void AddRange(ICollection collection);
The syntax of the List<T>.AddRange() method is:
public void AddRange(IEnumerable<T> collection);
The ArrayList.AddRange() method takes as argument a list created from a class that implements the ICollection interface. Here is an example:
void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Text = "Employees";
ComboBox cbx = new ComboBox();
cbx.Items.Add("Paul Bertrand Yamaguchi");
cbx.Items.Add("Helene Mukoko");
cbx.Items.Add("John Hancock");
cbx.Items.Add("Gertrude Monay");
lstNames = new ArrayList();
lstNames.AddRange(cbx.Items);
}
The List<T>.AddRange() method takes as argument a list created from a class that implements the generic IEnumerable<T> interface.
Creating a List from a List
The default constructor of the the ArrayList class allows you to create an empty list before adding values to it. If you already have an ICollection-based list, that is, a list created from a class that implements the ICollection interface, you can initialize your ArrayList object with it. To support this, the ArrayList class is equipped with the following constructor:
public ArrayList(ICollection c);
Here is an example of using that constructor:
void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ComboBox cbx = new ComboBox();
cbx.Items.Add("Paul Bertrand Yamaguchi");
cbx.Items.Add("Helene Mukoko");
cbx.Items.Add("John Hancock");
cbx.Items.Add("Gertrude Monay");
lstNames = new ArrayList(cbx.Items);
}
Managing a List
Getting an Item from a List
Once a list is ready, you can perform different types of operations on it. Besides adding items, one of the most regular operations performed on a list consists of locating and retrieving its values. You have various options.
To give you access to each member of their list, both the ArrayList and the List<> classes are equipped with the default Item property. The Item property is an indexer. The first value of the list has an index of 0. The second has an index of 1, and so on.
To retrieve a single value based on its position, you can apply the square brackets of arrays to the variable. Here is an example:
using System.Collections;
namespace Numerotation
{
public partial class Exercise : Form
{
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var lstNames = new ArrayList();
lstNames.Add("Christine Kingston");
lstNames.Add("Hermine Paulson");
lstNames.Add("William Harrison");
lstNames.Add("Ursula Morales");
lstNames.Add("Evan Lancos");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
lbxNames.Items.Add(lstNames[i]);
}
}
}

Another issue to keep in mind is that the ArrayList[] indexer returns an Object value. Therefore, you may have to cast this value to your type of value to get it right.
Besides using the index to access a value from the list, the ArrayList and the List<> classes implement the IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() method. For this reason, you can use the foreach loop to access each member of the collection. Here is an example:
void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Text = "Employees";
lstNames = new ArrayList();
lstNames.Add("Christine Kingston");
lstNames.Add("Hermine Paulson");
lstNames.Add("William Harrison");
lstNames.Add("Ursula Morales");
lstNames.Add("Evan Lancos");
foreach (string str in lstNames)
lbxNames.Items.Add(str);
}
You can use the Item property to change a value in the list. Because the Item property is used to access an existing value from the list, the value must have been created. If you try setting the value of a non existing item, the compiler would throw an ArgumentOutOfRangeException Exception. Here is an example:
void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var lstNames = new ArrayList();
lstNames[0] = "Paul Bertrand Yamaguchi";
}
Notice that at the time the 0 item is accessed, it has not previous been created. This would produce:

A review of the Details section shows:
System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException: Index was out of range.
Must be non-negative and less than the size of the collection.
Parameter name: index
at System.Collections.ArrayList.set_Item(Int32 index, Object value)
at Exercise.Exercise_Load(Object sender, EventArgs e)
in E:\Programs\VCSharp\Exercise1\Exercise1\Exercise.cs:line 31
This means that you can use the Item property only to change the value of a previous created item.
Checking the Existence of an Item
Instead of the square brackets that allow you to retrieve a value based on its position, you can look for a value based on its complete definition. You have various options. You can first "build" an item and ask the compiler to check whether any item in the list matches your definition. To perform this search, depending on your class, you can call either the ArrayList.Contains() or the List<>.Contains() method. The syntax of the System.Collections.ArrayList.Contains() method is:
public virtual bool Contains(object value);
The syntax of the System.Collections.Generic.List<>.Contains() method is:
public bool Contains(T value);
The value to look for is passed as argument to the method. The compiler would look for exactly that value, using its definition, in the list. If any detail of the argument fails to match any value of the list, the method would return false. If all characteristics of the argument correspond to a value of the list, the method returns true. Here is an example:
using System.Collections;
namespace Numerotation
{
public partial class Exercise : Form
{
ArrayList lstNames;
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
lstNames = new ArrayList();
lstNames.Add("Christine Kingston");
lstNames.Add("Hermine Paulson");
lstNames.Add("William Harrison");
lstNames.Add("Ursula Morales");
lstNames.Add("Evan Lancos");
foreach (string str in lstNames)
lbxNames.Items.Add(str);
}
private void btnResult_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string strFind = txtFind.Text;
if (lstNames.Contains(strFind) == true)
txtResult.Text = "Found";
else
txtResult.Text = "Not Found";
}
}
}
 |
 |
Searching for an Item
Another option to look for an item in a list consists of calling the BinarySearch() method of either the ArrayList or the List<> class. It is overloaded in three versions and one of them uses the following syntax:
public virtual int BinarySearch(object value); public int BinarySearch(T value);
The value to look for is passed argument to the method. Here is an example:
private void btnResult_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string strFind = txtFind.Text;
if( lstNames.BinarySearch(strFind) > 0 )
txtResult.Text = "Found";
else
txtResult.Text = "Not Found";
}
Removing Items from a List
Deleting an Item by Value
As opposed to adding a value to a list, you may want to remove one. To perform this operation, you have various options. You can ask the compiler to look for an item in the list and if, or once, the compiler finds it, it would delete the value. To let you perform this operation, both the ArrayList and the List<> classes are equipped with a method named Remove. The syntax for the ArrayList is:
public virtual void Remove(object value);
The syntax for the List<> is:
public bool Remove(T value);
This method accepts as argument the value that you want to delete from the list. To perform this operation, the list must not be read-only.
