|
Common Fields of Forms and Reports |
|
As we saw in previous lessons, fields are created on a table, then they can be added to a query. Based on the way Microsoft Access deals with fields, a field on a table cannot be created as a combination of other fields, as if it were an expression (unless the field is created as
"lookup")(We
know that other database environments, including Microsoft SQL Server and MySQL,
allow using an expression as the value of a column of a table but MS Access
doesn't). Instead, the fields on a table are primarily created to store data. On the other hand, as we will see in the next few lessons, a new field can be added to a query as a combination, through an expression, of other fields. Forms and reports present this same solution. Besides using the fields of a table or a query, a new
field can be added to a form or report. This is because forms and reports use objects called Windows controls.
|
A label is a static object that presents a word or a group of words. The user cannot (directly) change the value that a label is displaying. By default, a label displays its sentence on a gray background. |
|
A text box is a rectangular object with a white background and thick borders. On a form, a text box either presents information to the user, requests data from the user, or does both. On a report, a text box is used like a label: to display information that would be printed.
A text box may not be explicit enough to indicate what it is used for. For this reason, it is usually positioned next to a label. The label is usually positioned on top, or to the left, of the text box it is accompanying. For this reason, a text box is named after the label close to it. For example, and throughout this
site, if a text box is placed under, or on the right side of, a label that displays First Name, the text box would be called
"The First Name Text Box". |
|
A combo box is a type of text box that displays an item selected from a list it is holding. On a form, to change an item in a combo box, you can click its arrow and make your selection from the list. On a report, a combo box appears as such only when in
design. When printed, only its data displays. Although it depends on the programmer's configuration of the combo box, the user may not be allowed to enter in a combo box something that is
not part of the preset list. |
|
|

![]() Practical Learning: Reviewing Controls on Forms and Reports
Practical Learning: Reviewing Controls on Forms and Reports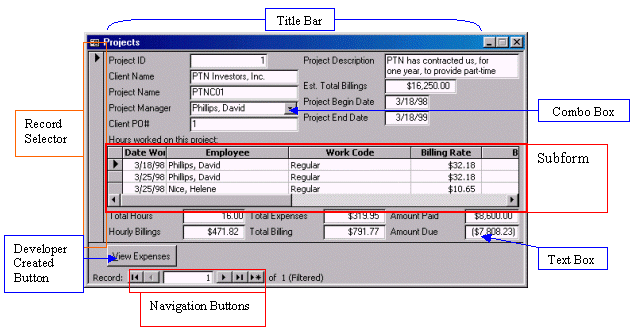
![]() Practical Learning: Reviewing Controls on Forms
Practical Learning: Reviewing Controls on Forms![]() Practical Learning: Reviewing Controls on Reports
Practical Learning: Reviewing Controls on Reports