Deleting an Item by Position
The Remove() method allows you to specify the exact value you want to delete from a list. Another option you have consists of deleting a value based on its position. To support this operation, both the ArrayList and the List<> classes are equipped with a method named RemoveAt. The syntax for the ArrayList is:
public virtual void RemoveAt(int index);
With this method, the position of the item is passed as argument. Here is an example:
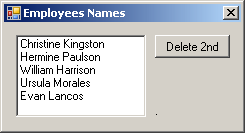
private void btnSecond_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
lstNames.RemoveAt(1);
lbxNames.Items.Clear();
foreach (string str in lstNames)
lbxNames.Items.Add(str);
}
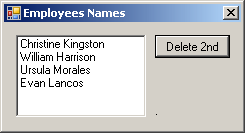
If the position is not valid because either it is lower or higher than the current Count, the compiler would throw an ArgumentOutOfRangeException exception.
The syntax for the RemoveAt() method of the List<> class is:
public void RemoveAt(int index);
Clearing a List
To let you remove all items from a list, both the ArrayList and the List<> classes are equipped with a method named Clear. The syntax for the ArrayList class is:
public virtual void Clear()
This method deletes all items from its list. Here is an example of calling this method:
using System.Collections;
namespace Numerotation
{
public partial class Exercise : Form
{
ArrayList lstNames;
public Exercise()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Show()
{
lbxNames.Items.Clear();
foreach (string str in lstNames)
lbxNames.Items.Add(str);
}
private void Exercise_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
lstNames = new ArrayList();
lstNames.Add("Christine Kingston");
lstNames.Add("Hermine Paulson");
lstNames.Add("William Harrison");
lstNames.Add("Ursula Morales");
lstNames.Add("Evan Lancos");
Show();
}
private void btnShow_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
lstNames.Clear();
Show();
}
}
}
![]() Practical Learning: Introducing .NET Collection Classes
Practical Learning: Introducing .NET Collection Classes
| Control | Text | Name | Other Properties | |
| Label | &Make: | |||
| TextBox | txtMake | Modifiers: Public | ||
| Button | &OK | btnOK | DialogResult: OK | |
| Button | &Cancel | btnCancel | DialogResult: Cancel | |
Form Characteristics
| Form Property | Value |
| FormBorderStyle | FixedDialog |
| Text | Make |
| StartPosition | CenterScreen |
| AcceptButton | btnOK |
| CancelButton | btnCancel |
| MaximizeBox | False |
| MinimizeBox | False |
| ShowInTaskbar | False |
| Control | Text | Name | Other Properties | |
| Label | &Model: | |||
| TextBox | txtModel | Modifiers: Public | ||
| Button | &OK | btnOK | DialogResult: OK | |
| Button | &Cancel | btnCancel | DialogResult: Cancel | |
Form Characteristics
| Form Property | Value |
| FormBorderStyle | FixedDialog |
| Text | Category Editor |
| StartPosition | CenterScreen |
| AcceptButton | btnOK |
| CancelButton | btnCancel |
| MaximizeBox | False |
| MinimizeBox | False |
| ShowInTaskbar | False |

| Control | Text | Name | Other Properties | |
| Label | C&ategory: | |||
| TextBox | txtCategory | Modifiers: Public | ||
| Button | &OK | btnOK | DialogResult: OK | |
| Button | &Cancel | btnCancel | DialogResult: Cancel | |
Form Characteristics
| Form Property | Value |
| FormBorderStyle | FixedDialog |
| Text | Category |
| StartPosition | CenterScreen |
| AcceptButton | btnOK |
| CancelButton | btnCancel |
| MaximizeBox | False |
| MinimizeBox | False |
| ShowInTaskbar | False |
| Control | (Name) | Text | Other Properties | |
| Label | &Part #: | |||
| Text Box | txtPartNumber | |||
| Button | btnSelectPicture | &Select Picture... | ||
| Label | lblPictureFile | . | ||
| Label | &Year: | |||
| Combo Box | cbxYears | |||
| Picture Box | pbxPartImage | BorderStyle: FixedSingle: SizeMode: AutoSize |
||
| Label | &Make: | |||
| Combo Box | cbxMakes | |||
| Button | btnNewMake | New M&ke... | ||
| Label | M&odel: | |||
| Combo Box | cbxModels | |||
| Button | New Mo&del | |||
| Label | Ca&tegory: | |||
| Combo Box | cbxCategories | |||
| Button | btnNewCategory | New Cat&egory... | ||
| Label | Part Na&me: | |||
| Text Box | txtPartName | ScrollBars: Vertical Multiline: True |
||
| Label | &Unit Price | |||
| Text Box | txtUnitPrice | |||
| Label | _________________ | |||
| Button | btnSaveAutoPart | Sa&ve Auto-Part | ||
| Button | btnClose | &Close | ||
| OpenFileDialog | ||||
using System.Xml.Serialization;
namespace CollegeParkAutoParts
{
public partial class StoreItemNew : Form
{
/* This property is used to hold the list of auto-parts of our application.
* (We didn't have to use a global variable. We could have used local variables.) */
List<AutoPart> AutoParts { get; set; } = new List<AutoPart>();
public StoreItemNew()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/* This function is used to reset the form.
* It can be called when necessary. */
private void InitializeAutoParts()
{
// This file is the repository of our database
string strFileName = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\AutoParts.xml";
// We will use XML serialization to manage the records of our database
XmlSerializer xsAutoParts = new XmlSerializer(typeof(List<AutoPart>));
/* Show the years in the top combo box.
* We will consider only the cars made in the last 20 years. */
for (int year = DateTime.Today.Year + 1; year >= DateTime.Today.Year - 20; year--)
cbxYears.Items.Add(year);
// Check whether the file that holds the store inventory was created already
if (File.Exists(strFileName))
{
Random rndNumber = new();
cbxMakes.Items.Clear();
cbxModels.Items.Clear();
cbxCategories.Items.Clear();
txtPartName.Text = string.Empty;
txtUnitPrice.Text = string.Empty;
txtPartNumber.Text = rndNumber.Next(100000, 999999).ToString();
// If the inventory file exists, open it
using (FileStream fsAutoParts = new FileStream(strFileName,
FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read,
FileShare.Read))
{
// Retrieve the list of items from file
AutoParts = (List<AutoPart>)xsAutoParts.Deserialize(fsAutoParts)!;
// Display the cars manufacturers in the combo box
for (int i = 0; i < AutoParts.Count; i++)
{
// Make sure the list box doesn't yet have the category being added
if (!cbxMakes.Items.Contains(AutoParts[i].Make))
cbxMakes.Items.Add(AutoParts[i].Make);
}
// Display the categories in the box
for (int i = 0; i < AutoParts.Count; i++)
{
// Make sure the list box doesn't yet have the category being added
if (!cbxCategories.Items.Contains(AutoParts[i].Category))
cbxCategories.Items.Add(AutoParts[i].Category);
}
}
}
lblPictureFile.Text = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png";
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(@"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png");
Width = pbxPartImage.Right + 40;
Height = pbxPartImage.Bottom + 75;
}
private void StoreItemNew_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
InitializeAutoParts();
}
private void btnSelectPicture_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if(ofdPictureFile.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
lblPictureFile.Text = ofdPictureFile.FileName;
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(ofdPictureFile.FileName);
}
else
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(@"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png");
Width = pbxPartImage.Right + 40;
Height = pbxPartImage.Bottom + 75;
}
private void cbxMakes_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
cbxModels.Text = "";
cbxModels.Items.Clear();
foreach (AutoPart part in AutoParts)
if (part.Make == cbxMakes.Text)
if (!cbxModels.Items.Contains(part.Model))
cbxModels.Items.Add(part.Model);
}
private void btnNewMake_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Make editor = new Make();
if (editor.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
if (editor.txtMake.Text.Length > 0)
{
string strMake = editor.txtMake.Text;
// Make sure the category is not yet in the list
if (cbxMakes.Items.Contains(strMake))
MessageBox.Show(strMake + " is already in the list.",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
else
{
// Since this is a new category, add it to the combo box
cbxMakes.Items.Add(strMake);
}
cbxMakes.Text = strMake;
}
}
}
private void btnNewModel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Model editor = new();
if (editor.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
if (editor.txtModel.Text.Length > 0)
{
string strModel = editor.txtModel.Text;
// Make sure the category is not yet in the list
if (cbxModels.Items.Contains(strModel))
MessageBox.Show(strModel + " is already in the list.",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
else
{
// Since this is a new category, add it to the combo box
cbxModels.Items.Add(strModel);
}
cbxModels.Text = strModel;
}
}
}
private void btnNewCategory_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var editor = new Category();
if (editor.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
if (editor.txtCategory.Text.Length > 0)
{
string strCategory = editor.txtCategory.Text;
// Make sure the category is not yet in the list
if (cbxCategories.Items.Contains(strCategory))
MessageBox.Show(strCategory + " is already in the list.",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
else
{
// Since this is a new category, add it to the combo box
cbxCategories.Items.Add(strCategory);
}
cbxCategories.Text = strCategory;
}
}
}
private void btnSaveAutoPart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Make sure the user had selected a year
if( string.IsNullOrEmpty(cbxYears.Text) )
{
MessageBox.Show("You must specify the year.",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
// Make sure the user had selected a make
if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(cbxMakes.Text) )
{
MessageBox.Show("You must specify the car name.",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
// Make sure the user had selected a model
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(cbxModels.Text) )
{
MessageBox.Show("You must specify the model of the car.",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
// Make sure the user had entered a name/description
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtPartName.Text) )
{
MessageBox.Show("You must enter the name (or a " +
"short description) for the part.",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
txtPartName.Focus();
return;
}
// Make sure the user had typed a price for the item
if( string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtUnitPrice.Text) )
{
MessageBox.Show("You must enter the price of the item.",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
txtUnitPrice.Focus();
return;
}
string strFileName = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\AutoParts.xml";
XmlSerializer xsAutoParts = new XmlSerializer(typeof(List<AutoPart>));
if (File.Exists(strFileName))
{
// If the inventory file exists, open it
using (FileStream fsAutoParts = new(strFileName, FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read))
{
// Retrieve the list of items from file
AutoParts = (List<AutoPart>)xsAutoParts.Deserialize(fsAutoParts)!;
}
}
AutoPart part = new AutoPart();
part.PartNumber = long.Parse(txtPartNumber.Text);
part.Year = int.Parse(cbxYears.Text);
part.Make = cbxMakes.Text;
part.Model = cbxModels.Text;
part.Category = cbxCategories.Text;
part.PartName = txtPartName.Text;
part.UnitPrice = double.Parse(txtUnitPrice.Text);
part.PictureFile = lblPictureFile.Text;
// Call the Add method of our collection class to add the part
AutoParts.Add(part);
TextWriter twAutoParts = new StreamWriter(strFileName);
xsAutoParts.Serialize(twAutoParts, AutoParts);
twAutoParts.Close();
InitializeAutoParts();
}
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
}
}| Control | (Name) | Text | |
| Button | btnFind | &Find | |
| Button | btnUpdateAutoPart | Up&date Auto-Part | |
using System.Xml.Serialization;
namespace CollegeParkAutoParts
{
public partial class StoreItemEditor : Form
{
List<AutoPart> AutoParts { get; set; } = new List<AutoPart>();
public StoreItemEditor()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void InitializeAutoPart()
{
txtMake.Text = string.Empty;
txtModel.Text = string.Empty;
txtCategory.Text = string.Empty;
txtPartName.Text = string.Empty;
txtUnitPrice.Text = string.Empty;
txtPartNumber.Text = string.Empty ;
lblPictureFile.Text = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png";
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(@"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png");
Width = pbxPartImage.Right + 40;
Height = pbxPartImage.Bottom + 75;
}
private void StoreItemEditor_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
InitializeAutoPart();
}
private void btnFind_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if( string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtPartNumber.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("You must enter a (valid) number for an auto-part.",
"College Park Auto-Parts", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
bool foundAutoPart = false;
string strFileName = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\AutoParts.xml";
XmlSerializer xsAutoParts = new XmlSerializer(typeof(List<AutoPart>));
if (File.Exists(strFileName))
{
using (FileStream fsAutoParts = new(strFileName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read))
{
AutoParts = (List<AutoPart>)xsAutoParts.Deserialize(fsAutoParts)!;
for (int i = 0; i < AutoParts.Count; i++)
{
if (AutoParts[i].PartNumber.Equals(long.Parse(txtPartNumber.Text)))
{
foundAutoPart = true;
txtMake.Text = AutoParts[i].Make;
txtModel.Text = AutoParts[i].Model;
txtCategory.Text = AutoParts[i].Category;
txtPartName.Text = AutoParts[i].PartName;
cbxYears.Text = AutoParts[i].Year.ToString();
txtUnitPrice.Text = AutoParts[i].UnitPrice.ToString("F");
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(AutoParts[i].PictureFile!);
lblPictureFile.Text = AutoParts[i].PictureFile;
break;
}
}
}
}
if(foundAutoPart == false)
{
MessageBox.Show("There is no auto-part with that number in our records.",
"College Park Auto-Parts", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
lblPictureFile.Text = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png";
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(@"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png");
}
Width = pbxPartImage.Right + 40;
Height = pbxPartImage.Bottom + 75;
}
private void btnSelectPicture_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (ofdPictureFile.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
lblPictureFile.Text = ofdPictureFile.FileName;
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(ofdPictureFile.FileName);
}
else
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(@"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png");
Width = pbxPartImage.Right + 40;
Height = pbxPartImage.Bottom + 75;
}
private void btnUpdateAutoPart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string strFileName = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\AutoParts.xml";
XmlSerializer xsAutoParts = new XmlSerializer(typeof(List<AutoPart>));
if (File.Exists(strFileName))
{
using (FileStream fsAutoParts = new FileStream(strFileName,
FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read,
FileShare.Read))
{
AutoParts = (List<AutoPart>)xsAutoParts.Deserialize(fsAutoParts)!;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < AutoParts.Count; i++)
{
if (AutoParts[i].PartNumber.Equals(long.Parse(txtPartNumber.Text)))
{
AutoParts[i].Year = Convert.ToInt32(cbxYears.Text);
AutoParts[i].Make = txtMake.Text;
AutoParts[i].Model = txtModel.Text;
AutoParts[i].Category = txtCategory.Text;
AutoParts[i].PartName = txtPartName.Text;
AutoParts[i].UnitPrice = Convert.ToDouble(txtUnitPrice.Text);
AutoParts[i].PictureFile = lblPictureFile.Text;
TextWriter twAutoParts = new StreamWriter(strFileName);
xsAutoParts.Serialize(twAutoParts, AutoParts);
twAutoParts.Close();
break;
}
}
InitializeAutoPart();
}
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
}
}| Control | (Name) | Text | |
| Text Box | txtYear | ||
| Label | btnDeleteAutoPart | Delete Auto-Part | |
using System.Xml.Serialization;
namespace CollegeParkAutoParts
{
public partial class StoreItemDelete : Form
{
List<AutoPart> AutoParts { get; set; } = new List<AutoPart>();
public StoreItemDelete()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void InitializeAutoPart()
{
txtMake.Text = string.Empty;
txtModel.Text = string.Empty;
txtCategory.Text = string.Empty;
txtPartName.Text = string.Empty;
txtUnitPrice.Text = string.Empty;
txtPartNumber.Text = string.Empty;
lblPictureFile.Text = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png";
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(@"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png");
Width = pbxPartImage.Right + 40;
Height = pbxPartImage.Bottom + 75;
}
private void StoreItemDelete_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
InitializeAutoPart();
}
private void btnFind_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtPartNumber.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("You must enter a (valid) number for an auto-part.",
"College Park Auto-Parts", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
bool foundAutoPart = false;
XmlSerializer xsAutoParts = new(typeof(List<AutoPart>));
string strFileName = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\AutoParts.xml";
if (File.Exists(strFileName))
{
using (FileStream fsAutoParts = new(strFileName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read))
{
AutoParts = (List<AutoPart>)xsAutoParts.Deserialize(fsAutoParts)!;
for (int i = 0; i < AutoParts.Count; i++)
{
if (AutoParts[i].PartNumber.Equals(long.Parse(txtPartNumber.Text)))
{
foundAutoPart = true;
txtMake.Text = AutoParts[i].Make;
txtModel.Text = AutoParts[i].Model;
txtCategory.Text = AutoParts[i].Category;
txtPartName.Text = AutoParts[i].PartName;
txtYear.Text = AutoParts[i].Year.ToString();
txtUnitPrice.Text = AutoParts[i].UnitPrice.ToString("F");
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(AutoParts[i].PictureFile!);
lblPictureFile.Text = AutoParts[i].PictureFile;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (foundAutoPart == false)
{
MessageBox.Show("There is no auto-part with that number in our records.",
"College Park Auto-Parts", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
lblPictureFile.Text = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png";
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(@"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png");
}
Width = pbxPartImage.Right + 40;
Height = pbxPartImage.Bottom + 75;
}
private void btnDeleteAutoPart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
XmlSerializer xsAutoParts = new(typeof(List<AutoPart>));
string strFileName = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\AutoParts.xml";
if (File.Exists(strFileName))
{
using FileStream fsAutoParts = new(strFileName, FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read);
AutoParts = (List<AutoPart>)xsAutoParts.Deserialize(fsAutoParts)!;
}
for (int i = 0; i < AutoParts.Count; i++)
{
if (AutoParts[i].PartNumber.Equals(long.Parse(txtPartNumber.Text)))
{
AutoParts.Remove(AutoParts[i]);
TextWriter twAutoParts = new StreamWriter(strFileName);
xsAutoParts.Serialize(twAutoParts, AutoParts);
twAutoParts.Close();
break;
}
}
InitializeAutoPart();
}
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
}
}
| Control | (Name) | Text | Other Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Label | College Park Auto-Parts | Font: Times New Roman, 24pt, style=Bold ForeColor: Blue |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PictureBox | BackColor: Black Size -> Height: 5 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GroupBox | Part Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TreeView | tvwAutoParts | ImageList: AutoPartsImages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GroupBox | Available Parts | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ListView | lvwAvailableParts | View: Details FullRowSelect: True GridLines: True |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Columns |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PictureBox | pbxPartImage | BorderStyle: FixedSingle SizeMode: AutoSize |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GroupBox | Selected Parts | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Label | Part # | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Label | Part Name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Label | Unit Price | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Label | Qty | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Label | Sub-Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Text Box | txtPartNumber | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Text Box | txtPartName | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Text Box | txtUnitPrice | TextAlign: Right | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Text Box | txtQuantity | TextAlign: Right | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Text Box | txtSubTotal | TextAlign: Right | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Button | btnAdd | Add/Select | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ListView | lvwSelectedParts | View: Details FullRowSelect: True GridLines: True |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Columns |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GroupBox | Order Summary | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Button | btnNewAutoPart | New Auto Part... | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Button | btnUpdateAutoPart | Update Auto Part... | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Label | Selected Parts Total: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Text Box | txtSelectedPartsTotal | TextAlign: Right | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Label | Tax Rate: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Text Box | txtTaxRate | TextAlign: Right | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Label | Tax Amount: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Text Box | txtTaxAmount | TextAlign: Right | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Label | Order Total: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Text Box | txtOrderTotal | TextAlign: Right | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Button | btnDeleteAutoPart | Delete Auto Part... | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Button | btnClose | Close | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
using System.Xml.Serialization;
namespace CollegeParkAutoParts
{
public partial class StoreInvetory : Form
{
/* We will need a list of auto-parts.
* For demonstration purpose, we are creating the list as a property
* (but a global list is not necessary; we could have used local list variables).*/
public List<AutoPart> AutoParts { get; set; } = new List<AutoPart>();
public StoreInvetory()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// This function is used to reset the form
void InitializeAutoParts()
{
// When the form must be reset, removes all nodes from the tree view
tvwAutoParts.Nodes.Clear();
// Create the root node of the tree view
TreeNode nodRoot = tvwAutoParts.Nodes.Add("College Park Auto-Parts",
"College Park Auto-Parts", 0, 1);
/* Add the cars years to the tree view.
* Our application will deal only with the cars in the last 21 years. */
for (int years = DateTime.Today.Year + 1; years >= DateTime.Today.Year - 20; years--)
nodRoot.Nodes.Add(years.ToString(), years.ToString(), 2, 3);
// Select the root node
tvwAutoParts.SelectedNode = nodRoot;
// Expand the root node
tvwAutoParts.ExpandAll();
// AutoParts = new List<AutoPart>();
// This is the file that holds the list of auto parts
string strFileName = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\AutoParts.xml";
XmlSerializer xsAutoParts = new(typeof(List<AutoPart>));
if (File.Exists(strFileName))
{
// If the inventory file exists, open it
using (FileStream fsAutoParts = new FileStream(strFileName,
FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read,
FileShare.Read))
{
// Retrieve the list of items from file
AutoParts = (List<AutoPart>)xsAutoParts.Deserialize(fsAutoParts)!;
// Show the makes nodes
foreach (TreeNode nodYear in nodRoot.Nodes)
{
List<string> lstMakes = new List<string>();
foreach (AutoPart part in AutoParts)
{
if (nodYear.Text == part.Year.ToString())
{
if (!lstMakes.Contains(part.Make!))
lstMakes.Add(part.Make!);
}
}
foreach (string strMake in lstMakes)
nodYear.Nodes.Add(strMake, strMake, 4, 5);
}
// Showing the models nodes
foreach (TreeNode nodYear in nodRoot.Nodes)
{
foreach (TreeNode nodMake in nodYear.Nodes)
{
List<string> lstModels = new List<string>();
foreach (AutoPart part in AutoParts)
{
if( (nodYear.Text == part.Year.ToString() ) &
(nodMake.Text == part.Make))
{
if (!lstModels.Contains(part.Model!))
lstModels.Add(part.Model!);
}
}
foreach (string strModel in lstModels)
nodMake.Nodes.Add(strModel, strModel, 6, 7);
}
}
// Showing the categories nodes
foreach (TreeNode nodYear in nodRoot.Nodes)
{
foreach (TreeNode nodMake in nodYear.Nodes)
{
foreach (TreeNode nodModel in nodMake.Nodes)
{
List<string> lstCategories = new List<string>();
foreach (AutoPart part in AutoParts)
{
if ((nodYear.Text == part.Year.ToString()) &
(nodMake.Text == part.Make) &
(nodModel.Text == part.Model))
{
if (!lstCategories.Contains(part.Category!))
lstCategories.Add(part.Category!);
}
}
foreach (string strCategory in lstCategories)
nodModel.Nodes.Add(strCategory, strCategory, 8, 9);
}
}
}
}
}
lvwSelectedParts.Items.Clear();
lvwAvailableParts.Items.Clear();
txtTaxRate.Text = string.Empty;
txtPartName.Text = string.Empty;
txtQuantity.Text = string.Empty;
txtSubTotal.Text = string.Empty;
txtUnitPrice.Text = string.Empty;
txtTaxAmount.Text = string.Empty;
txtOrderTotal.Text = string.Empty;
txtPartNumber.Text = string.Empty;
txtSelectedPartsTotal.Text = string.Empty;
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(@"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png");
}
private void StoreInvetory_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
InitializeAutoParts();
}
private void btnNewAutoPart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StoreItemNew sin = new StoreItemNew();
sin.ShowDialog();
InitializeAutoParts();
}
private void lvwAvailableParts_ItemSelectionChanged(object sender, ListViewItemSelectionChangedEventArgs e)
{
bool pictureFound = false;
string strFileName = @"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\AutoParts.xml";
XmlSerializer xsAutoParts = new XmlSerializer(typeof(List<AutoPart>));
if (File.Exists(strFileName))
{
// If the inventory file exists, open it
using (FileStream fsAutoParts = new FileStream(strFileName,
FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read,
FileShare.Read))
{
// Retrieve the list of items from file
AutoParts = (List<AutoPart>)xsAutoParts.Deserialize(fsAutoParts)!;
foreach (AutoPart part in AutoParts)
{
if( part.PartNumber == long.Parse(e.Item.SubItems[0].Text))
{
pictureFound = true;
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(part.PictureFile!);
break;
}
}
}
}
if(pictureFound == false)
{
pbxPartImage.Image = Image.FromFile(@"C:\College Park Auto-Parts\Generic.png");
}
Width = pbxPartImage.Right + 40;
Height = pbxPartImage.Bottom + 75;
}
private void lvwAvailableParts_DoubleClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ListViewItem lviAutoPart = lvwAvailableParts.SelectedItems[0];
if ((lvwAvailableParts.SelectedItems.Count == 0) ||
(lvwAvailableParts.SelectedItems.Count > 1))
return;
txtPartNumber.Text = lviAutoPart.Text;
txtPartName.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems[1].Text;
txtUnitPrice.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems[2].Text;
txtQuantity.Text = "1";
txtSubTotal.Text = lviAutoPart.SubItems[2].Text;
txtQuantity.Focus();
}
private void txtUnitPrice_Leave(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
double subTotal;
double unitPrice = 0D;
double quantity = 0.00d;
try
{
unitPrice = double.Parse(txtUnitPrice.Text);
}
catch (FormatException)
{
MessageBox.Show("Invalid Unit Price!",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
try
{
quantity = int.Parse(txtQuantity.Text);
}
catch (FormatException)
{
MessageBox.Show("Invalid Quandtity!",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
subTotal = unitPrice * quantity;
txtSubTotal.Text = subTotal.ToString("F");
}
internal void CalculateOrder()
{
// Calculate the current total order and update the order
double partsTotal = 0.00D;
double taxRate = 0.00D;
double taxAmount, orderTotal;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtTaxRate.Text))
txtTaxRate.Text = "7.25";
foreach (ListViewItem lvi in lvwSelectedParts.Items)
{
ListViewItem.ListViewSubItem SubItem = lvi.SubItems[4];
partsTotal += double.Parse(SubItem.Text);
}
try
{
taxRate = double.Parse(txtTaxRate.Text) / 100;
}
catch (FormatException)
{
MessageBox.Show("Invalid Tax Rate",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
taxAmount = partsTotal * taxRate;
orderTotal = partsTotal + taxAmount;
txtSelectedPartsTotal.Text = partsTotal.ToString("F");
txtTaxAmount.Text = taxAmount.ToString("F");
txtOrderTotal.Text = orderTotal.ToString("F");
}
private void txtPartNumber_Leave(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool found = false;
// After the user had entered a part number,
// check the whole list of parts
foreach (AutoPart part in AutoParts)
{
// If you find a part that holds the number the user had entered
if (part.PartNumber == long.Parse(txtPartNumber.Text))
{
// Show the corresponding part name and unit price
txtPartName.Text = part.PartName;
txtUnitPrice.Text = part.UnitPrice.ToString("F");
if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtQuantity.Text))
txtQuantity.Text = "1";
txtSubTotal.Text = part.UnitPrice.ToString("F");
// Give focus to the quantity in case the user was to increase it
txtQuantity.Focus();
// And update the flag that specifies that the part has been found
found = true;
break;
}
// If the part number was not found, check the next
} // If no part has that number, the found flag is marked as false
// If no part with that number was found...
if (found == false)
{
// Since no part with that number was found,
// reset the text boxes
txtPartName.Text = "";
txtUnitPrice.Text = "0.00";
txtQuantity.Text = "0";
txtSubTotal.Text = "0.00";
// Let the user know that the part number that
// was entered is not in the list
MessageBox.Show("There is no part with that number.",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
private void btnAdd_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtPartNumber.Text) )
{
MessageBox.Show("There is no part to be added to the order.",
"College Park Auto-Parts",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
foreach (AutoPart part in AutoParts)
{
if (part.PartNumber == long.Parse(txtPartNumber.Text))
{
ListViewItem lviSelectedPart = new ListViewItem(part.PartNumber.ToString());
lviSelectedPart.SubItems.Add(part.PartName);
lviSelectedPart.SubItems.Add(part.UnitPrice.ToString());
lviSelectedPart.SubItems.Add(txtQuantity.Text);
lviSelectedPart.SubItems.Add(txtSubTotal.Text);
lvwSelectedParts.Items.Add(lviSelectedPart);
}
}
CalculateOrder();
}
private void lvwSelectedParts_DoubleClick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ListViewItem lviSelectedPart = lvwSelectedParts.SelectedItems[0];
if ((lvwSelectedParts.SelectedItems.Count == 0) ||
(lvwSelectedParts.SelectedItems.Count > 1))
return;
txtPartNumber.Text = lviSelectedPart.Text;
txtPartName.Text = lviSelectedPart.SubItems[1].Text;
txtUnitPrice.Text = lviSelectedPart.SubItems[2].Text;
txtQuantity.Text = lviSelectedPart.SubItems[3].Text;
txtSubTotal.Text = lviSelectedPart.SubItems[4].Text;
lvwSelectedParts.Items.Remove(lviSelectedPart);
CalculateOrder();
}
private void tvwAutoParts_NodeMouseClick(object sender, TreeNodeMouseClickEventArgs e)
{
TreeNode nodClicked = e.Node;
if (nodClicked.Level == 4)
lvwAvailableParts.Items.Clear();
try
{
foreach (AutoPart part in AutoParts)
{
if ((part.Category == nodClicked.Text) &&
(part.Model == nodClicked.Parent.Text) &&
(part.Make == nodClicked.Parent.Parent.Text) &&
(part.Year.ToString() == nodClicked.Parent.Parent.Parent.Text))
{
ListViewItem lviAutoPart = new ListViewItem(part.PartNumber.ToString());
lviAutoPart.SubItems.Add(part.PartName);
lviAutoPart.SubItems.Add(part.UnitPrice.ToString("F"));
lvwAvailableParts.Items.Add(lviAutoPart);
}
}
}
catch (NullReferenceException)
{
}
}
private void btnUpdateAutoPart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StoreItemEditor sie = new StoreItemEditor();
sie.ShowDialog();
InitializeAutoParts();
}
private void btnDeleteAutoPart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StoreItemDelete sid = new StoreItemDelete();
sid.ShowDialog();
InitializeAutoParts();
}
private void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
}
}| Part # | Year | Make | Model | Category | Item Name | Unit Price | Picture File |
| 393795 | 2015 | Buick | Regal | Alternators & Generators | DB Electrical Alternator | 218.74 | 928037 |
| 928374 | 2018 | Chevrolet | Express 3500 | Shocks, Struts & Suspension | Suspension Kit (Front; with 3 Groove Pitman Arm) | 142.44 | 304031 |
| 730283 | 2020 | Jeep | Wrangler Unlimited Sahara | Oil Filters | Hydraulic Cylinder Timing Belt Tensioner | 14.15 | 730283 |
| 290741 | 2015 | Ford | F-150 XL 3.5L V6 Flex Regular Cab 2 Full-Size Doors | Shocks, Struts & Suspension | Front Strut and Coil Spring Assembly - Set of 2 | 245.68 | 290741 |
| 740248 | 2013 | Chevrolet | Equinox | Bearings & Seals | Wheel hub bearing Assembly | 99.95 | 740248 |
| 283759 | 2012 | Dodge | Charger 3.6L | Starters | DB Electrical SND0787 Starter | 212.58 | 283759 |
| 799428 | 2012 | Cadillac | XTS | Bearings & Seals | Front/Rear Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly 5 Lugs w/ABS | 79.97 | 799428 |
| 648203 | 2018 | Honda | CRV | Alternator | Alternator | 202.47 | 593804 |
| 502853 | 2014 | GMC | Terrain | Bearings & Seals | Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly | 48.85 | 927944 |
| 520384 | 2020 | Jeep | Wrangler Unlimited Sahara | Drum Brake | Rear Dynamic Friction Company True-Arc Brake Shoes | 42.22 | 520384 |
| 727394 | 2018 | Toyota | Corolla SE 1.8L L4 Gas | Alternators | DB Electrical 400-40169 Alternator Compatible With/Replacement For 125 Internal Fan Type Decoupler Pulley Type Internal Regulator CW Rotation | 215.84 | 727394 |
| 927944 | 2017 | Chevrolet | Equinox | Bearings & Seals | Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly | 48.85 | 927944 |
| 749471 | 2019 | Toyota | Prius | Shocks, Struts & Suspension | 2-Piece Suspension Strut and Coil Spring Kit (593024) | 299.97 | 593024 |
| 927307 | 2014 | Buick | Regal | Alternators & Generators | DB Electrical Alternator | 218.74 | 928037 |
| 304031 | 2017 | Chevrolet | Express 2500 | Shocks, Struts & Suspension | Suspension Kit (Front; with 3 Groove Pitman Arm) | 142.44 | 304031 |
| 497249 | 2013 | GMC | Sierra 1500 | Drum Brake | ACDelco Gold 17960BF1 Bonded Rear Drum Brake Shoe Set | 58.92 | 497249 |
| 973947 | 2012 | Honda | Accord | Brake Kits | R1 Concepts Front Rear Brakes and Rotors Kit |Front Rear Brake Pads| Brake Rotors and Pads| Ceramic Brake Pads and Rotors | 292.84 | 973947 |
| 182694 | 2016 | Chevrolet | Impala | Bearings & Seals | Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly | 48.85 | 927944 |
| 497249 | 2013 | Chevrolet | Silverado 1500 | Drum Brake | ACDelco Gold 17960BF1 Bonded Rear Drum Brake Shoe Set | 58.92 | 497249 |
| 297149 | 2020 | Jeep | Wrangler | Air Filters | ACDelco Gold A3408C Air Filter | 22.83 | 297149 |
| 927397 | 2016 | Chevrolet | Impala | Bearings & Seals | Front/Rear Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly 5 Lugs w/ABS | 79.97 | 799428 |
| 392972 | 2020 | Toyota | Prius AWD-e | Shocks, Struts & Suspension | 2-Piece Suspension Strut and Coil Spring Kit (593024) | 299.97 | 593024 |
| 928037 | 2017 | Buick | Regal | Alternators & Generators | DB Electrical Alternator | 218.74 | 928037 |
| 502481 | 2016 | Chevrolet | Equinox | Bearings & Seals | Wheel hub bearing Assembly | 99.95 | 740248 |
| 593804 | 2019 | Honda | Accord LX 1.5L L4 Gas | Alternator | Alternator | 202.47 | 593804 |
| 293748 | 2014 | Toyota | Corolla SE 1.8L L4 Gas | Alternators | DB Electrical 400-40169 Alternator Compatible With/Replacement For 125 Internal Fan Type Decoupler Pulley Type Internal Regulator CW Rotation | 215.84 | 727394 |
| 639704 | 2021 | Kia | Sorento | Brake Kits | Rear Brakes and Rotors Kit |Rear Brake Pads| Brake Rotors and Pads| Optimum OEp Brake Pads and Rotors | 125.15 | 639704 |
| 829385 | 2020 | Jeep | Wrangler Unlimited Sahara | Drum Brake | Centric Brake Shoe | 22.05 | 829385 |
| 484695 | 2014 | GMC | Terrain | Bearings & Seals | Front/Rear Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly 5 Lugs w/ABS | 79.97 | 799428 |
| 807204 | 2016 | Chevrolet | Camaro | Alternators & Generators | DB Electrical Alternator | 218.74 | 928037 |
| 939283 | 2015 | Chevrolet | Equinox | Bearings & Seals | Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly | 48.85 | 927944 |
| 738628 | 2021 | Toyota | Prius AWD-e | Shocks, Struts & Suspension | 2-Piece Suspension Strut and Coil Spring Kit (593024) | 299.97 | 593024 |
| 186950 | 2017 | Honda | CRV | Alternator | Alternator | 202.47 | 593804 |
| 329573 | 2012 | Chevrolet | Equinox | Bearings & Seals | Front/Rear Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly 5 Lugs w/ABS | 79.97 | 799428 |
| 594085 | 2015 | Buick | Regal | Bearings & Seals | Front/Rear Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly 5 Lugs w/ABS | 79.97 | 799428 |
| 928405 | 2018 | Chevrolet | Camaro | Alternators & Generators | DB Electrical Alternator | 218.74 | 928037 |
| 927937 | 2012 | Ford | Focus SE | Starters | Duralast Starter 19481 | 188.88 | 927937 |
| 283948 | 2018 | GMC | Savana 3500 | Shocks, Struts & Suspension | Suspension Kit (Front; with 3 Groove Pitman Arm) | 142.44 | 304031 |
| 495116 | 2020 | Chrysler | Voyager | Brake Kits | Power Stop K7845 Rear Z23 Carbon Fiber Brake Pads with Drilled & Slotted Brake Rotors Kit | 269.75 | 293748 |
| 180400 | 2012 | Cadillac | CTS FWD | Bearings & Seals | Front/Rear Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly 5 Lugs w/ABS | 79.97 | 799428 |
| 593024 | 2021 | Toyota | Prius | Shocks, Struts & Suspension | 2-Piece Suspension Strut and Coil Spring Kit (593024) | 299.97 | 593024 |
| 302839 | 2014 | Chevrolet | Equinox | Bearings & Seals | Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly | 48.85 | 927944 |
| 649394 | 2020 | Jeep | Wrangler Unlimited Sahara | Brake Kits | Power Stop K7940 Front Z23 Evolution Sport Brake Upgrade Kit | 354.46 | 495116 |
| 820684 | 2015 | Buick | LaCrosse | Bearings & Seals | Front/Rear Wheel Hub Bearing Assembly 5 Lugs w/ABS | 79.97 | 799428 |
| 602839 | 2017 | GMC | Savana 2500 | Shocks, Struts & Suspension | Suspension Kit (Front; with 3 Groove Pitman Arm) | 142.44 | 304031 |
| Previous | Copyright © 2010-2023, FunctionX | Last Update: Friday 02 December 2022 | Next |